Difference between revisions of "CSC111 Lab 1 2014"
| (10 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 199: | Line 199: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
===Playing with Lists and Loops=== | ===Playing with Lists and Loops=== | ||
* Create a new program in '''Idle''' with this new piece of code: | * Create a new program in '''Idle''' with this new piece of code: | ||
| − | + | <br /> | |
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <source lang="python"> | ||
list = [ "Lea Jones", "Julie Fleur", "Anu Vias" ] | list = [ "Lea Jones", "Julie Fleur", "Anu Vias" ] | ||
for name in list: | for name in list: | ||
print( name ) | print( name ) | ||
| − | + | </source> | |
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
<tanbox>Observe that the line that starts with ''print'' is indented from the line that starts with ''for''. This is a '''very important''' detail: Python uses ''indentation'' to influence how statements depend on each other. | <tanbox>Observe that the line that starts with ''print'' is indented from the line that starts with ''for''. This is a '''very important''' detail: Python uses ''indentation'' to influence how statements depend on each other. | ||
| Line 245: | Line 240: | ||
* Play with these different code segments, each one on its own. Make sure you understand how each one works when you execute the program. | * Play with these different code segments, each one on its own. Make sure you understand how each one works when you execute the program. | ||
| − | + | <br /> | |
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <source lang="python"> | ||
list = [ "Lea Jones", "Julie Fleur", "Anu Vias" ] | list = [ "Lea Jones", "Julie Fleur", "Anu Vias" ] | ||
for name in list: | for name in list: | ||
print( name ) | print( name ) | ||
print( "-" ) | print( "-" ) | ||
| − | + | </source> | |
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
* and this one: | * and this one: | ||
| − | + | <br /> | |
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <source lang="python"> | ||
list = [ "Lea Jones", "Julie Fleur", "Anu Vias" ] | list = [ "Lea Jones", "Julie Fleur", "Anu Vias" ] | ||
for name in list: | for name in list: | ||
print( name, len( name ) ) | print( name, len( name ) ) | ||
| − | + | </source> | |
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
* or: | * or: | ||
| − | + | <br /> | |
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <source lang="python"> | ||
list = [ "Lea Jones", "Julie Fleur", "Anu Vias" ] | list = [ "Lea Jones", "Julie Fleur", "Anu Vias" ] | ||
for name in list: | for name in list: | ||
print( name ) | print( name ) | ||
print ( len( name ) ) | print ( len( name ) ) | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | * Still some more | ||
| − | + | <br /> | |
| − | + | <br /> | |
| + | <source lang="python"> | ||
list = [ "Lea Jones", "Julie Fleur", "Anu Vias" ] | list = [ "Lea Jones", "Julie Fleur", "Anu Vias" ] | ||
for name in list: | for name in list: | ||
print( name, '-' * len( name ) ) | print( name, '-' * len( name ) ) | ||
| − | + | </source> | |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| Line 308: | Line 318: | ||
Lea Jones | Lea Jones | ||
--------- | --------- | ||
| − | + | ||
----------- | ----------- | ||
Julie Fleur | Julie Fleur | ||
----------- | ----------- | ||
| − | + | ||
-------- | -------- | ||
Anu Vias | Anu Vias | ||
| Line 333: | Line 343: | ||
| Lea Jones | | | Lea Jones | | ||
------------- | ------------- | ||
| − | + | ||
--------------- | --------------- | ||
| Julie Fleur | | | Julie Fleur | | ||
--------------- | --------------- | ||
| − | + | ||
------------ | ------------ | ||
| Anu Vias | | | Anu Vias | | ||
------------ | ------------ | ||
| + | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| Line 351: | Line 362: | ||
| Lea Jones | | | Lea Jones | | ||
+-----------+ | +-----------+ | ||
| − | + | ||
+-------------+ | +-------------+ | ||
| Julie Fleur | | | Julie Fleur | | ||
+-------------+ | +-------------+ | ||
| − | + | ||
+----------+ | +----------+ | ||
| Anu Vias | | | Anu Vias | | ||
+----------+ | +----------+ | ||
| − | + | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| Line 371: | Line 382: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | + | [[CSC111 Lab 1 Solutions 2014 |Solution to the Challenges...]] | |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
Latest revision as of 16:41, 30 January 2014
--D. Thiebaut (talk) 10:39, 28 January 2014 (EST)
Contents
- 1 FUN WITH PYTHON
- 2 Installing and Running Python on your Laptop
- 3 Starting Python on a Lab Computer
- 3.1 Idle
- 3.2 Some Python Code to play with
- 3.2.1 Playing with numbers
- 3.2.2 Using Strings of characters
- 3.2.3 Challenge #1
- 3.2.4 Playing with Strings
- 3.2.5 Challenge #2
- 3.2.6 Repeating Strings
- 3.2.7 Challenge #3
- 3.2.8 Challenge #4 (tricky)
- 3.2.9 Playing with Lists and Loops
- 3.2.10 Challenge #5
- 3.2.11 Repeating several statements
- 3.2.12 Challenge #6
- 3.2.13 Challenge #7
- 3.2.14 Challenge of the Day
FUN WITH PYTHON
This lab is just an introduction to having fun with Python. It's purpose is to have you explore the different systems that are available to you, and get a sense of how to program in an "intuitive" fashion.
Installing and Running Python on your Laptop
- Skip this section if you are working on one of the computers in FH241.
- Follow the directions from this tutorial which will help you install Python Version 3 on your laptop: https://wiki.python.org/moin/BeginnersGuide/Download
Note that we will be using Python Version 3 for this class, and NOT VERSION 2. As long as your version of Python is 3.xxx where xxx is any series of numbers, you should be fine.
- Once the installation is complete, look for the Python IDLE application in your All Programs or Applications areas, depending on whether you're using a Windows or a Mac computer. Once you start it, you should see something similar to this:
- If you only see the Python Shell window, use the menu and click on File, New Window to bring the editor window up
- You are now ready for this lab!
Starting Python on a Lab Computer
- If your computer is not on, turn it ON, please!
- When prompted for booting Mac or Windows, select the Mac if you have the choice.
- Login using the Smith credentials (or the account that was given to you as a 5-college or high school student)
- Once you see the Desktop, click on the Finder (bottom left icon on the Desktop), and look in the Science Apps folder for Python 3.2.
- Start IDLE
Tip: if you can't find Idle, use the magnifying glass icon at the top right of the screen and search for idle and you should find it!
Idle
- Idle is the name of an editor one can use to create Python program on the Mac.
- If the window you start with looks like this (see below), then use the top menu and click File, New Window to open an editing window.
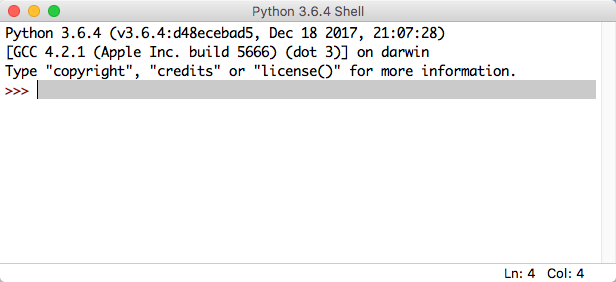
- You should now have two windows on your screen, one the editing window, the other the shell window, where the program will send its output.
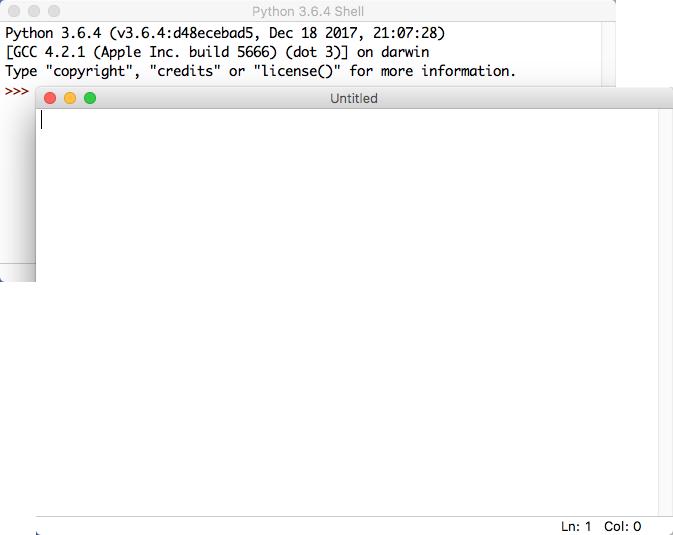
Some Python Code to play with
Playing with numbers
- Enter the following code in the Untitled window:
a = 3 b = 5 c = 10 print( a, b, c, a+b+c )
- Press F5 to run the program. When prompted to save the program, save it as lab1.py
- Look at the Console window. Some numbers appear... Do they make sense?
- change the numbers that are assigned to a, b, or c and see how your program reacts when you run it.
Using Strings of characters
- Modify the print statement so that it reads like this:
print (a, b, c, "sum = ", a+b+c )
- Run your new program. Do you understand how your modification made the program run differently? Does the output still make sense? Don't worry too much for today if it doesn't. Be sure to ask questions to your instructor or to the TAs if you're unsure about anything.
- Another modification. Replace your print statement by two statements:
print( a, b, c ) print( "sum = ", a+b+c )
- Run your program again. How does having a second print statement modify the behavior of your program?
Challenge #1 |
- Now, use your intuition and what you have just learned and see if you can modify your program to make it display this output:
a = 3 b = 10 c = 20 sum = 33
- Keep at it if you don't get there right away. Remember, this is a language, and you have many different ways to say the same thing...
Playing with Strings
- The goal of this section if for you to modify your program and try different Python statements and use intuition to understand how they work, and how the Python language is organized.
- Type the following three lines of code in your program (you can keep the old lines and add new lines at the end, or you can erase everything and type the new ones), and run the program.
print( "hello" ) print( "hello", "there!" ) print( "hello" + "there!" )
- Observe how the different ways to write the print statments influence how the information is printed.
- Now, try these lines of code:
word1 = "hello" word2 = "there!" print( word1, word2 ) print( word1, "who is", word2 )
- Question: What is the role of word1 or word2 in the program?
- Question: What is the role of the double quote character in Python?
Challenge #2 |
- Modify your program but keep the two variables word1 and word2, and make it print this:
hello there! there! hello hello hello hello hello there! there! hello
Repeating Strings
- Try this:
word1 = "hello"
print( word1 * 2 ) print( word1 * 5 ) print( word1 * 10 )
- See how you can multiply a string?
Challenge #3 |
- Modify your program and make it print this:
hello hello hello hello there! hello there! there! there! there! there! hello
Challenge #4 (tricky) |
- See if you can make your program print this, using string multiplication:
hellothere!hellothere!hellothere!hellothere!hellothere!
Playing with Lists and Loops
- Create a new program in Idle with this new piece of code:
list = [ "Lea Jones", "Julie Fleur", "Anu Vias" ]
for name in list:
print( name )
Observe that the line that starts with print is indented from the line that starts with for. This is a very important detail: Python uses indentation to influence how statements depend on each other.
- Press F5. Observe the output.
Challenge #5 |
- Add three new names to the list and make your program output them all one above the other.
Repeating several statements
- Play with these different code segments, each one on its own. Make sure you understand how each one works when you execute the program.
list = [ "Lea Jones", "Julie Fleur", "Anu Vias" ]
for name in list:
print( name )
print( "-" )
- and this one:
list = [ "Lea Jones", "Julie Fleur", "Anu Vias" ]
for name in list:
print( name, len( name ) )
- or:
list = [ "Lea Jones", "Julie Fleur", "Anu Vias" ]
for name in list:
print( name )
print ( len( name ) )
- Still some more
list = [ "Lea Jones", "Julie Fleur", "Anu Vias" ]
for name in list:
print( name, '-' * len( name ) )
Challenge #6 |
- Make your program display the names with a bar made of minus signs under each name. The length of the bar should be the same as the length of the name. For example:
Lea Jones --------- Julie Fleur ----------- Anu Vias --------
Challenge #7 |
- Similar question, but now like this:
--------- Lea Jones --------- ----------- Julie Fleur ----------- -------- Anu Vias --------
Challenge of the Day |
- Make your program display a box around each name:
------------- | Lea Jones | ------------- --------------- | Julie Fleur | --------------- ------------ | Anu Vias | ------------
- And... if you are done, and are really rolling and want some more of a challenge, try to make your program output this:
+-----------+ | Lea Jones | +-----------+ +-------------+ | Julie Fleur | +-------------+ +----------+ | Anu Vias | +----------+








