Difference between revisions of "CSC111 Lab 7 2015b"
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | + | <showafterdate after="20151021 12:00" before="20151231 00:00"> | |
| − | <showafterdate after=" | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<bluebox> | <bluebox> | ||
| Line 200: | Line 199: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<bluebox> | <bluebox> | ||
| − | In this lab you will play with a graphics library. A graphic library typically allows the user to draw simple shapes on the screen. You will also write some boolean functions that will help you control the dynamic movement of objects on the screen | + | In this second part of the lab you will play with a graphics library. A graphic library typically allows the user to draw simple shapes on the screen. You will also write some boolean functions that will help you control the dynamic movement of objects on the screen. When your programs for the challenges work, make sure to demonstrate your solutions to the lab instructor (or the TA). You must submit your solution program to Moodle before Friday 10/23/15 at 11:55 p.m. |
| − | |||
</bluebox> | </bluebox> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | + | [[File:TaxiCabCSC111.png|150px|right]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[File:TaxiCabCSC111.png|150px]] | ||
| − | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
Revision as of 19:06, 19 October 2015
--D. Thiebaut (talk) 16:13, 17 October 2015 (EDT)
Preparation
- Copy paste the program below in a new Idle window, and call it lab7Companion.py.
- Save your new program to your working directory, where you normally save your lab programs.
- Run the program. It should create 3 text files in your folder. You will be using them in this lab. The files are called:
- chocoQuotes.txt
- hargitay.txt
- joanneHarris.txt
# lab7Companion.py # D. Thiebaut # This program will create several files in the directory # where you will run it. # The files are retrieved from a Web server, stored temporarily # in a string, and stored in a local file on your disk. # The 3 files are very, very short. # Their names are: # - chocoQuotes.txt # - hargitay.txt # - joanneHarris.txt import urllib.request # the lib that handles the url stuff # main program def main(): # list of files to retrieve fileNames = [ "chocoQuotes.txt", "hargitay.txt", "joanneHarris.txt" ] # get each file, one at a time for fileName in fileNames: # url where the files are located url = "http://cs.smith.edu/~dthiebaut/111/files/" + fileName # fetch the file and put its contents in the # string text. response = urllib.request.urlopen( url ) text = response.read().decode( 'UTF-8' ) # write text to file, in the same directory as this program. file = open( fileName, "w" ) file.write( text + "\n" ) file.close() # give feedback to user. print( "File {0:1} created in your folder".format( fileName ) ) main()
<showafterdate after="20151021 12:00" before="20151231 00:00">
Although this lab has only 2 Moodle submissions, make sure you work on all the challenges. If you skip them, you are only making it harder for you to learn Python and making future challenges that much harder. A little bit of effort regularly beats a huge effort later! The Moodle submissions are due on Friday 10/23/15 at 11:55 p.m. Hope you enjoy this lab!
Contents
- 1 Preparation
- 2 Reading Text From File
- 3 Writing Text to File
- 4 Setup for Graphics
- 5 Simple Animation: Moving a Ball on the Graphic Window
- 6 Adding an Obstacle
- 7 Adding a Second Obstacle
- 8 Using Boolean Functions
- 9 IsLeftSide() Boolean Function
- 10 isUpperHalf Boolean Function
- 11 getColor() Function
- 12 Solution Programs
Challenge #1 |
- Make your program print the poem in a box. The top and bottom lines have 50 dashes in them.
- Expected output
+--------------------------------------------------+ | CHOCOLATE | | Chocolate is the first luxury. | | It has so many things wrapped up in it: | | Deliciousness in the moment, | | childhood memories, | | and that grin-inducing | | feeling of getting a reward for being good. | | --Mariska Hargitay| +--------------------------------------------------+
Reading Text From File
- Open Finder or Windows Explorer and go to the folder that contains your lab7.py program, as well as your lab7Companion.py programs. Make sure the folder contains the 3 text files you created earlier.
- Open the file name hargitay.txt. Verify that it contains the same poem we have been playing with.
- Either create a new program or add a new main() function to your existing program (rename the original main, main2(), maybe?), and put the code below in the new function:
def main(): fileName = "hargitay.txt" file = open( fileName, "r" ) lines = file.readlines() file.close() for line in lines: print( line )
- Run the program. Observe its output.
- The reason for the double-spacing is that each line read from the file contains a '\n' at the end of it. And when you print such a line, the print() function adds its own \n at the end. This is why you get a blank line in between lines.
- One way to remove the '\n' at the end of each line is to print the line as follows: print( line.rstrip() ). The rstrip() method right-strips the string of all white-space characters, which include spaces, tabs, and '\n'-characters.
Challenge #2 |
- Make your program get the name of the file from the user, with an input() statement.
- Then, make your program output the contents of the file in a box, as you did in Challenge 4.
- Test your program by providing it with different file names:
- hargitay.txt
- joanneHarris.txt
- chocoQuotes.txt
- Adjust the width of the box if necessary.
Challenge #3 |
- Exact same challenge as Challenge 5, but this time start with this program, where I have replaced the .readlines() method with .read().
def main(): fileName = input( "File name? " ) file = open( fileName, "r" ) text = file.read() file.close() print( "The type of text is", type( text ) ) print( "text = ", text )
- Note
- when Python says that something is of type <class 'str'>, it means that it is a string.
Writing Text to File
- Try this new version of main:
def main(): fileName = "hargitay.txt" file = open( fileName, "r" ) text = file.read() file.close() text = text.replace( "chocolate", "carrot" ) text = text.replace( "Chocolate", "Carrot" ) file = open( fileName, "w" ) file.write( text + "\n" ) file.close()
- Open Finder or Windows Explorer, and take a look at the file "hargitay.txt", either with TextEdit or with Notepad. See anything different?
- BTW, You can recreate the original file by running the lab7Companion.py program again.
Challenge #4 |
- Modify the program so that it prompts the user for
- The name of the file to read from and write to, and
- a word
- and make the program read the file, replace the word chocolate in it with the word the user picked, and save the resulting text back to the file.
- Verify that your program works correctly, and that it modifies the file you select and replaces chocolate with the word you choose.
Moodle Submission
Rename your program lab7_4.py, and submit your solution program for Challenge #4 to Moodle, in the Lab 7 PB 4 section.
In this second part of the lab you will play with a graphics library. A graphic library typically allows the user to draw simple shapes on the screen. You will also write some boolean functions that will help you control the dynamic movement of objects on the screen. When your programs for the challenges work, make sure to demonstrate your solutions to the lab instructor (or the TA). You must submit your solution program to Moodle before Friday 10/23/15 at 11:55 p.m.
Setup for Graphics
Step 1: Download the graphics.py Library
- Copy/Paste the code from this page to Idle and save it in the directory where you will save your programs for Week 7, under the name graphics.py.
Step 2: Testing your installation
- With graphics.py in your Idle window, simply click run to run the library. Normally libraries are not run by themselves, but this library has its own test program to help users verify that the library is working properly.
- If everything goes well, you should see this simple window appear on your screen:
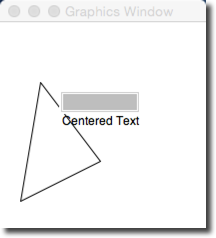
- Click a few times on the window and verify that the window responds by changing the color or size of various graphic objects.
Graphics programs have to be run from Idle to work correctly, and need the graphics.py library distributed by Zelle, the author of our textbook.
<showafterdate after="20150311 12:00" before "20150601 00:00">
Step 3: A simple Graphics Program
- Create a new program and call it lab7.py.
- Important: save your program in the same directory/folder where you saved the graphics.py library.
- Copy the code below in it.
# lab7.py # your name # draws a circle in a window that is 600x400. from graphics import * def main(): win = GraphWin("My Circle", 600, 400) c = Circle(Point(50,50), 10) c.draw(win) win.getMouse() # Pause to view result win.close() # Close window when done main()
- Run the program. Verify that you see a single circle in the graphic window.
- Click with the mouse on the graphics window to close it.
Step 4: Explanations
- Observe the program from Step 3 above and recognize the main features:
- First we open a new graphic window on our desktop with the win = GraphWin( ... ) statement. 600 and 400 define how wide and high the window will be. "My Circle" is the title that will appear at the top of the window.
- Next, we create a circle object with the statement c = Circle( Point(50,50), 10 ). This does not draw the circle. It simply creates one in memory, centered on the point of coordinates 50, 50, with a radius of 10.
- Once the circle is created in memory, we make it appear on the graphic window with c.draw( win ).
- Finally, we wait for the user to click on the graphic window, and then close the window.
Step 5: Modifications
- Modify your program, so that it looks like the code shown below:
# lab7.py # your name # Uses graphics.py from Zelle # # This program displays a red circle, a label # and a rectangle. from graphics import * def main(): #open the graphic window. win = GraphWin( "Lab 7 Demo", 600, 400 ) # create and draw a red circle center = Point( 100, 100 ) circ = Circle( center, 30 ) circ.setFill( 'red' ) circ.draw( win ) # add a label inside the circle label = Text( Point( 100, 100 ), "red circle" ) label.draw( win ) # create and draw a rectangle rect = Rectangle( Point( 30, 30 ), Point( 70, 70 ) ) rect.draw( win ) win.getMouse() # Pause to view result win.close() # Close window when done main()
- The program uses 2 new objects: a rectangle, defined by its upper-left and bottom-right corners, and a label (text) that simply is a string of characters drawn at a given point on the screen. The string is automatically centered around the given point.
- Using this new bit of knowledge, can you generate the figure below? Note that the graphics system used here can recognize many different colors, all defined by strings, such as 'red' used above. You can find all the available colors on this page.
Simple Animation: Moving a Ball on the Graphic Window
- Create a new program similar to the one covered in Monday's lecture.
# Uses graphics.py from Zelle # # This program displays the basic elements of a program # from graphics import * def main(): win = GraphWin( "Lab 7 Moving ball", 600, 400 ) # create and draw a red circle center = Point( 100, 100 ) circ = Circle( center, 30 ) circ.setFill( 'red' ) circ.draw( win ) # define the direction the circle will start moving in. # 5 pixels to the right every move, and 0.25 pixels down # every move. dx = 5 dy = 0.25 # as long as the mouse hasn't been clicked on the window # keep on looping. while win.checkMouse() == None: # move the circle in the current direction. circ.move( dx, dy ) # get the x and y of the center of the circle. x = circ.getCenter().getX() y = circ.getCenter().getY() # if the center is outside the right or left boundary, # reverse the x direction of movement. if x > 600 or x < 0: dx = -dx # if we're here, it's because the the user clicked on the graphic window. # we can close everything and quit. win.close() main()
- Run the program. Verify that the circle/ball bounces off the left and right boundaries of the window, but disappears down the bottom of the screen. If the ball is moving too fast (it does run at various speeds depending on what computer you're running on), you may want to change the values assigned to dx and dy to these values:
dx = 0.025 dy = 0.025
- You can stop the program by clicking on the graphic window a couple of times.
Challenge 1 |
- Modify your program so that it makes the ball bounce off the bottom and top boundaries of the window.
Challenge 2 |
- Modify your program so that the ball bounces when its side (and not its center) touches the "walls" of the graphics window.
Adding an Obstacle
- Add a rectangle in the middle of the graphic window. You should declare it at the beginning of your main() function, as illustrated here:
def main(): win = GraphWin( "Lab 7 Moving ball", 600, 400 ) # create a green obstacle in the middle of the window x1 = 200 y1 = 200 x2 = 250 y2 = 250 obstacle1 = Rectangle( Point( x1, y1 ), Point( x2, y2 ) ) obstacle1.setFill( "green" ) obstacle1.draw( win ) # the remaining part of your code follows below...
Challenge 3 |
- Make your ball stop when its center enters the green rectangle. The image below illustrates this situation.
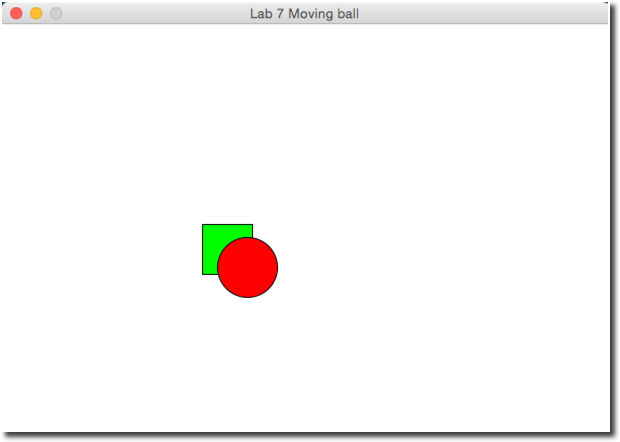
- Hints: to make an object stop, you can simply set its displacement to 0, so that the while-loop makes it move by 0 pixels every loop.
Challenge 4 |
- Modify your program one more time, and this time the ball will bounce off the obstacle. When you detect that the center of the ball is inside the green rectangle, change dx and dy to their opposite. Note that this will make the ball bounce back on the same path it came from. It is quite challenging to make the ball bounce in a realistic way, and you are welcome to try to make it happen, but it's trickier. Bouncing off in the opposite direction is fine for this lab!
if ... : dx = -dx dy = -dy
Adding a Second Obstacle
- Add a second rectangle in the graphic window. Make it magenta in color. You should declare it at the beginning of your main() function, as illustrated here:
def main(): win = GraphWin( "Lab 7 Moving ball", 600, 400 ) # create a green obstacle in the middle of the window x1 = 200 y1 = 200 x2 = 250 y2 = 250 obstacle1 = Rectangle( Point( x1, y1 ), Point( x2, y2 ) ) obstacle1.setFill( "green" ) obstacle1.draw( win ) # create another green rectangle on the right of the first one x3 = 350 y3 = 200 x4 = 400 y4 = 250 obstacle2 = Rectangle( Point( x3, y3 ), Point( x4, y4 ) ) obstacle2.setFill( "magenta" ) obstacle2.draw( win ) # the remaining part of your code follows below...
- Feel freel to position it at a different location than the one used above.
Challenge 5 |
- Make your ball stop when its center is fully inside the first green obstacle, and bounce off the magenta obstacle. For this challenge, simply make the ball bounce off the second obstacle when its center enters the obstacle.
- If you find that the ball never gets to hit both boxes, you may want to change the initial direction and add decimal digits to the dx and dy to create an angle that yields a path that eventually will hit the obstacles. For example:
dx = 5.111 dy = -2.51
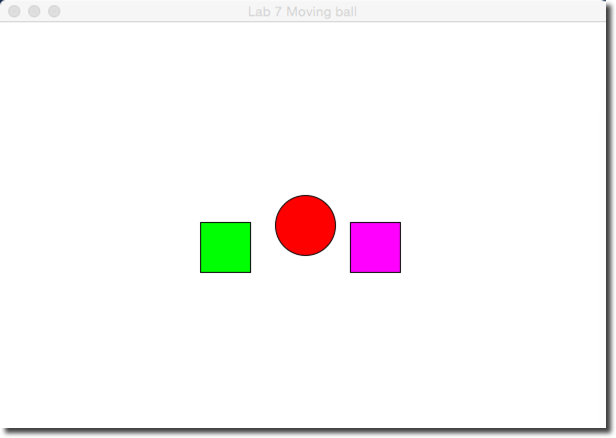
Using Boolean Functions
isInside()
- Add the code of the function isInside(), shown below, to your last program, above the main() function.
# ifInside: returns true of the coordinates of a point defined by # its coordinates ballX and ballY, are inside the rectangle defined by a top # left point of coordinates obsX1, obsY1, and a bottom-right point # with coordinates obsX2, obsY2. Returns false if the point is outside # the rectangle. def isInside( ballX, ballY, obsX1, obsY1, obsX2, obsY2 ): if obsX1 < ballX < obsX2 and obsY1 < ballY < obsY2: return True else: return False
- Modify the code inside the while loop in your main function, so that it uses the isInside() function to detect contact with Obstacle1 and with Obstacle2.
- Here's what your code should look like (you will have to pass the appropriate parameters to the function):
# if the center of the ball is inside the first obstacle, stop # the ball. if isInside( ... ) == True: dx = 0 dy = 0 # if the center of the ball is inside the second obstacle, bounce # off if isInside( ... ) == True: dx = -dx dy = -dy
IsLeftSide() Boolean Function
- Add a new boolean function to your program called isLeftSide(). This function receives 3 parameters, in this order:
- an x coordinate
- a y coordinate
- the width of the window.
- and it returns true if the point (x, y) is on the left side of the window, and false if the point (x, y) is on the right side of the window. This function basically compares the x coordinate to the midpoint on the x axis of the window.
- Use your new function to color the ball rid when it is moving on the left side of the window, and yellow when it is moving on the right side of the window. Example:
if isLeftSide( x, y, win.getWidth() ) == True: circ.setFill( 'red' ) else: circ.setFill( 'yellow' )
isUpperHalf Boolean Function
- Comment out or remove the previous if statement that changes the color of the ball, so that it won't interfere with the code you are about to write.
- Create a new boolean function called isUpperHalf(), that takes 3 parameters, the first two being the coordinates of a point, the third one the height of the window, and that returns true if the point is in the top half of the screen, an false otherwise.
- Use your new function to control the color of the ball as it moves around the window. The ball should be 'blue' when it is in the upper half of the screen, and 'brown' when it is in the lower half.
Demonstrate the correct operations of your programs to your Lab Instructor, and you will be instructed on the process of submitting your lab to Moodle.
getColor() Function
- Instead of having two boolean functions that detect if the point of coordinates x and y is in one part of the window or not, we now want to create a function that will receive the x, and y coordinate of the center of the ball, and the width and height of the window, and that will return a string. The function is called getColor(). If the x and y coordinates are inside the top left quarter of the window, it will return the color 'yellow'. If the x and y coordinates are inside the top right quarter, the function will return 'red'. For the lower-left quarter, the function will return 'blue'. And finally, the function will return 'brown' for the bottom-right quarter.
- Here is an example of how the function can be used inside the while loop:
# get the x and y of the center of the circle. x = circ.getCenter().getX() y = circ.getCenter().getY() # set color of circle according to its position color = getColor( x, y, win.getWidth(), win.getHeight() ) circ.setFill( color )
</showafterdate>
<showafterdate after="20150313 11:00" before "20150601 00:00">
Solution Programs
The programs below show the evolution of the initial program through many transformations, solving the various challenges contained in this lab.
demo0.py
# Uses graphics.py from Zelle
#
# This program displays the basic elements of a program
#
from graphics import *
def main():
win = GraphWin("Demo #0", 400, 300)
c = Circle(Point(50,50), 10)
c.draw(win)
win.getMouse() # Pause to view result
win.close() # Close window when done
main()
demo1.py
# Uses graphics.py from Zelle
#
# This program displays the basic elements of a program
#
from graphics import *
def main():
win = GraphWin("Demo #0", 600, 400)
c1 = Circle( Point(50,150), 20 )
c1.draw( win )
c2 = Circle( Point( 100, 150 ), 20 )
c2.draw( win )
r1 = Rectangle( Point( 10, 100 ), Point( 150, 150 ) )
r1.draw( win )
win.getMouse() # Pause to view result
win.close() # Close window when done
main()
demo2.py
# Uses graphics.py from Zelle
#
# This program displays the basic elements of a program
#
from graphics import *
def main():
win = GraphWin( "Lab 7 Demo", 600, 400 )
# create and draw a red circle
center = Point( 100, 100 )
circ = Circle( center, 30 )
circ.setFill( 'red' )
circ.draw( win )
# add a label inside the circle
label = Text( center, "red circle" )
label.draw( win )
# create and draw a rectangle
rect = Rectangle( Point( 30, 30 ), Point( 70, 70 ) )
rect.draw( win )
win.getMouse() # Pause to view result
win.close() # Close window when done
main()
demo3.py
# Uses graphics.py from Zelle
#
# This program displays the basic elements of a program
#
from graphics import *
def main():
win = GraphWin( "Lab 7 Moving ball", 600, 400 )
# create and draw a red circle
center = Point( 100, 100 )
circ = Circle( center, 30 )
circ.setFill( 'red' )
circ.draw( win )
dx = 5
dy = 0.25
while win.checkMouse() == None:
circ.move( dx, dy )
x = circ.getCenter().getX()
y = circ.getCenter().getY()
if ( x > 600 ):
dx = -dx
if ( x < 0 ):
dx = -dx
win.close() # Close window when done
main()
demo4.py
# Uses graphics.py from Zelle
#
# This program displays the basic elements of a program
#
from graphics import *
def main():
win = GraphWin( "Lab 7 Moving ball", 600, 400 )
# create a green obstacle in the middle of the window
x1 = 200
y1 = 200
x2 = 250
y2 = 250
obstacle = Rectangle( Point( x1, y1 ), Point( x2, y2 ) )
obstacle.setFill( "green" )
obstacle.draw( win )
# create and draw a red circle
radius = 30
center = Point( 100, 100 )
circ = Circle( center, radius )
circ.setFill( 'red' )
circ.draw( win )
# define the direction the circle will start moving in.
# 5 pixels to the right every move, and 0.25 pixels down
# every move.
dx = 5
dy = 2.5
# as long as the mouse hasn't been clicked on the window
# keep on looping.
while win.checkMouse() == None:
# move the circle in the current direction.
circ.move( dx, dy )
# get the x and y of the center of the circle.
x = circ.getCenter().getX()
y = circ.getCenter().getY()
# if the center of the ball is outside the right or left boundary,
# reverse the x direction of movement.
if x > 600 - radius or x < radius:
dx = -dx
if y > 400 - radius or y < radius:
dy = -dy
# if the center of the ball is inside the obstacle, stop
# the ball.
if x1 < x < x2 and y1 < y < y2 :
dx = 0
dy = 0
# if we're here, it's because the the user clicked on the graphic window.
# we can close everything and quit.
win.close()
main()
demo5.py
# Uses graphics.py from Zelle
#
# This program displays the basic elements of a program
#
from graphics import *
def main():
win = GraphWin( "Lab 7 Moving ball", 600, 400 )
# create a green obstacle in the middle of the window
x1 = 200
y1 = 200
x2 = 250
y2 = 250
obstacle1 = Rectangle( Point( x1, y1 ), Point( x2, y2 ) )
obstacle1.setFill( "green" )
obstacle1.draw( win )
# create another green rectangle on the right of the first one
x3 = 350
y3 = 200
x4 = 400
y4 = 250
obstacle2 = Rectangle( Point( x3, y3 ), Point( x4, y4 ) )
obstacle2.setFill( "magenta" )
obstacle2.draw( win )
# create and draw a red circle
radius = 30
center = Point( 100, 100 )
circ = Circle( center, radius )
circ.setFill( 'red' )
circ.draw( win )
# define the direction the circle will start moving in.
# 5 pixels to the right every move, and 0.25 pixels down
# every move.
dx = 5.1
dy = 2.51
# as long as the mouse hasn't been clicked on the window
# keep on looping.
while win.checkMouse() == None:
# move the circle in the current direction.
circ.move( dx, dy )
# get the x and y of the center of the circle.
x = circ.getCenter().getX()
y = circ.getCenter().getY()
# if the center of the ball is outside the right or left boundary,
# reverse the x direction of movement.
if x > 600 - radius or x < radius:
dx = -dx
if y > 400 - radius or y < radius:
dy = -dy
# if the center of the ball is inside the first obstacle, stop
# the ball.
if x1 < x < x2 and y1 < y < y2 :
dx = 0
dy = 0
# if the center of the ball is inside the second obstacle, bounce
# off
if x3 < x < x4 and y3 < y < y4 :
dx = -dx
dy = -dy
# if we're here, it's because the the user clicked on the graphic window.
# we can close everything and quit.
win.close()
main()
demo6.py
# Uses graphics.py from Zelle
#
# This program displays the basic elements of a program
#
from graphics import *
# ifInside: returns true of the coordinates of a point defined by
# its coordinates ballX and ballY, are inside the rectangle defined by a top
# left point of coordinates obsX1, obsY1, and a bottom-right point
# with coordinates obsX2, obsY2. Returns false if the point is outside
# the rectangle.
def isInside( ballX, ballY, obsX1, obsY1, obsX2, obsY2 ):
if obsX1 < ballX < obsX2 and obsY1 < ballY < obsY2:
return True
else:
return False
def main():
win = GraphWin( "Lab 7 Moving ball", 600, 400 )
# create a green obstacle in the middle of the window
x1 = 200
y1 = 200
x2 = 250
y2 = 250
obstacle1 = Rectangle( Point( x1, y1 ), Point( x2, y2 ) )
obstacle1.setFill( "green" )
obstacle1.draw( win )
# create another green rectangle on the right of the first one
x3 = 350
y3 = 200
x4 = 400
y4 = 250
obstacle2 = Rectangle( Point( x3, y3 ), Point( x4, y4 ) )
obstacle2.setFill( "magenta" )
obstacle2.draw( win )
# create and draw a red circle
radius = 30
center = Point( 100, 100 )
circ = Circle( center, radius )
circ.setFill( 'red' )
circ.draw( win )
# define the direction the circle will start moving in.
# 5 pixels to the right every move, and 0.25 pixels down
# every move.
dx = 5.111
dy = -2.51
# as long as the mouse hasn't been clicked on the window
# keep on looping.
while win.checkMouse() == None:
# move the circle in the current direction.
circ.move( dx, dy )
# get the x and y of the center of the circle.
x = circ.getCenter().getX()
y = circ.getCenter().getY()
# if the center of the ball is outside the right or left boundary,
# reverse the x direction of movement.
if x > 600 - radius or x < radius:
dx = -dx
if y > 400 - radius or y < radius:
dy = -dy
# if the center of the ball is inside the first obstacle, stop
# the ball.
if isInside( x, y, x1, y1, x2, y2 ):
dx = 0
dy = 0
# if the center of the ball is inside the second obstacle, bounce
# off
if isInside( x, y, x3, y3, x4, y4 ):
dx = -dx
dy = -dy
# if we're here, it's because the the user clicked on the graphic window.
# we can close everything and quit.
win.close()
main()
demo7.py
# Uses graphics.py from Zelle
#
# This program displays the basic elements of a program
#
from graphics import *
# ifInside: returns true of the coordinates of a point defined by
# its coordinates ballX and ballY, are inside the rectangle defined by a top
# left point of coordinates obsX1, obsY1, and a bottom-right point
# with coordinates obsX2, obsY2. Returns false if the point is outside
# the rectangle.
def isInside( ballX, ballY, obsX1, obsY1, obsX2, obsY2 ):
if obsX1 < ballX < obsX2 and obsY1 < ballY < obsY2:
return True
else:
return False
def isLeftSide( x, y, width ):
if x < width//2:
return True
else:
return False
def main():
win = GraphWin( "Lab 7 Moving ball", 600, 400 )
# create a green obstacle in the middle of the window
x1 = 200
y1 = 200
x2 = 250
y2 = 250
obstacle1 = Rectangle( Point( x1, y1 ), Point( x2, y2 ) )
obstacle1.setFill( "green" )
obstacle1.draw( win )
# create another green rectangle on the right of the first one
x3 = 350
y3 = 200
x4 = 400
y4 = 250
obstacle2 = Rectangle( Point( x3, y3 ), Point( x4, y4 ) )
obstacle2.setFill( "magenta" )
obstacle2.draw( win )
# create and draw a red circle
radius = 30
center = Point( 100, 100 )
circ = Circle( center, radius )
circ.setFill( 'red' )
circ.draw( win )
# define the direction the circle will start moving in.
# 5 pixels to the right every move, and 0.25 pixels down
# every move.
dx = 5.111
dy = -2.51
# as long as the mouse hasn't been clicked on the window
# keep on looping.
while win.checkMouse() == None:
# move the circle in the current direction.
circ.move( dx, dy )
# get the x and y of the center of the circle.
x = circ.getCenter().getX()
y = circ.getCenter().getY()
# if the center of the ball is outside the right or left boundary,
# reverse the x direction of movement.
if x > 600 - radius or x < radius:
dx = -dx
if y > 400 - radius or y < radius:
dy = -dy
# if the center of the ball is inside the first obstacle, stop
# the ball.
if isInside( x, y, x1, y1, x2, y2 ):
dx = 0
dy = 0
# if the center of the ball is inside the second obstacle, bounce
# off
if isInside( x, y, x3, y3, x4, y4 ):
dx = -dx
dy = -dy
# if the ball is on the left side of the window, its color is
# red, else its color is yellow.
if isLeftSide( x, y, win.getWidth() )==True:
circ.setFill( 'red' )
else:
circ.setFill( 'yellow' )
# if we're here, it's because the the user clicked on the graphic window.
# we can close everything and quit.
win.close()
main()
demo8.py
# Uses graphics.py from Zelle
#
# This program displays the basic elements of a program
#
from graphics import *
# ifInside: returns true of the coordinates of a point defined by
# its coordinates ballX and ballY, are inside the rectangle defined by a top
# left point of coordinates obsX1, obsY1, and a bottom-right point
# with coordinates obsX2, obsY2. Returns false if the point is outside
# the rectangle.
def isInside( ballX, ballY, obsX1, obsY1, obsX2, obsY2 ):
if obsX1 < ballX < obsX2 and obsY1 < ballY < obsY2:
return True
else:
return False
def isLeftSide( x, y, width ):
if x < width//2:
return True
else:
return False
def getColor( x, y, w, h ):
if x < w/2 and y < h/2:
return 'yellow'
elif x < w/2 and y > h/2:
return 'blue'
elif x > w/2 and y < h/2:
return 'red'
else:
return 'brown'
def main():
win = GraphWin( "Lab 7 Moving ball", 600, 400 )
# create a green obstacle in the middle of the window
x1 = 200
y1 = 200
x2 = 250
y2 = 250
obstacle1 = Rectangle( Point( x1, y1 ), Point( x2, y2 ) )
obstacle1.setFill( "green" )
obstacle1.draw( win )
# create another green rectangle on the right of the first one
x3 = 350
y3 = 200
x4 = 400
y4 = 250
obstacle2 = Rectangle( Point( x3, y3 ), Point( x4, y4 ) )
obstacle2.setFill( "magenta" )
obstacle2.draw( win )
# create and draw a red circle
radius = 30
center = Point( 100, 100 )
circ = Circle( center, radius )
circ.setFill( 'red' )
circ.draw( win )
# define the direction the circle will start moving in.
# 5 pixels to the right every move, and 0.25 pixels down
# every move.
dx = 5.111
dy = -2.51
# as long as the mouse hasn't been clicked on the window
# keep on looping.
while win.checkMouse() == None:
# move the circle in the current direction.
circ.move( dx, dy )
# get the x and y of the center of the circle.
x = circ.getCenter().getX()
y = circ.getCenter().getY()
circ.setFill( getColor( x, y, win.getWidth(), win.getHeight() ) )
# if the center of the ball is outside the right or left boundary,
# reverse the x direction of movement.
if x > 600 - radius or x < radius:
dx = -dx
if y > 400 - radius or y < radius:
dy = -dy
# if the center of the ball is inside the first obstacle, stop
# the ball.
if isInside( x, y, x1, y1, x2, y2 ):
dx = 0
dy = 0
# if the center of the ball is inside the second obstacle, bounce
# off
if isInside( x, y, x3, y3, x4, y4 ):
dx = -dx
dy = -dy
# if the ball is on the left side of the window, its color is
# red, else its color is yellow.
"""
if isLeftSide( x, y, win.getWidth() )==True:
circ.setFill( 'red' )
else:
circ.setFill( 'yellow' )
"""
# if we're here, it's because the the user clicked on the graphic window.
# we can close everything and quit.
win.close()
main()
</showafterdate>