Difference between revisions of "CSC231 Homework 6 Fall 2017"
(→Examples) |
|||
| (18 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
--[[User:Thiebaut|D. Thiebaut]] ([[User talk:Thiebaut|talk]]) 12:59, 5 November 2017 (EST) | --[[User:Thiebaut|D. Thiebaut]] ([[User talk:Thiebaut|talk]]) 12:59, 5 November 2017 (EST) | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <bluebox> | ||
| + | This homework is due on 11/13/17 at 11:55 p.m. | ||
| + | </bluebox> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | __TOC__ | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
=Problem #1= | =Problem #1= | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | * Assume that you have | + | * Assume that you have an ''assembly'' program that uses a loop to compute Fibonacci numbers. |
* The Fibonacci terms get stored in an array called Fib as they are computed. The array is an array of '''dwords'''. | * The Fibonacci terms get stored in an array called Fib as they are computed. The array is an array of '''dwords'''. | ||
* In the loop, the program computes | * In the loop, the program computes | ||
| Line 12: | Line 19: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
* The program uses some form of addressing mode to store each '''Fib[i]''' term in the array. | * The program uses some form of addressing mode to store each '''Fib[i]''' term in the array. | ||
| − | * If we are not worried about possible overflow of the arithmetic, i.e. we are not worried that the computation might become invalid at some point, and if we assume that the array can be as large as we want (we have a large amount of RAM in our computer), '''what is a good approximation to the maximum number of Fibonacci terms an assembly program can compute in 1 second, if our computer has a 2.5 GHz Pentium processor?''' | + | * If we are not worried about possible overflow of the arithmetic, i.e. we are not worried that the computation might become invalid at some point, and if we assume that the array can be as large as we want (we have a large amount of RAM in our computer), '''what is a good approximation to the maximum number of Fibonacci terms an assembly program can compute in 1 second, if our computer has a 2.5 GHz Pentium processor?''' In other words, try to write the loop that computes the Fibonacci terms with as few instructions as possible; that will give you the maximum number of terms that can be computed per second. |
* Answer the multiple-choice question on Moodle. | * Answer the multiple-choice question on Moodle. | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| + | Note: You do not have to submit code for this section, but you should probably write the assembly code that computes the Fibonacci terms, just to see how tight you can make the loop, and find the maximum number of terms that can be computed... | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
=Problem #2= | =Problem #2= | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | When you were a kid, you may have exchanged secret messages with friends. An easy way to | + | When you were a kid, you may have exchanged secret messages with friends. An easy way to generated coded messages is to assign a different letter to each letter of the alphabet. For example: |
a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z | a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z | ||
| Line 25: | Line 33: | ||
b c d a f g h e m n i j k l p o r q t s x y z u v w | b c d a f g h e m n i j k l p o r q t s x y z u v w | ||
| − | If you wanted to send a secret message containing the word "hello" to a friend, you would need to ''encode'' it first. For this, you would look up each letter of the word in the first line above (normal alphabet), find the letter directly underneath (in the scrambled alphabet), and make up a new word with the letters from the second line. 'h' would become 'e', 'e' would become 'f', 'l' would become 'j', and 'o' would become 'p'. So 'hello' would be | + | If you wanted to send a secret message containing the word "hello" to a friend, you would need to ''encode'' it first. For this, you would look up each letter of the word in the first line above (normal alphabet), find the letter directly underneath (in the scrambled alphabet), and make up a new word with the letters from the second line. 'h' would become 'e', 'e' would become 'f', 'l' would become 'j', and 'o' would become 'p'. So 'hello' would be 'encoded' as 'efjjp'. Your friend then would decode 'efjjp' back into 'hello' by using a similar process, explained below. |
To decode the message, your friend could use the same method you used, but with a different second scrambled alphabet: | To decode the message, your friend could use the same method you used, but with a different second scrambled alphabet: | ||
| Line 35: | Line 43: | ||
To decode 'efjjp', your friend would look up 'e' in the first alphabet above, and find 'h' just below. 'h' would be the first letter of the encoded message. 'f' is above 'e', so 'e' is the second letter. 'j' is above 'l', so the next letters are 'll'. And finally 'p' is above 'o', so the final letter of the encoded message had to be 'o': "hello." | To decode 'efjjp', your friend would look up 'e' in the first alphabet above, and find 'h' just below. 'h' would be the first letter of the encoded message. 'f' is above 'e', so 'e' is the second letter. 'j' is above 'l', so the next letters are 'll'. And finally 'p' is above 'o', so the final letter of the encoded message had to be 'o': "hello." | ||
| − | For this assignment, you are given the executable version of an encoder, which uses the process illustrated above. Your assignment is to write the decoder that will take words in lowercase and | + | For this assignment, you are given the executable version of an encoder, which uses the process illustrated above. Your assignment is to write the decoder that will take words in lowercase and will decode them to their original version. |
You can get a copy of the executable version of the encoder as follows: | You can get a copy of the executable version of the encoder as follows: | ||
| Line 52: | Line 60: | ||
==Additional Information== | ==Additional Information== | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| + | ===Coding Hints=== | ||
* To transform a character into another character, you can use a simple trick. | * To transform a character into another character, you can use a simple trick. | ||
| − | * | + | * First declare an array, say ''table'', containing a scrambled version of the alphabet: |
| − | + | <br /> | |
| − | + | ::<source lang="text"> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 25 | |
| − | +-+-+-+-+- | + | +---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---...+---+ |
| + | Table | b | c | d | a | f | g | h | e | m | n | i | j | k | l | p | o .. w | | ||
| + | +---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---...+---+ | ||
| + | |||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | * Then when you get a character to encode, say 'h', subtract 'a' from it. This gives you the number 7. | ||
| + | * Then go in the array ''Table'', at ''index'' 7, and grab the letter there: 'e'. 'e' is the encoded version of 'h'. | ||
| + | * By removing 'a' from the character to encode, you actually use the array ''Table'' as if its Index 0 was actually 'a', Index 1, the letter 'b', Index 2, the letter 'c', etc. | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | ===Restrictions=== | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | * The input strings your decode program will be subjected to will never be longer than 256 characters. | ||
| + | * The input strings your decode program will be subjected to will only contain lowercase characters. | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | ==Submission== | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | Submit your program on Moodle in the Homework 6 Problem 2 section. Make sure you document your code well. | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Problem 3= | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | Assume that we have an application that uses signed integers of 11 bits. The integers are coded using 2's complement. The following questions should be answered on Moodle, in the Homework 6 Problem 3 section. | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | ;Question 1 | ||
| + | : What is the smallest (most negative) number that can be represented with this format? Use a decimal number when entering your answer in Moodle. | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | ;Question 2 | ||
| + | : What is the largest (most positive) number that can be represented with this format? Use a decimal number when entering your answer in Moodle. | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | ;Question 3 | ||
| + | : What is the decimal equivalent of 0x7FF in this format? Use a decimal number when entering your answer in Moodle. | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | ; Question 4 | ||
| + | : What is the decimal equivalent of 0x400 in this format? Use a decimal number when entering your answer in Moodle. | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | ; Question 5 | ||
| + | : What is the decimal equivalent of 0x3FF in this format? Use a decimal number when entering your answer in Moodle. | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | ; Question 6 | ||
| + | : Assume that we code +255 (decimal) and +256 (decimal) in this 11-bit, 2's complement integer format. Will the sum of these two numbers be stored correctly in 11 bits or will the result overflow the 11 bits? | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | =Solution Assembly Program= | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | ==Fast Fibs== | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | ::<source lang="asm"> | ||
| + | ;;; Solution for Homework 6 Problem 1 | ||
| + | ;;; D. Thiebaut | ||
| + | |||
| + | section .data | ||
| + | Fib times 100 dd 0 | ||
| + | |||
| + | section .text | ||
| + | global _start | ||
| + | extern _printInt, _println | ||
| + | _start: | ||
| + | ;;; initialize first 2 fibs | ||
| + | |||
| + | mov dword[Fib], 1 ;Fib[0] <- 1 | ||
| + | mov dword[Fib+4], 1 ;Fib[1] <- 1 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ;;; setup the loop | ||
| + | mov ebx, Fib+8 ;ebx points to Fib[2] | ||
| + | mov eax, 1 ;eax contains Fib[1] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ;;; loop away! Once the loop goes a few times, eax | ||
| + | ;;; will contain Fib[n-1] and ebx will point to Fib[n-2] | ||
| + | mov ecx, 10 | ||
| + | for: add eax, dword[ebx-8] ;add to eax Fib[n-2] | ||
| + | mov dword[ebx], eax ;Fib[n] <- Fib[n-1]+Fib[n-2] | ||
| + | |||
| + | call _printInt ;if you remove these two statements | ||
| + | call _println ;you get a loop of 4 instructions! | ||
| + | |||
| + | add ebx, 4 ;n <- n+1 | ||
| + | loop for | ||
| + | |||
| + | ;;; exit | ||
| + | mov eax, 1 | ||
| + | mov ebx, 0 | ||
| + | int 0x80 | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | ==Encode/Decode== | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | ::<source lang="asm"> | ||
| + | ;;; hw6decode.asm | ||
| + | ;;; D. Thiebaut | ||
| + | ;;; This file decodes words (no spaces, only lowercase) that are given | ||
| + | ;;; after the prompt. Only one word at a time. | ||
| + | ;;; The words have been encoded with a dictionary declared as | ||
| + | ;;; | ||
| + | ;;; dict db 'asemblyfordcghijknpqtuvwxz' | ||
| + | ;;; | ||
| + | ;;; Example: | ||
| + | ;;; nasm -f elf hw6decode.asm | ||
| + | ;;; ld -melf_i386 -o hw6decode hw6decode.o 231Lib.o | ||
| + | ;;; cs231a@aurora ~/HWs/HW6/PB2 $ ./hw6code | ||
| + | ;;; > hello | ||
| + | ;;; fbcci | ||
| + | ;;; cs231a@aurora ~/HWs/HW6/PB2 $ ./hw6decode | ||
| + | ;;; > fbcci | ||
| + | ;;; hello | ||
| + | ;;; | ||
| + | |||
| + | section .data | ||
| + | ;;; asemblyfordcghijknpqtuvwxz | ||
| + | ;;; abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz | ||
| + | dict db 'aelkchmnopqfdristjbuvwxygz' ; the dictionary used for decoding | ||
| + | prompt db '> ' | ||
| + | input dd 0 ;save address of string input by user | ||
| + | noChars dd 0 ;number of chars typed by user | ||
| + | temp dd 0 ;to save ecx when needed (we don't now | ||
| + | ; push yet) | ||
| + | |||
| + | section .txt | ||
| + | global _start | ||
| + | extern _printString | ||
| + | extern _getString | ||
| + | extern _println | ||
| + | |||
| + | _start: | ||
| + | ;;; get a string from the user. Print | ||
| + | ;;; prompt first, then save the address | ||
| + | ;;; of first byte of string in input, and | ||
| + | ;;; number of chars in input in noChars | ||
| + | |||
| + | mov ecx, prompt | ||
| + | mov edx, 2 | ||
| + | call _printString | ||
| + | call _getString | ||
| + | mov dword[noChars], edx | ||
| + | mov dword[input], ecx | ||
| + | |||
| + | ;;; get ready to loop over all the chars in string | ||
| + | ;;; entered by user. | ||
| + | ;;; for each char found, subtract 'a' from it | ||
| + | ;;; and make it an index in dict. Fetch the char | ||
| + | ;;; at that index and print it. | ||
| + | mov ecx, dword[noChars] | ||
| + | mov ebx, dword[input] | ||
| + | |||
| + | for: mov eax, 0 ; eax will be address of char in dict | ||
| + | mov al, byte[ebx] ; make eax 32-bit version of char | ||
| + | sub al, 'a' ; subtract 'a' to get index in dict | ||
| + | add eax, dict ; make eax addess of char in dict | ||
| + | mov al, byte[eax] ; get char in dict | ||
| + | mov byte[ebx],al ; replace original char | ||
| + | inc ebx | ||
| + | loop for | ||
| + | |||
| + | ;;; print the decoded string on the screen | ||
| + | mov ecx, dword[input] | ||
| + | mov edx, dword[noChars] | ||
| + | call _printString | ||
| + | call _println | ||
| + | |||
| + | ;;; exit | ||
| + | mov eax, 1 | ||
| + | mov ebx, 0 | ||
| + | int 0x80 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | [[Category:CSC231]][[Category:Homework]][[Category:Nasm]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:44, 15 November 2017
--D. Thiebaut (talk) 12:59, 5 November 2017 (EST)
This homework is due on 11/13/17 at 11:55 p.m.
Contents
Problem #1
- Assume that you have an assembly program that uses a loop to compute Fibonacci numbers.
- The Fibonacci terms get stored in an array called Fib as they are computed. The array is an array of dwords.
- In the loop, the program computes
Fib[ i ] = Fib[ i-1 ] + Fib[ i-2 ];
- The program uses some form of addressing mode to store each Fib[i] term in the array.
- If we are not worried about possible overflow of the arithmetic, i.e. we are not worried that the computation might become invalid at some point, and if we assume that the array can be as large as we want (we have a large amount of RAM in our computer), what is a good approximation to the maximum number of Fibonacci terms an assembly program can compute in 1 second, if our computer has a 2.5 GHz Pentium processor? In other words, try to write the loop that computes the Fibonacci terms with as few instructions as possible; that will give you the maximum number of terms that can be computed per second.
- Answer the multiple-choice question on Moodle.
Note: You do not have to submit code for this section, but you should probably write the assembly code that computes the Fibonacci terms, just to see how tight you can make the loop, and find the maximum number of terms that can be computed...
Problem #2
When you were a kid, you may have exchanged secret messages with friends. An easy way to generated coded messages is to assign a different letter to each letter of the alphabet. For example:
a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | b c d a f g h e m n i j k l p o r q t s x y z u v w
If you wanted to send a secret message containing the word "hello" to a friend, you would need to encode it first. For this, you would look up each letter of the word in the first line above (normal alphabet), find the letter directly underneath (in the scrambled alphabet), and make up a new word with the letters from the second line. 'h' would become 'e', 'e' would become 'f', 'l' would become 'j', and 'o' would become 'p'. So 'hello' would be 'encoded' as 'efjjp'. Your friend then would decode 'efjjp' back into 'hello' by using a similar process, explained below.
To decode the message, your friend could use the same method you used, but with a different second scrambled alphabet:
a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | d a b c h e f g k l m n i j p o r q t s x y z u v w
To decode 'efjjp', your friend would look up 'e' in the first alphabet above, and find 'h' just below. 'h' would be the first letter of the encoded message. 'f' is above 'e', so 'e' is the second letter. 'j' is above 'l', so the next letters are 'll'. And finally 'p' is above 'o', so the final letter of the encoded message had to be 'o': "hello."
For this assignment, you are given the executable version of an encoder, which uses the process illustrated above. Your assignment is to write the decoder that will take words in lowercase and will decode them to their original version.
You can get a copy of the executable version of the encoder as follows:
getcopy hw6code
Call your program hw6decode.asm and submit it to Moodle when done.
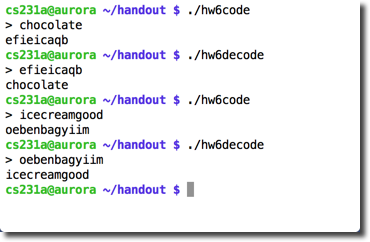
Examples
The following examples illustrate how your program must work when working
Additional Information
Coding Hints
- To transform a character into another character, you can use a simple trick.
- First declare an array, say table, containing a scrambled version of the alphabet:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 25 +---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---...+---+ Table | b | c | d | a | f | g | h | e | m | n | i | j | k | l | p | o .. w | +---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---...+---+
- Then when you get a character to encode, say 'h', subtract 'a' from it. This gives you the number 7.
- Then go in the array Table, at index 7, and grab the letter there: 'e'. 'e' is the encoded version of 'h'.
- By removing 'a' from the character to encode, you actually use the array Table as if its Index 0 was actually 'a', Index 1, the letter 'b', Index 2, the letter 'c', etc.
Restrictions
- The input strings your decode program will be subjected to will never be longer than 256 characters.
- The input strings your decode program will be subjected to will only contain lowercase characters.
Submission
Submit your program on Moodle in the Homework 6 Problem 2 section. Make sure you document your code well.
Problem 3
Assume that we have an application that uses signed integers of 11 bits. The integers are coded using 2's complement. The following questions should be answered on Moodle, in the Homework 6 Problem 3 section.
- Question 1
- What is the smallest (most negative) number that can be represented with this format? Use a decimal number when entering your answer in Moodle.
- Question 2
- What is the largest (most positive) number that can be represented with this format? Use a decimal number when entering your answer in Moodle.
- Question 3
- What is the decimal equivalent of 0x7FF in this format? Use a decimal number when entering your answer in Moodle.
- Question 4
- What is the decimal equivalent of 0x400 in this format? Use a decimal number when entering your answer in Moodle.
- Question 5
- What is the decimal equivalent of 0x3FF in this format? Use a decimal number when entering your answer in Moodle.
- Question 6
- Assume that we code +255 (decimal) and +256 (decimal) in this 11-bit, 2's complement integer format. Will the sum of these two numbers be stored correctly in 11 bits or will the result overflow the 11 bits?
Solution Assembly Program
Fast Fibs
;;; Solution for Homework 6 Problem 1 ;;; D. Thiebaut section .data Fib times 100 dd 0 section .text global _start extern _printInt, _println _start: ;;; initialize first 2 fibs mov dword[Fib], 1 ;Fib[0] <- 1 mov dword[Fib+4], 1 ;Fib[1] <- 1 ;;; setup the loop mov ebx, Fib+8 ;ebx points to Fib[2] mov eax, 1 ;eax contains Fib[1] ;;; loop away! Once the loop goes a few times, eax ;;; will contain Fib[n-1] and ebx will point to Fib[n-2] mov ecx, 10 for: add eax, dword[ebx-8] ;add to eax Fib[n-2] mov dword[ebx], eax ;Fib[n] <- Fib[n-1]+Fib[n-2] call _printInt ;if you remove these two statements call _println ;you get a loop of 4 instructions! add ebx, 4 ;n <- n+1 loop for ;;; exit mov eax, 1 mov ebx, 0 int 0x80
Encode/Decode
;;; hw6decode.asm ;;; D. Thiebaut ;;; This file decodes words (no spaces, only lowercase) that are given ;;; after the prompt. Only one word at a time. ;;; The words have been encoded with a dictionary declared as ;;; ;;; dict db 'asemblyfordcghijknpqtuvwxz' ;;; ;;; Example: ;;; nasm -f elf hw6decode.asm ;;; ld -melf_i386 -o hw6decode hw6decode.o 231Lib.o ;;; cs231a@aurora ~/HWs/HW6/PB2 $ ./hw6code ;;; > hello ;;; fbcci ;;; cs231a@aurora ~/HWs/HW6/PB2 $ ./hw6decode ;;; > fbcci ;;; hello ;;; section .data ;;; asemblyfordcghijknpqtuvwxz ;;; abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz dict db 'aelkchmnopqfdristjbuvwxygz' ; the dictionary used for decoding prompt db '> ' input dd 0 ;save address of string input by user noChars dd 0 ;number of chars typed by user temp dd 0 ;to save ecx when needed (we don't now ; push yet) section .txt global _start extern _printString extern _getString extern _println _start: ;;; get a string from the user. Print ;;; prompt first, then save the address ;;; of first byte of string in input, and ;;; number of chars in input in noChars mov ecx, prompt mov edx, 2 call _printString call _getString mov dword[noChars], edx mov dword[input], ecx ;;; get ready to loop over all the chars in string ;;; entered by user. ;;; for each char found, subtract 'a' from it ;;; and make it an index in dict. Fetch the char ;;; at that index and print it. mov ecx, dword[noChars] mov ebx, dword[input] for: mov eax, 0 ; eax will be address of char in dict mov al, byte[ebx] ; make eax 32-bit version of char sub al, 'a' ; subtract 'a' to get index in dict add eax, dict ; make eax addess of char in dict mov al, byte[eax] ; get char in dict mov byte[ebx],al ; replace original char inc ebx loop for ;;; print the decoded string on the screen mov ecx, dword[input] mov edx, dword[noChars] call _printString call _println ;;; exit mov eax, 1 mov ebx, 0 int 0x80