Difference between revisions of "CSC111 Lab 9 2015"
(→Part 2: Exercise) |
(→Part 2: Exercise) |
||
| Line 69: | Line 69: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| + | ==Review Class Example== | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | * Below is an example program taken from Zelle, and that shows how we can guard some code against several types of errors. Review it. You will need to follow this example for the next set of exercises. | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | ::<source lang="python"> | ||
| + | def ZelleExample(): | ||
| + | import math | ||
| + | print( "solution to quadratic equation" ) | ||
| + | try: | ||
| + | a, b, c = eval( input( "enter 3 coefficients (a,b,c) " ) ) | ||
| + | disc = math.sqrt( b*b - 4*a*c ) | ||
| + | root1 = (-b + disc )/ (2*a) | ||
| + | root2 = (+b + disc )/ (2*a) | ||
| + | print( "solutions: ", root1, root2 ) | ||
| + | except NameError: | ||
| + | print( "You didn't enter 3 numbers" ) | ||
| + | except TypeError: | ||
| + | print( "Your inputs were not all numbers" ) | ||
| + | except SyntaxError: | ||
| + | print( "Forgot commas between the numbers?" ) | ||
| + | except ValueError: | ||
| + | print( "No real roots, negative discriminent" ) | ||
| + | except: | ||
| + | print( "Something went wrong..." ) | ||
| + | |||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
==Part 2: Exercise== | ==Part 2: Exercise== | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
Revision as of 07:19, 29 March 2015
--D. Thiebaut (talk) 07:14, 29 March 2015 (EDT)
Exceptions
Part 1: Preparation
- Create a new program called lab9_1.py, and copy this code to the new Idle window.
# lab9_1.py # Your name here # getInput: returns an integer larger # than 0. Expected to be robust def getInput(): while True: x = int( input( "Enter an integer greater than 0: " ) ) if x <= 0: print( "Invalid entry. Try again!" ) else: return x def main(): num = getInput() print( "You have entered", num ) main()
- Test it with numbers such as -3, -10, 0, 5. Verify that the input function works well when you enter numbers.
- Test your program again, and this time enter expressions such as "6.3", or "hello" (without the quotes).
- Make a note of the Error reported by Python:
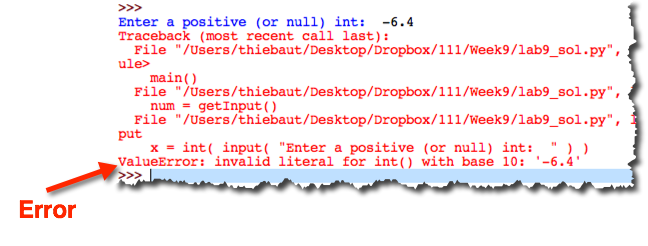
- Modify your function and add the highlighted code below by hand. This code will catch the ValueError exception.
# getInput: returns an integer larger # than 0. Catches Value errors def getInput(): # repeat forever... while True: # try to get an int try: x = int( input( "Enter an integer greater than 0: " ) ) except ValueError: # the user must have entered something other than an int print( "Invalid entry. Not an integer. Try again!" ) continue # No errors caught. See if the number is negative if x <= 0: print( "You entered a negative number. Try again!" ) else: # finally, we can return x as it is an int that is >0 return x
- Run your program and try different invalid inputs, such as strings or floats. You can also try just pressing the Return key, indicating that you are not providing anything to the input function. Verify that your program catches all these invalid entries and does not crash.
Review Class Example
- Below is an example program taken from Zelle, and that shows how we can guard some code against several types of errors. Review it. You will need to follow this example for the next set of exercises.
def ZelleExample(): import math print( "solution to quadratic equation" ) try: a, b, c = eval( input( "enter 3 coefficients (a,b,c) " ) ) disc = math.sqrt( b*b - 4*a*c ) root1 = (-b + disc )/ (2*a) root2 = (+b + disc )/ (2*a) print( "solutions: ", root1, root2 ) except NameError: print( "You didn't enter 3 numbers" ) except TypeError: print( "Your inputs were not all numbers" ) except SyntaxError: print( "Forgot commas between the numbers?" ) except ValueError: print( "No real roots, negative discriminent" ) except: print( "Something went wrong..." )
Part 2: Exercise
- Create a new program called lab9_2.py with the code below:
def example1(): for i in range( 3 ): x = int( input( "enter an integer: " ) ) y = int( input( "enter another integer: " ) ) print( x, '/', y, '=', x/y ) def example2( L ): print( "\n\nExample 2" ) sum = 0 for i in range( len( L ) ): sum += L[i] print( "sum of items in ", L, "=", sum ) def printUpperFile( fileName ): file = open( fileName, "r" ) for line in file: print( line.upper() ) file.close() def createTextFile( fileName ): file = open( fileName, "w" ) file.write( "Welcome\nto\nCSC111\nIntroduction\nto\nComp.\nSci.\n" ) file.close() def main(): # create a text file for use later... createTextFile( "csc111.txt" ) # test first function example1() # test second function L = [ 10, 3, 5, 6, 9, 3 ] example2( L ) #example2( [ 10, 3, 5, 6, "NA", 3 ] ) # test third function fileName = input( "Enter name of file to display (type csc111.txt): " ) printUpperFile( fileName ) main()
- The program above has many flaws; it is not very robust. We can easily make it crash.
- Observe each function. Run your program a few times.
- Figure out how to make each function crash
- Go ahead and start forcing the first function to crash. Register the XXXXError that is generated. For example, if the output of the crash looks like this:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/Users/thiebaut/Desktop/except0.py", line 29, in <module>
main()
File "/Users/thiebaut/Desktop/except0.py", line 27, in main
example3( [ 10, 3, 5, 6 ] )
File "/Users/thiebaut/Desktop/except0.py", line 18, in example3
sum = sum + L[i]
IndexError: list index out of range
- what you are interested in is IndexError. This is the exception you want to guard your code against.
try: ........ ........ except IndexError: .........
- Add the try/except statement inside the function, and verify that your function is now more robust and does not crash on the same input that made it crash before.
- Repeat the same process for the other functions.