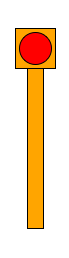Difference between revisions of "CSC111 Lab 13 2011"
(→Blinking Light) |
|||
| Line 147: | Line 147: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
=Blinking Light= | =Blinking Light= | ||
| − | + | [[Image:CSC111BlinkingLight.png|50px|right]] | |
* Below is the beginning of a class for a blinking light. | * Below is the beginning of a class for a blinking light. | ||
| Line 221: | Line 221: | ||
* Verify that you do not have any syntax errors. | * Verify that you do not have any syntax errors. | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | |||
{| style="width:100%; background:silver" | {| style="width:100%; background:silver" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 246: | Line 249: | ||
* Check that you can change the state of the lights | * Check that you can change the state of the lights | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
{| style="width:100%; background:silver" | {| style="width:100%; background:silver" | ||
Revision as of 08:53, 8 December 2011
--D. Thiebaut 18:28, 1 December 2011 (EST)
Contents
Fish
(this section was originally in Lab 12).
- Point your browser to this page...
- See all the fish? Pick one that you like. If you are working in Mac or Windows mode, just right-click on the fish and save a copy of it on your computer, in the directory where you have your python programs. If you are on beowulf, just type the command
getcopy fishxx.gif
where xx is the number of the fish you selected.
- Verify that the fish file is in your directory, in the local terminal.
- Write a new graphics program and copy/paste the following code in it:
.
from graphics import *
H = 600
W = 400
def waitForClick( win, message ):
""" waitForClick: stops the GUI and displays a message.
Returns when the user clicks the window. The message is erased."""
# wait for user to click mouse to start
startMsg = Text( Point( win.getWidth()/2, win.getHeight()/2 ), message )
startMsg.draw( win ) # display message
win.getMouse() # wait
startMsg.undraw() # erase
def main():
global H, W
win = GraphWin( "Fish Tank", W, H )
waitForClick( win, "click to start" )
fish = Image( Point( W/2, H/2 ), "fish15.gif" ) # replace 15 by the number of your fish
fish.draw( win )
waitForClick( win, "click to end" )
win.close()
main()
.
- Add a for loop and make the object fish move by dx, dy some fixed number of steps...
- Instead of using the image of the fish by itself and having the program remember by what amount to move it every time through the loop, let's create a class for the fish, and make the fish remember what
- Create a an new class which is a fish, with its own file name, and its own dx (and maybe dy).
class Fish:
def __init__( self, fileName, dirX, dirY ):
self.image = Image( ... )
self.dx = dirX
self.dy = dirY
def draw( ... ):
self.image.draw( win, dirX, dirY )
...
- Create an object issued from the class. Verify that you can make the object move on the screen.
Challenge 1 |
- Create a school of several fish (the same fish replicated several times is fine for this exercise) that move around the screen. The fish may move in opposite directions, but we'll assume that all fish move in the direction of where their head points to!!!
- In case your fish move too fast, you can use the sleep() function in the time module.
Challenge 2 |
- Make the fish go up or down, slightly, randomly, as it moves forward...
- Hint: random.choice( [ 1, -1, 0, -2, 2, 0, 0, 0, ] ) will return random numbers that are either -2, -1, 0, 1, or 2, and will return 0 half of the time (because there are as many 0s as other numbers in the list).
Aquarium
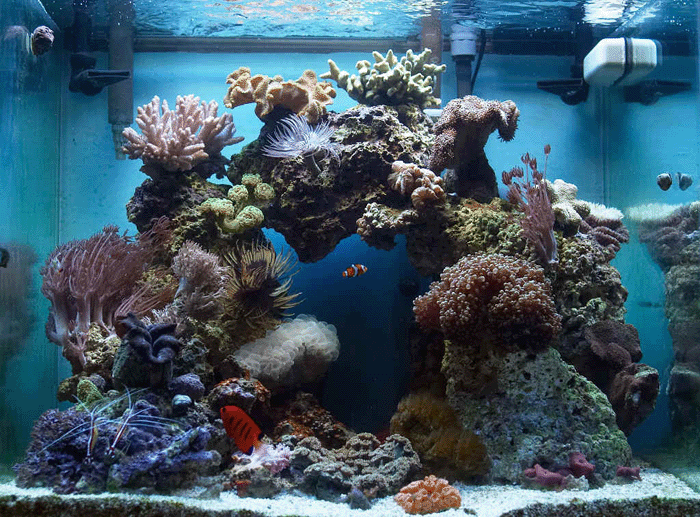
In this section you will apply a background image to the window. It will be the image of a fish tank, and you will make your fish move about in the tank.
- Get a copy of this image to the local terminal. You know how to capture the image! :-)
- Modify your python program and make the graphics window as wide and as high as the image, which is 700 × 517 pixels.
- Paint the image on your graphic window as a background image as follows:
H = 700 # use the same number as above W = 517 # use the same number as above win = GraphWin( "111a-xx Aquarium", W, H ) background = Image( Point( W/2, H/2 ), "tank2.gif" ) background.draw( win )
- Verify that you get a nice aquarium and that your fish swim in it!
Blinking Light
- Below is the beginning of a class for a blinking light.
class BlinkingLight:
"""The blinking light contains a long vertical pole,
a square box at the top, and a circle for the light.
Methods supported:
draw( win ): draws the whole light on the graphic
window
"""
def __init__( self, basePoint, w, h ):
"""builds the graphical obect.
basePoint is a point on the ground, in the middle of the pole
w is the width of the top box
h is the height of the pole plus the box at top"""
#--- save geometry of blinking light and pole ---
self.basePoint = basePoint
self.w = w
self.h = h
self.isOn = True
#--- create the pole ---
x = self.basePoint.getX()
y = self.basePoint.getY()
x1 = x - self.w/5
x2 = x + self.w/5
y1 = y - self.h
y2 = y
self.pole = Rectangle( Point( x1, y1), Point( x2, y2 ) )
self.pole.setFill( "orange" )
#--- create the top box ---
x1 = x - self.w/2
x2 = x + self.w/2
y1 = y - self.h
y2 = y - self.h + self.w
self.top = Rectangle( Point( x1, y1), Point( x2, y2 ) )
self.top.setFill( "orange" )
#--- create the light in the top box ---
xc = (x1+x2)/2
yc = (y1+y2)/2
radius = self.w * 4 / 5 / 2
self.light = Circle( Point( xc, yc ), radius )
if self.isOn:
self.light.setFill( "red" )
else:
self.light.setFill( "black" )
- Put the class in a program that uses the graphics library and the time module, and that contains an animation loop:
while True:
if win.checkMouse() != None:
break
# slow down the loop by 0.2 seconds
time.sleep( 0.2 )
- Verify that you do not have any syntax errors.
Challenge 3 |
- Add a draw() method to the class, and create a couple of blinking light objects in your main() function. Make the objects draw themselves before the animation loop.
- Make sure you see your two lights (they are not blinking yet!)
Changing the color of the light
- Add a method to the BlinkingLight class called switchState(). This method will change the member variable isOn to its opposite, and at the same time will change the color of the light.
- if isOn is True, then the method changes it to False, and sets the color of the circle to black.
- if isOn is False, then the method changes it to True, and sets the color to red.
- Note: You do not need to redraw the lights. Once they are drawn on the window with the draw() method, you can then change the color automatically but simply using setFill()
- Add some code to your animation loop so that if the user clicks the mouse in the window, instead of breaking out of the loop, you will ask your lights to switch state:
if win.checkMouse() != None:
blink1.switchState()
blink2.switchState()
- Check that you can change the state of the lights
Challenge 4: Blinking |
- Let's make the lights blink on their own now. The idea for making the light blink is for it to be told every time we go through the animation loop. The lights increment a counter, in essence counting how many frames they are in a particular state (On or Off). Whenever some fixed number of loops have elapsed, say, 10, the lights will reset their counter and change state.
- Here is how you are going to do this:
- Add a new member variable called self.counter to your class.
- Initialize it inside the __init__() method and set it to 0
- Add a new method to the BlinkingLight class called update().
- In update(), increment your counter. If it gets greater than 10 (or some similar number), reset it to 0 and make update() call switchState().
- Go ahead and see if your blinking lights blink on their own...
You may start on Homework 11!