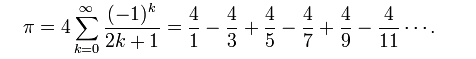Difference between revisions of "CSC111 Lab 8 2015"
| Line 146: | Line 146: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| + | ==Exercise 4: A bit of mathematics== | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | Pi can be computed by adding the following terms (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pi): | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center> | ||
| + | [[Image:pi_expansion.png]] | ||
| + | </center> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | Here's a program that shows how the variable '''sum''', where we accumulate the terms, gets closer and closer to PI: | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | ::<source lang="python"> | ||
| + | def computePi(): | ||
| + | sum = 0 | ||
| + | multiplier = 1 | ||
| + | |||
| + | for i in range( 1, 20, 2 ): | ||
| + | sum = sum + multiplier * 4.0 / i | ||
| + | multiplier = -multiplier | ||
| + | print( "Pi = ", sum ) | ||
| + | |||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Modify this program so that it stops when the first 3 digits of sum are equal to 3.14. In other words you need to change the loop to a while loop, and make it stop when the sum is a number of the form 3.14xxxxxxx. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
</showafterdate> | </showafterdate> | ||
Revision as of 14:03, 22 March 2015
--D. Thiebaut (talk) 14:10, 22 March 2015 (EDT)
<showafterdate after="20150325" before="20150601">
Contents
Part 1: While Loops
Exercise 1: Robust Input with While
def getPositiveNumber(): # # put your code here # return 10 # just to make sure the code is accepted by Idle def main(): # Part 1, Exercise 1 x = getPositiveNumber() print( "getPositiveNumber() returned", x ) main()
Complete the function getPositiveNumber() so that it asks the user for a number larger than 0, and keeps on prompting the user as long as she doesn't enter a valid number.
Below is an example of the interaction between computer and user.
Please enter a number greater than 0: -1 -1 is invalid. Please enter a number greater than 0: -3 -3 is invalid. Please enter a number greater than 0: 0 0 is invalid. Please enter a number greater than 0: 20 getPositiveNumber() returned 20 >>>
Exercise 2: Ask for Yes/No answer
Same idea as in Exercise 1, but this time the new function, called getYesNo() will keep on asking a question until the user's input is "YES", "yes", "y", "NO", "no", or "n". Any combination of lower/upper case in the spelling is accepted ("yES" is valid).
- Source
def getYesNo(): # # put your code here # return "Y" # just to make sure the code works as is. def main(): # Part1, Exercise 2 likesChoco = getYesNo() if likesChoco in ["YES", "Y" ]: print( "Me too!" ) else: print( "Sorry to hear that!" ) main()
- Example output
Do you like chocolate (Y/N)? possibly please enter by 'Yes' or 'No' Do you like chocolate (Y/N)? I don't know please enter by 'Yes' or 'No' Do you like chocolate (Y/N)? Oui please enter by 'Yes' or 'No' Do you like chocolate (Y/N)? y Me too!
Exercise 3: While Loop and Reading File
# createFile: creates a text file containing a haiku followed by the line <<<END>>> # followed by some text about the source of the haiku and the rights of use. def createFile( fileName ): # open the file file = open( fileName, "w" ) # write some text file.write(""" An old pond! A frog jumps in- The sound of water. <<<END>>> Haikus from http://www.toyomasu.com/haiku/ Feel free to use anything from this page as long as you make references and links to HAIKU for PEOPLE. Last updated: Jan 10th. 2001. Edited by Kei Grieg Toyomasu, kei at toyomasu dot com""" ) # close the file file.close() def readFileTillMarker( fileName ): # # add your code here # return [] # just to make sure the code compiles. def main(): # Part 1, Exercise 3 # create a sample text file for testing. The file will contain the string <<<END>>> # in it. createFile( "lab8Demo.txt" ) # get all the lines before but not including <<<END>>> lines = readFileTillMarker( "lab8Demo.txt" ) # display the lines returned. We strip them to remove the extra \n at the end and # the extra spaces at the front of each line. print( "Lines found by readFileTillMarker(): " ) for line in lines: print( line.strip() ) main()
Same idea as the previous 2 exercises. This time you need to add code to the function readFileTillMarker() so that it will read all the lines contained in the file whose name is passed as a parameter, and that appear before the marker string <<<END>>>. In other words, the function reads the lines, adds them to a list of lines, until it finds a line containing the string <<<END>>>. It returns a list of all the lines read.
The function createFile() creates a simple file you can use for testing. Take a look at it to make sure you understand the format of the data.
Here's an example of how your program should work.
Lines found by readFileTillMarker(): An old pond! A frog jumps in- The sound of water.
Exercise 4: A bit of mathematics
Pi can be computed by adding the following terms (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pi):
Here's a program that shows how the variable sum, where we accumulate the terms, gets closer and closer to PI:
def computePi(): sum = 0 multiplier = 1 for i in range( 1, 20, 2 ): sum = sum + multiplier * 4.0 / i multiplier = -multiplier print( "Pi = ", sum )
Modify this program so that it stops when the first 3 digits of sum are equal to 3.14. In other words you need to change the loop to a while loop, and make it stop when the sum is a number of the form 3.14xxxxxxx.
</showafterdate>