Difference between revisions of "CSC270 Lab 5 2016"
(→Part 3) |
|||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
This lab presents Finite State Machines (FSM) and will you have explore a couple Moore machines. | This lab presents Finite State Machines (FSM) and will you have explore a couple Moore machines. | ||
</bluebox> | </bluebox> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
=Finite State Machine= | =Finite State Machine= | ||
| Line 35: | Line 28: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
* Wire up a circuit that implements this FSM. Demonstrate its correct behavior to your instructor. | * Wire up a circuit that implements this FSM. Demonstrate its correct behavior to your instructor. | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | =Minimal and Controllable Moore FSM (Optional)= | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | * This part is optional, and has to be done only if you have time. | ||
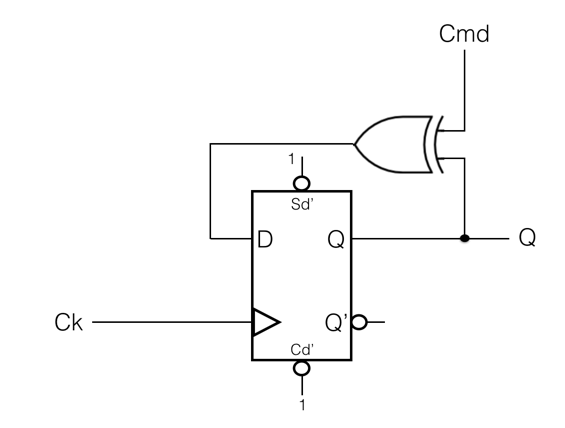
| + | * Implement this FMS shown below and observe its behavior. It uses half of a 74LS74 D Flip-flop. Generate the timing diagram for it. Include the timing diagram in your report, as well as its state diagram. | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | [[Image:SimpleFSM.png|400px|center]] | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
Revision as of 18:33, 24 February 2016
--D. Thiebaut (talk) 18:12, 24 February 2016 (EST)
This lab presents Finite State Machines (FSM) and will you have explore a couple Moore machines.
Contents
Finite State Machine
- Word problem
- Implement a sequencer (FSM) which controls 3 lights: a green light, a yellow light, and a red light. The lights operate in a cycle, as follows:
- Green is ON for 1 second, and turns OFF. Then
- Yellow is ON for 1 second, then turns OFF. Then
- Red is ON for 2 seconds, and stays ON. Then
- Yellow turns ON for 1 second, and after that both Red and Yellow turn OFF.
Part 1
- Generate the timing diagram, and the state diagram.
- Find the number of flip-flops required to implement the FSM.
- Find the boolean functions that will generate the D inputs to the flip-flops, and the R, G, and Y outputs.
Part 2
- Verify that your design is correct by coding your equations in a Python simulator.
Part 3
- Wire up a circuit that implements this FSM. Demonstrate its correct behavior to your instructor.
Minimal and Controllable Moore FSM (Optional)
- This part is optional, and has to be done only if you have time.
- Implement this FMS shown below and observe its behavior. It uses half of a 74LS74 D Flip-flop. Generate the timing diagram for it. Include the timing diagram in your report, as well as its state diagram.