Difference between revisions of "Debugging with Eclipse: A Quick Introduction"
(→Debugging DebugDemo) |
(→Debugging DebugDemo) |
||
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
* In the '''Package Explorer''' tab (left tab), '''right/control click''' on ''DebugDemo'' and select '''Debug As''' and '''Java Application'''. | * In the '''Package Explorer''' tab (left tab), '''right/control click''' on ''DebugDemo'' and select '''Debug As''' and '''Java Application'''. | ||
| − | * The windows will reorganize themselves: | + | * The windows will reorganize themselves (if not, see below): |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<center>[[Image:EclipseDebugger1.png|700px]]</center> | <center>[[Image:EclipseDebugger1.png|700px]]</center> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | * If you do not get the window shown above, click on the little "table and plus symbol" in the top right of the window, and pick '''Debug''' in the new pop-up window | + | * If you do not get the window shown above, click on the little "table and plus symbol" in the top right of the window, and pick '''Debug''' in the new pop-up window : |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<center>[[Image:EclipseDebugger2.png|700px]]</center> | <center>[[Image:EclipseDebugger2.png|700px]]</center> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
* You can switch back and forth between Java coding and debugging using the '''Java''' and '''Debug''' buttons in the top right of the Eclipse window. | * You can switch back and forth between Java coding and debugging using the '''Java''' and '''Debug''' buttons in the top right of the Eclipse window. | ||
Revision as of 09:54, 22 October 2014
--D. Thiebaut (talk) 10:44, 22 October 2014 (EDT)
Contents
This is a short tutorial on how to get started with the Eclipse Debugger. Mastering the debugger takes time. The purpose of this lab/tutorial is just to show you how to get started.
Getting Started
- Open Eclipse
- Create a New Java Class. Call it DebugDemo.
- Enter this code in it:
// DebugDemo.java // D. Thiebaut // CSC212 import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Iterator; class Pair { public String name; public int age; Pair( String f, int s ) { name=f; age=s; } public String toString() { return name+"("+age+") "; } } public class DebugDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList<Pair> A = new ArrayList<Pair>(); int increment = 3; A.add( new Pair( "Alice", 10 ) ); A.add( new Pair( "Bob", 7 ) ); Iterator<Pair> it = A.iterator(); while ( it.hasNext() ) { Pair p = it.next(); p.age += increment; } for ( int i=0; i<3; i++ ) { Pair p = A.get( i ); System.out.println( A.get( i ) ); } } }
- Run it.
- Observe what the program does. It simply creates an array of 2 pairs, containing Alice(10) and Bob(7), and modify the age of both by an increment of 3.
Debugging DebugDemo
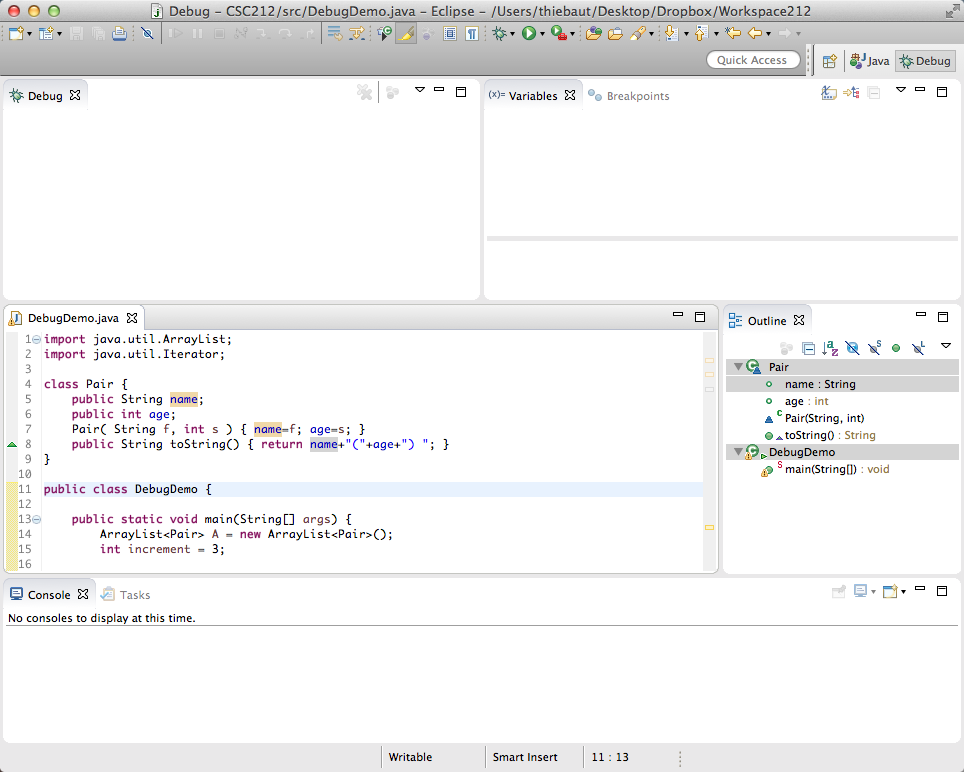
- In the Package Explorer tab (left tab), right/control click on DebugDemo and select Debug As and Java Application.
- The windows will reorganize themselves (if not, see below):
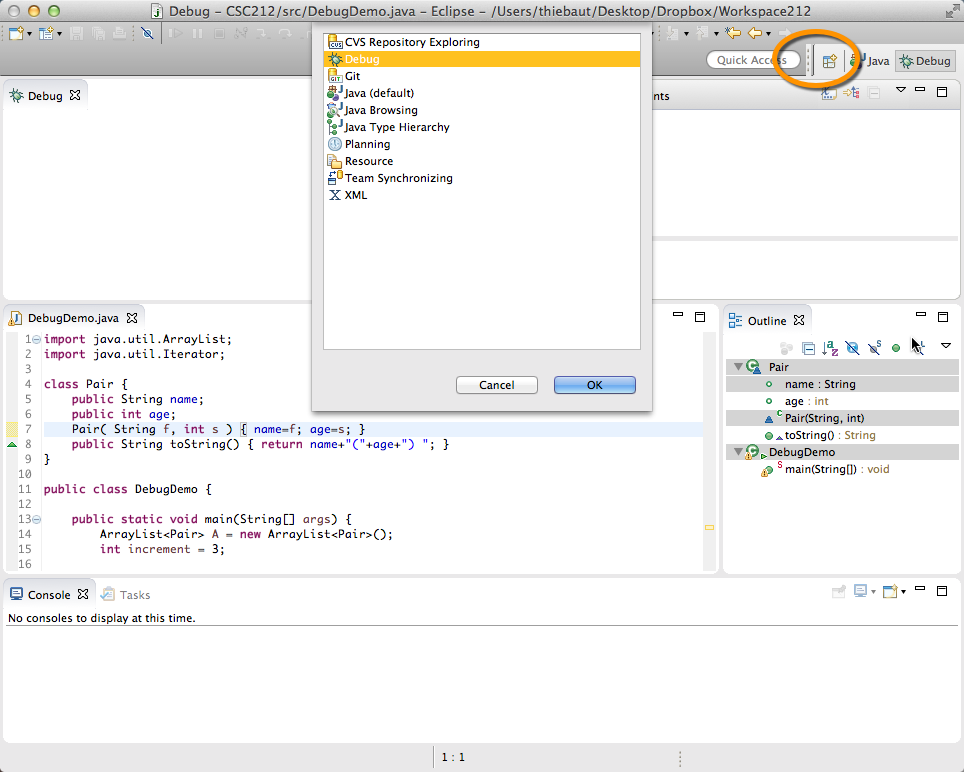
- If you do not get the window shown above, click on the little "table and plus symbol" in the top right of the window, and pick Debug in the new pop-up window :
- You can switch back and forth between Java coding and debugging using the Java and Debug buttons in the top right of the Eclipse window.