Difference between revisions of "CSC231 Schedule 2010"
(→Weekly Schedule) |
|||
| (41 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | --[[User:Thiebaut|D. Thiebaut]] 08:28, 6 January 2011 (EST) | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br /> | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
[[CSC231 | Back to Main Page]] | [http://cs.smith.edu/classwiki/index.php/CSC231_Page_(2010) Class Wiki] | [[CSC231 | Back to Main Page]] | [http://cs.smith.edu/classwiki/index.php/CSC231_Page_(2010) Class Wiki] | ||
| Line 272: | Line 276: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
* [[CSC231 Lab 7 2010 | Lab 7]] | * [[CSC231 Lab 7 2010 | Lab 7]] | ||
| − | * [[CSC231 Homework 8 2010 | Homework 8]] | + | * [[CSC231 Homework 8 2010 | Homework 8]] and [[CSC231 Homework 8 Solution Program 2010 | solution program]] |
|| | || | ||
| Line 288: | Line 292: | ||
* Continuation of [[CSC231 Exercises with conditional jumps | Exsercises]] on conditional jumps | * Continuation of [[CSC231 Exercises with conditional jumps | Exsercises]] on conditional jumps | ||
; Friday 11/19 | ; Friday 11/19 | ||
| − | * | + | * Functions + tests = '''Recursion''' |
| + | * [[CSC220 Factorial.asm | factorial.asm]] | ||
---- | ---- | ||
* No homework assignment this week! | * No homework assignment this week! | ||
| Line 301: | Line 306: | ||
|| | || | ||
; Monday | ; Monday | ||
| − | * | + | * Continuation of Coverage of Recursion |
| + | * <!--videoflash>5X8cM2JiqzI</videoflash--> | ||
| + | * Video: History of Computers | ||
<tanbox> | <tanbox> | ||
| − | [[Image:dancingCalving.gif | right]] | + | <!--[[Image:dancingCalving.gif | right]]--> |
| + | [[Image:turkeyCarcass.jpg | 200px | right]] | ||
; Wednesday: '''Thanksgiving Break''' | ; Wednesday: '''Thanksgiving Break''' | ||
; Friday: '''Thanksgiving Break''' | ; Friday: '''Thanksgiving Break''' | ||
| Line 316: | Line 324: | ||
| Week 13 <br /> 11/29 | | Week 13 <br /> 11/29 | ||
|| | || | ||
| − | * | + | ; Monday 11/29 |
| + | * More on Recursion: Multiplication | ||
| + | * [[CSC231 Recursive Multiplication | Recursive Multiplication Algorithm]] | ||
| + | ; Wednesday 12/1 | ||
| + | * [[CSC231 FindLargestOfArray.asm | Searching a 1-dimensional array for the largest/smallest element]] | ||
| + | * Sketching binary-search on an array | ||
| + | * A demo: comparison of interpreted versus compiled languages: [[CSC231: N-Queens Problem: interpreted vs compiled|The N-Queens test]] | ||
| + | ; Friday 12/3 | ||
| + | * Discussion: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Compiler_optimization compiler optimizations] | ||
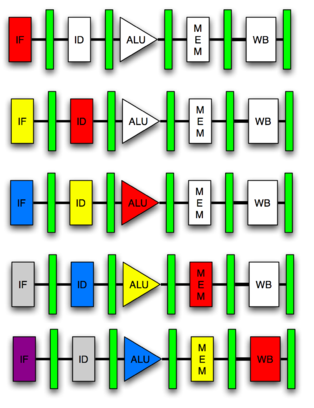
| + | * [http://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Microprocessor_Design/Pipelined_Processors Pipelines] | ||
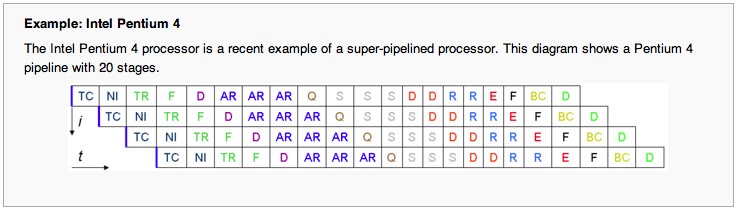
| + | ** <center>[[Image:CSC231_pipeline1.png|200px]]</center> | ||
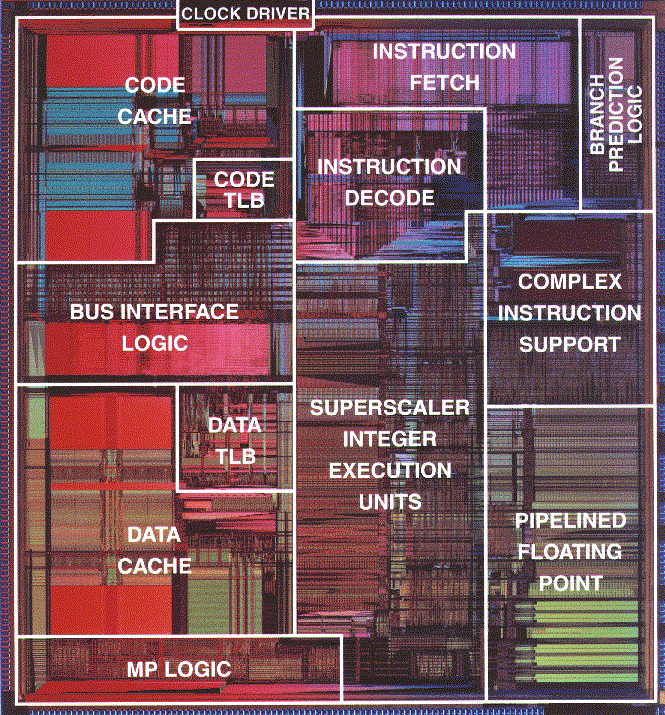
| + | ** <center>[[Image:CSC231_pipeline2.png|400px]]</center> | ||
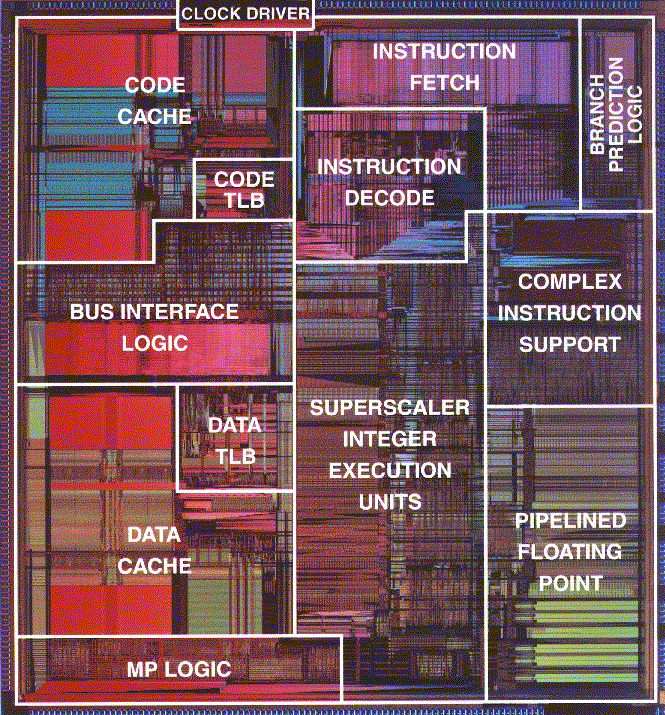
| + | ** <center>[[Image:CSC231_PentiumDie2.gif|400px]]</center> | ||
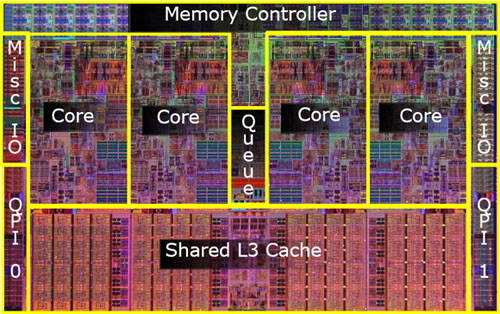
| + | ** <center>[[Image:CSC231_PentiumDie6core.jpg|400px]]</center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | * [[CSC231 Homework 9 2010 | Homework #9]] and [[CSC231 Homework 9 Solution 2010 | Solution Program]] | ||
|| | || | ||
| − | * | + | * [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Compiler_optimization Compiler optimization] on wikipedia. |
| − | + | * [http://cs.smith.edu/~thiebaut/classes/231_0405/doc/pcasm-book.pdf Section 4.8] of Carter's Assembly Manual on recursion. | |
| + | * [http://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Microprocessor_Design/Pipelined_Processors Pentium pipelining] | ||
| + | * A very good description of the Pentium 4 Architecture at [http://www.hardwaresecrets.com/article/235 www.hardwaresecrets.com] | ||
| + | * Some parameters for virtual memory (taken from [http://www.cp.eng.chula.ac.th/~piak/teaching/ca/vm.htm www.cp.eng.chula.ac.th]): | ||
| + | **Typical range of parameters for virtual memory | ||
| + | ** | ||
| + | <center> | ||
| + | {| | ||
| + | |block (page) size | ||
| + | |512-8192 bytes | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |hit time | ||
| + | |1-10 clock cycles | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |miss penalty | ||
| + | |100,000-600,000 clocks | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |(access time) | ||
| + | | (100,000-500,000 clocks) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |(transfer time) | ||
| + | | (10,000-100,000 clocks) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |miss rate | ||
| + | |0.00001% - 0.001% | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |main memory size | ||
| + | |4 MB - 2048 MB | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </center> | ||
|- style="background:#eeeeff" valign="top" | |- style="background:#eeeeff" valign="top" | ||
| Week 14 <br /> 12/06 | | Week 14 <br /> 12/06 | ||
|| | || | ||
| − | * | + | ; Monday 12/06 |
| + | * Continue with pipelines | ||
| + | * Virtual Memory | ||
| + | ; Wednesday 12/08 | ||
| + | * Cache Memory | ||
| + | * Average Access Time | ||
| + | * Back to compiler optimization | ||
| + | **Pipeline-related | ||
| + | ***Delayed branches | ||
| + | ***Instruction reordering | ||
| + | **Cache-oriented | ||
| + | ***use of registers instead of memory ([http://ee.hawaii.edu/~tep/EE160/Book/chap14/subsection2.1.1.2.html register variables]) | ||
| + | * A [[CSC231 generateRandomNumbers.asm| program]] to generate random numbers | ||
| + | ; Friday 12/10 | ||
| + | * 2-D arrays | ||
| + | * Floating Point Numbers | ||
| + | ** Fixed-point format | ||
| + | ** [http://maven.smith.edu/~thiebaut/classes/231/floatingpoint.html Floating-Point Converter] applet. | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | * | + | * [[CSC231 Homework 10 2010 | (''Optional'') Homework #10]] and [[CSC231 Homework 10 Solution 2010| solution program]] |
|| | || | ||
| + | * [http://webster.cs.ucr.edu/AoA/Windows/HTML/Arraysa2.html 2D Arrays] | ||
| + | * [http://steve.hollasch.net/cgindex/coding/ieeefloat.html A good introduction to Floating Point Numbers], nicely presented. Similary, a [http://www.cs.princeton.edu/introcs/91float/ page] from Princeton's Intro to CS on floating points. | ||
| + | * [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Floating_point General description] of the floating-point notation on Wikipedia. | ||
| + | * [http://www.python.org/doc/2.5.2/tut/node16.html A very good description of the limitations] of floating-point numbers in Python: Read it! | ||
| + | * Also, not to be missed: [http://www.lahey.com/float.htm The perils of floating-point] | ||
| + | * [http://www.programmers-corner.com/tutorial/31?PHPSESSID=4bbf1f2b76df390e1bad01a9f8462854 Floating Point in Assembly]: some high level stuff! | ||
* | * | ||
| + | |||
| Line 333: | Line 410: | ||
| Week 15 <br /> 12/13 | | Week 15 <br /> 12/13 | ||
|| | || | ||
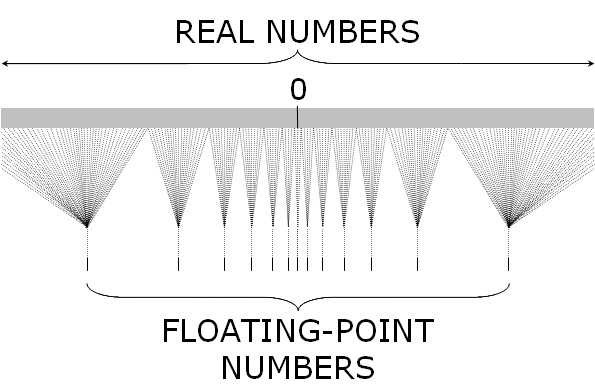
| − | + | [[Image:CSC231RangeOfFloats.jpg |200px|right|link=http://jasss.soc.surrey.ac.uk/9/4/4.html]] | |
| + | ; '''Monday''' ''<font color="magenta">Last Class</font>'' | ||
| + | * IEEE Floating-Point Representation | ||
| + | ** Exponent: 4 special cases: zero, denormalized numbers, infinity, NaN | ||
| + | ** [http://maven.smith.edu/~thiebaut/classes/231/floatingpoint.html Floating-Point Converter] applet. | ||
| + | ** Range of IEEE Floats | ||
| + | ** Compare range of floats to ints. Ask [http://www.wolframalpha.com/input/?i=10^32+inches Wolfram Alpha] what is 10^32 inches! | ||
| + | ** Adding two floats | ||
| + | ** Examples of Floating-Point operations in Assembly | ||
| + | *** [[CSC231 Float1.asm | float1.asm]]: printing a float in assembly | ||
| + | *** [[CSC231 Float2.asm | float2.asm]]: transforms an int into a float | ||
| + | *** [[CSC231 Float3.asm | float3.asm]]: computes a = 10.5; b = 5.5; y = 3 * ( a - b ) + PI in assembly. | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | |||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | * | + | * [[CSC231_Lab_8 2010 | A Lab on Floating-Point Numbers] to explore on your own! |
| + | * [[CSC231 Final Exam 2010 | Final Exam]] --> due date = ''12:00 p.m. on Monday December 20, 2010'' | ||
|| | || | ||
| − | * | + | * [http://www.cs.umd.edu/class/spring2003/cmsc311/Notes/BinMath/addFloat.html Notes on adding floating-point numbers] |
| Line 350: | Line 444: | ||
== Assembly== | == Assembly== | ||
| − | * [[ | + | * [[:Category:Asm | Assembly Programs]] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
=Miscellaneous Information= | =Miscellaneous Information= | ||
Latest revision as of 20:43, 3 November 2014
--D. Thiebaut 08:28, 6 January 2011 (EST)
Contents
Weekly Schedule
| Week | Topics | Reading | ||||||||||||||
| Week 1 9/08 |
|
| ||||||||||||||
| Week 2 9/13 |
nasm -f elf -F stabs -l helloworld.S helloworld.asm
|
| ||||||||||||||
| Week 3 9/20 |
|
| ||||||||||||||
| Week 4 9/27 |
|
| ||||||||||||||
| Week 5 10/04 |
|
| ||||||||||||||
| Week 6 10/11 |
|
| ||||||||||||||
| Week 7 10/18 |
|
| ||||||||||||||
| Week 8 10/25 |
|
| ||||||||||||||
| Week 9 11/01 |
|
| ||||||||||||||
| Week 10 11/08 |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Week 11 11/15 |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Week 12 11/22 |
|
| ||||||||||||||
| Week 13 11/29 |
|
| ||||||||||||||
| Week 14 12/06 |
|
| ||||||||||||||
| Week 15 12/13 |
|
|
List of Selected Programs
Assembly
Miscellaneous Information
- Things to remember when working on homework assignments...
Linux Related