Difference between revisions of "CSC111 Homework 4 2011"
(→The graphics module) |
|||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
==First, let's explore the Python '''random''' module== | ==First, let's explore the Python '''random''' module== | ||
| − | === | + | ===Downloading the graphics module=== |
* Download the graphics module from this [http://mcsp.wartburg.edu/zelle/python/ this page]. | * Download the graphics module from this [http://mcsp.wartburg.edu/zelle/python/ this page]. | ||
Revision as of 18:11, 4 October 2011
--D. Thiebaut 12:42, 4 October 2011 (EDT)
This assignment is due on Oct. 12th evening, at midnight (you get 2 extra days because of the break. You can work on it individually or in pair-programming mode.
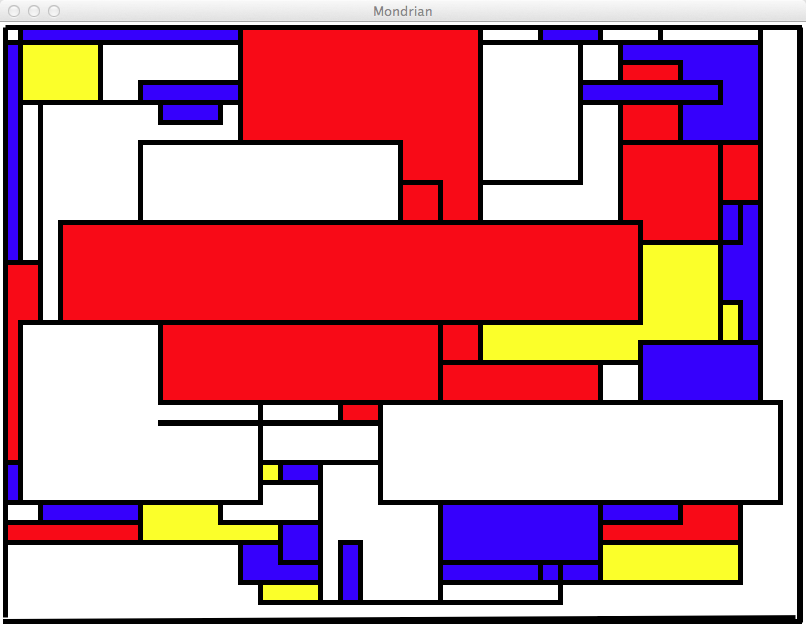
Mondrian
Piet Mondrian is famous for his very geometric paintings with simple colors with mostly white, red, yellow and blue rectangles between black lines. This style has been applied to many different articles, as shown below.
This assignment is inspired by this style and asks you to write a graphics program that will display 1000 random rectangles filled with random colors.
First, let's explore the Python random module
Downloading the graphics module
- Download the graphics module from this this page.
- Copy it to the same folder (directory) where you will be developing your graphics program.
Picking an item at random in a list
- The random module is a standard module in Python. It is part of the language and can be used to generate randomness. Actually, pseudo-randomness, because all randomness generated by programs cannot be purely random, since it is always based on some mathematical algorithm.
- Visit the official python.org documentation on the random module, and in particular scroll down to the Examples and Recipes section. It shows many different ways to get random information.
- For example. If I wanted to pick a random color out of a set of colors, here's a way we could do it:
import random
def main():
colors = ["blue", "red" ]
for i in range( 10 ):
print( random.choice( colors ) )
main()
- I have used a for-loop just to test the choice() function several times, and verify that it picks a random color every time.
- By the way, a list of the color names that are recognized by the graphics module is available here.
- Add a few more colors to your list and run your program again. See that it picks them at random?
Generating a random number
- The Examples and Recipes section of the documentation of the random module also shows that you can also pick a random number in a range. For example, if you want an even random number between 0 and 100, included, you can do this:
random.randrange(0, 101, 2) # Even integer from 0 to 100
- Try it by typing in the program below and running it a few times:
import random
def main():
# generate 10 random even numbers between 0 and 100:
for i in range( 10 ):
x = random.randrange( 0, 101, 2 )
print( "x = ", x )
main()
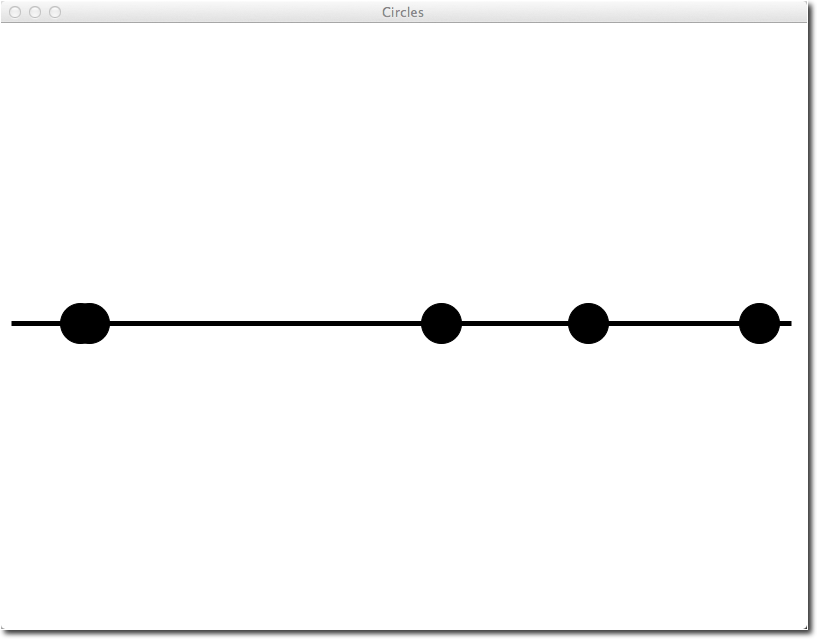
Generating random circles
- Let's generate 5 circles on a line (like a music notes on a score), and pick their placement at random.
def main2():
# define the width and height of our window (so that we can easily
# change the geometry if needed)
width = 800
height = 600
# open a graphics window
win = GraphWin( "Circles", width, height )
# draw a line
line =Line( Point( 10, height/2 ), Point( width-10, height/2 ) )
line.setFill( "black" )
line.setWidth( 5 )
line.draw( win )
# draw 5 circles placed at random x positions on the line
for i in range( 5 ):
radius = 20
x = random.randrange( 0+radius, width-radius )
c = Circle( Point( x, height/2 ), radius )
c.setFill( "black" )
c.draw( win )
win.getMouse()
win.close()
- Here's an example of the output of the program:
- Two of the circles overlap, but that's fine for our purpose.
Generating rectangles
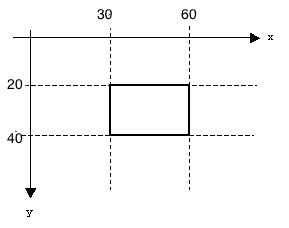
- Let's draw a red rectangle that is 30 pixels wide, and 20 pixels high, and such that its top left corner is at Coordinates (30, 20) and the bottom right at (60, 40). Remember that in graphics mode, the top left corner is at (0, 0).
- Below is the code to do that. Type it in and test it out! Play with it. Modify some of the numbers/colors/thicknesses to understand how the rectangle works.
from graphics import *
import random
def main():
width = 200
height = 100
win = GraphWin( "RedRed", width, height )
# create 2 points for the top-left and bottom-right corners
topLeft = Point( 30, 20 )
botRight= Point( 60, 40 )
rect = Rectangle( topLeft, botRight )
rect.setFill( "red" )
rect.setWidth( 5 ) # the width of the line
rect.draw( win )
# wait for user to click the mouse on the window...
win.getMouse()
win.close()
main()
Your Assignment
- Generate a Mondrian-type image with 1000 random rectangles, located at random locations, of random widths and random heights, with a limited color palette. The image below shows an example of what your program could generate.
- Note that some shapes do not look like rectangles. It is because every time a rectangle is drawn on the window, it will overlap other rectangles and the visible part that will be left may not be exactly rectangular.
Requirements
- Your program should wait for the user to click the mouse for it to stop.
- Each rectangle should have a fairly wide black border (I used 5 pixels in the example above)
- Your rectangles should have width and heights that are multiples of 20 (to give them a nicer look).
- You do not have to use the palette I have used here. Feel free to use as many colors as you want.
Submission
- Call your program hw4a.py and submit it as follows:
rsubmit hw4 hw4a.py
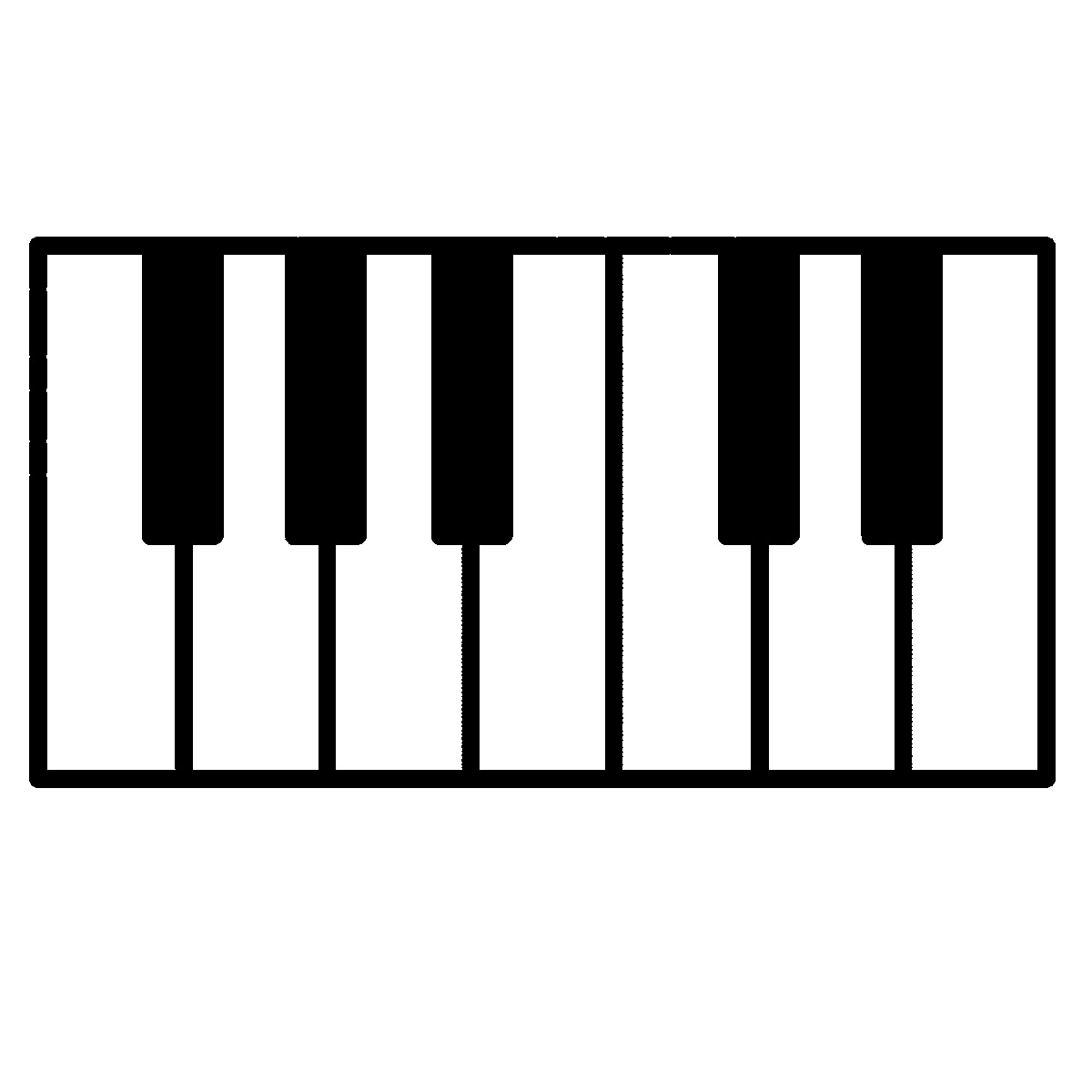
Musical Notes
- Your assignment is to generate a graphics program with Python that is inspired by the image above.
- Your program should draw 7 notes on a score, at the location of your choosing. They can represent the scale or not. It can be the beginning of your favorite tune.
- Your program should also represent the keys of a piano underneath the score. It is not required for the piano keys to be related to the notes in the score. You should, however, show white keys and black keys. At least 7 keys are required.
- Your notes may have a stem attached to the head, but it is not required. See wikipedia for more information.
Submission
- call your program hw4b.py and submit it as follows:
rsubmit hw4 hw4b.py
Optional and Extra Credit
- Same program as for the previous problem, but you must use a loop to generate the notes, and a loop to generate the keys (one loop generate both the black and the white keys!)
- Hints: the MacDonals assignment should be helpful for this problem...
Submission
- Call your program hw4x.py and submit it as follows:
submit hw4 hw4x.py