Difference between revisions of "CSC111 Lab 12 2011"
(→Fish!) |
|||
| Line 186: | Line 186: | ||
=Fish! = | =Fish! = | ||
| − | + | The Fish section has been reported to next week's lab, [[CSC111 Lab 13 2011 | Lab 13]]. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[ | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
Latest revision as of 18:27, 1 December 2011
--D. Thiebaut 09:42, 30 November 2011 (EST)
This lab will have you play with classes and objects: the essence of Object Oriented Programming!
Contents
Part 1: A Bus
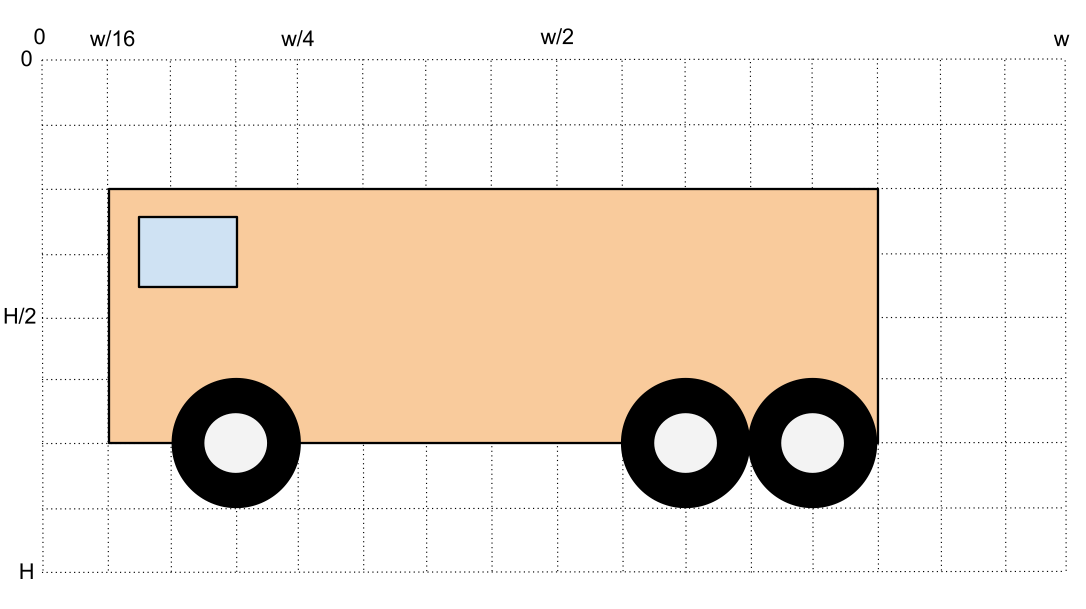
- Using the example we did in class on Tuesday as inspiration (see similar code below), create a new program that draws the bus shown above.
- Your program should have two classes:
- class Wheel
- class Bus
# A program with a car and a wheel class.
# Thanks to Victoria for providing the code!
#
from graphics import *
W = 400
H = 400
# creating a class for a taxicab
#start with class for wheel; two concentric circles of different colors
class Wheel:
def __init__(self, center, r1, r2 ): #__init__() is constructor; self is part of init; center, r1, r2 match parameters
self.center = center
r1, r2 = min(r1, r2), max(r1, r2)
self.radius1 = r1
self.radius2 = r2
self.c1 = Circle( center, r1 )
self.c2 = Circle( center, r2 )
def setFill( self, col1, col2 ):
self.c2.setFill( col1 )
self.c1.setFill( col2 )
def draw( self, win): #win matches parameter sent to draw in main
self.c2.draw( win )
self.c1.draw( win )
#class for car
class Car:
def __init__(self, p1, p2 ):
self.rect = Rectangle( p1, p2 )
length = abs( p1.getX() - p2.getX() )
xWheel1 = p1.getX() + length/4
yWheel1 = p2.getY()
xWheel2 = p2.getX() - length/4
yWheel2 = yWheel1
self.w1 = Wheel( Point(xWheel1, yWheel1), length/16, length/8 )
self.w2 = Wheel( Point(xWheel2, yWheel2), length/16, length/8 )
def draw( self, win ):
self.w2.draw( win )
self.rect.draw( win )
self.w1.draw( win )
def setFill( self, col1, col2, col3 ):
self.rect.setFill( col1 )
self.w1.setFill( col2, col3 )
self.w2.setFill( col2, col3 )
def main():
global W, H
win = GraphWin( "Wheel Class Demo", W, H)
car = Car( Point( 50,50 ), Point( 250, 100 ) )
car.setFill( "yellow", "white", "black" )
car.draw( win )
win.getMouse()
win.close()
main()
Challenge 1 |
- Add a for-loop that makes your bus disappear from the window. Make it go in the forward direction (i.e. left for the bus in the image above).
Part 2: Trees
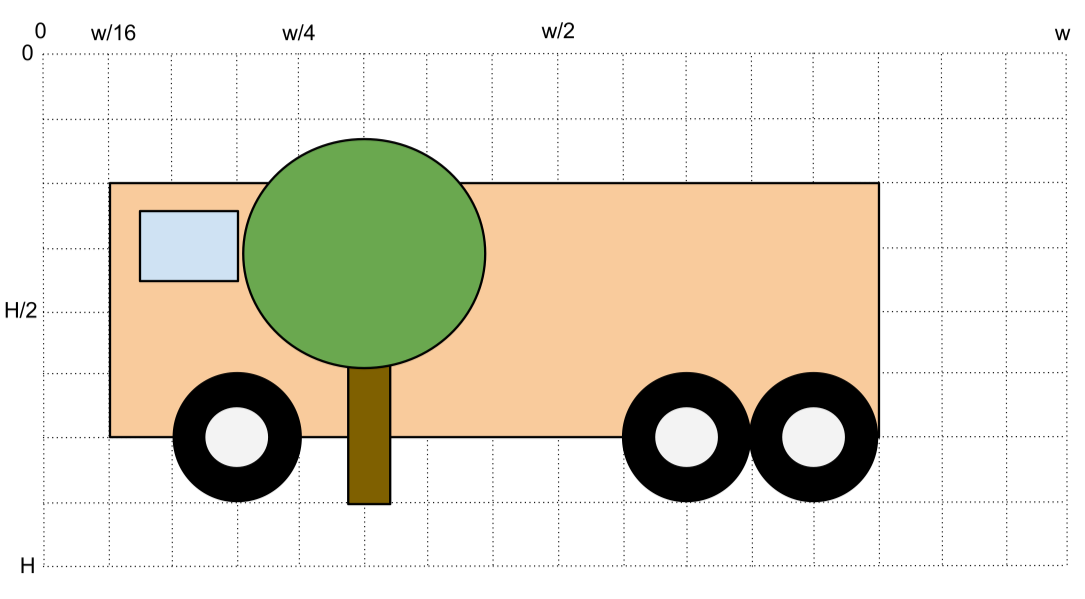
- Create a new class in your program called Tree. It will represent a simplified tree, with its green head of leaves, and its brown trunk.
- Make your program display the bus and the tree. It doesn't matter if the tree is in front or behind the bus.
- Below is a minimum class outline for the tree class...
class Tree:
def __init__( ... ):
...
def draw( ... ):
...
Challenge 2 |
- Make the bus stand still and the tree move in the direction opposite to that of the bus.
- Make the tree move out of the window for right now. No need to make it come back...
Challenge 3 |
- Add another tree object. One class: two objects.
- Place the trees in different locations so that they do not overlap
- Make your program display the two trees and the bus
Challenge 4 |
- Make the two trees move to the right and disappear from the window
Challenge 5 |
- Make the trees that disappear from the right reappear on the left, giving the illusion of a real cartoon!
- One way to make this happen is to edit the move method of the Tree class so that if the x location of some point associated with the tree is out of the window then you make the tree trunk and head move by a large x value proportional to the width of the window.
class Tree:
...
def move( ... ):
...
x = ...
if x > ...:
trunk.move( ... )
head.move( ... )
def main():
...
Fish!
The Fish section has been reported to next week's lab, Lab 13.




