Difference between revisions of "CSC270 Lab 7 2016"
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
Revision as of 21:25, 21 March 2016
--D. Thiebaut (talk) 22:20, 21 March 2016 (EDT)
This lab is your first introduction to the 6811 microprocessor Kit.
Contents
Engineering/Exploration
- Remove the processor cartridge, grab a phillips screw driver and open it up.
- Find the 6811, and identify as many of the other parts as you can.
- Include a picture of the printed circuit board in your lab report along with a list of the parts you were able to identify.
Introduction
First, let's explore the kits. The keyboard can be used to enter hexadecimal value into memory as well as into CPU registers. The table below lists the main commands and the actions they perform. You can get more information by checking this Heathkit document starting Page 15 in the pdf, which corresponds to Page 13 of the actual document. The full description of all the keys and what they do can be found in this pdf of the HeathKit manual.
| Key | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
RESET |
Takes you out of trouble! Press this key whenever you want to return to the "main prompt" showing CPU UP. |
|
|
RPO |
Return to Previous Operation. |
|
- |
Return |
Press the RETURN key to exit a function and save data contained in the CPU registers. |
|
+ |
List |
Use List in break mode to list the breakpoints. |
|
RPO |
Help |
Display a help message. Keep pressing it for more messages. |
|
D |
RS-232 |
Press this key to transfer control from the kit's keyboard to the serial port. |
|
E |
Baud |
Press this key to set the transfer rate to the outside serial port. |
|
F |
Insert |
Use Insert to change the contents of the memory. |
|
A |
Load |
Use Load to transfer a file stored in the memory module to the memory in the kit. We will not use the memory module in this course. |
|
B |
Save |
Use Save to transfer a file from the kit memory to the memory module. We will not use the memory module in this course. |
|
C |
Dup |
Press Dup (Duplicate) to copy a fie from one memory module to another. |
|
7 |
Break |
Use the Break key to set a breakpoint in memory. |
|
8 |
W Reg |
Use W-Reg to break a program when a register value reaches a desired value |
|
9 |
W Loc |
Press the W-Loc key to break a program when an address location reaches a desired value. This mode is similar to Break. |
|
4 |
M Blk |
Use the M-Bkl key to move a block of data in memory from another memory location. |
|
5 |
I Blk |
Press the I-Blk key to set a block of memory to a desired value. First enter the start address, then the end address. |
|
6 |
Down |
Press Down to download a Motoral Shex file into the kit's memory. |
|
1 |
Exm Mem |
Pressing this key in the select mode lets you examine the contents of any memory location. |
|
2 |
Exm Reg |
Pressing this key in the select mode allows you to modify any of the CPU registers |
|
3 |
Go |
Press Go to run a program in memory. The default start address is 0000H, but you can specify another address. |
|
0 |
SS |
Allows for single stepping the program. |
|
|
NMI |
Press NMI to interrupt any program running, or operation being performed by the trainer. The memory is not modified. |
|
|
Reset |
Press Reset to reinitialize the Trainer to its power-up state. All breakpoints are erased. |
Inputing your first program in the Kit
Your next step is to enter a test program in memory. The code of the assembled program is shown in hexadecimal below, with the address in the leftmost column, and the contents of the bytes on the right hand side. These bytes must be stored starting at address 0000 in memory. Do not worry about how this program works for right now. This is simply a test that will get you familiar with the kit and entering hex information.
ADDR BYTES
0000 CC 00 18
0003 BD C0 1B
0006 BD C0 27
0009 CC 00 27
000C BD C0 1B
000F BD C0 27
0012 BD C0 27
0015 BD C0 00
0018 50 72 6F 67 72 61 6D 6D 69 6E 67 20 69 73
0026 00
0027 0D
0028 45 61 73 79 20 61 6E 64 20 46 75 6E 21 21 21
0037 00
To enter the program, follow these steps:
- 1. press
I 0000
- for Insert starting at Address 0)
- 2. Then enter the bytes, pressing the corresponding keys. The kit will automatically show you the address of the byte you are entering. Be carefull to wait until your 2-digit value is accepted before entering the next one.
- 3. If you make an entry error, press the - key. Pressing the - key backs you up one address at a time. When you reach the byte with the wrong information, retype it. You can go up and down the memory with - and + keys. .
- 4. The series of byte is a simple program that should display two strings on the kit. Be careful, the display lasts a few seconds and disappears to show the Kit's greeting line.
- 5. When you are done, press
NMI
- to stop the insert mode and return to the kit's logo.
- 6. Press
Exm Mem 0000
- to examine the memory starting at 0000. Press the + and - keys to go forward or backward in the memory. When you are satisfied that you have entered the sequence correctly, press
NMI
- again.
- 7. Now make the processor start the program:
Go 0000
- 8. You should two strings appear in the display. If nothing of the sort happens, you probably have an error in your program. Check it again by comparing the contents of the memory to the string of hex numbers in the code above!
Hacking in Hexadecimal
Figure out how to make the program above display your name(s).
- In a first step, it's ok if the program displays extra characters besides your name
- In a second step, figure out (you have to do some guessing) how to make it print only your name(s) and no other characters!
You will need an ASCII table for this:
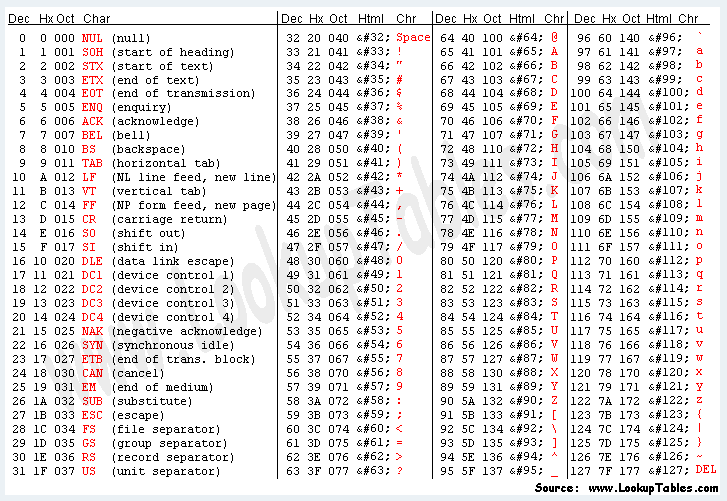
Your own test
It is now your turn to write a program, assemble it by hand, and enter it in the kit.
ORG 0000 ; specifies starting address 0000
LDAA 10 ; get Mem[0000] in ACCA (direct addressing)
LDAB 11 ; get Mem[0001] in ACCB
ABA ; ACCA <- ACCA + ACCB
STAA 12 ; Mem[0002] <- ACCA
ORG 0010 ; specifies starting address 0
a DB 2 ; 2 is stored at 0010
b DB 3 ; 3 is stored at 0011
result DB ? ;
The ORG statement specifies that the next assembly directive is to take place at the address specified after it. Assemble your program by hand, and use this page of 6800 opcodes to find the opcodes. Remember that when variables are in the first 256 bytes of RAM, you can use direct mode rather than extended. In direct mode you only use the lower byte of an address, not the full two bytes.
Find the hexadecimal values that must be stored in memory, starting with addresses 0 and 0010. You may want to use the table below to store your opcodes.
Address Op-Code/Bytes
0000 ____________
0001 ____________
0002 ____________
0003 ____________
0004 ____________
0005 ____________
0006 ____________
0007 ____________
0008 ____________
0009 ____________
000A ____________
000B ____________
...
0010 02
0011 03
0012 00
In the next section you are going to test your program by single-stepping it.
You should include the listing of your program, along with the assembled code in hex in your report. Use the example shown below (sum of array of 5 bytes) as an example of the format to use.
Running your program
- Then let's initialize ACCA and ACCB to 0.
2(Exm Reg) + 00 00
- Instead of launching your program with Go 0010 (why isn't it a good idea?), you will single-step it starting at Address 0010
NMI
0(SS) 0000
- The display is probably something like this (unless you have used extended mode, in case it should read B6 00 00):
0000 96 00
LDAA 00
- That's the next instruction the kit is about to execute. Note that it is disassembling the instruction for us! (Disassembling means decoding the numbers in hex and figuring out what the name of the instruction is.)
- Keep pressing SS until the Kit is about to execute the instruction ABA (add ACCB to ACCA)
SS SS ...
- Let's examine the registers to see that ACCA and ACCB contain 2 and 3:
Exm Reg
+ +
- Have ACCA and ACCB changed and do they contain the right values?
- Continue single stepping until you pass the last instruction of our program and see some strange instruction left over in memory.
RPO (Return to Previous Operation)
SS
...
- Examine the registers again and verify that ACCA contains the sum of its old value plus that in ACCB.
- Examine the memory starting at 0010 and verify that ACCA was correctly stored in memory at Address 0012.
RPO
Exm Reg
+
+
- If everything went well, the sum of [0010] and [0011] will have been stored in [0012]. If not, you probably have a bug in your program. Double check it, and do not go further until you have figured out the problem, and fixed it!
Endless Loop
- Add a jump instruction (mnemonic JMP, addressing mode EXTENDED) at the end of your program to create an endless loop. The jmp should take you back to the beginning of your program. If you need to see the instruction set, use this reference.
- Single step your program again, and to verify that the branch takes you to the correct location.
Five Fibonaccis
- Write the program that computes the first 5 fibonaccis. The algorithm you should use is the following:
1. fib[1] = 1
2. fib[2] = 1
3. fib[3] = fib[2] + fib[1]
4. fib[4] = fib[3] + fib[2]
5. fib[5] = fib[4] + fib[3]
In other words, no need of loops for tonight!
The best way to write this program is using indexing mode. It is one of the more challenging addressing modes to grasp, but if you feel up to it, try it. Otherwise use direct or extended mode. The program below illustrates indexing mode and computes the sum of 5 bytes that is then stored in the variable sum. Use it for inspiration!
; compute the sum of the contents of an array (table)
; of 5 bytes. The result is stored in a variable called
; sum
;--- data section ---
ORG 0000
0000 02 table FCB 2,3,4,1,7 ; create an array of 5 bytes
0001 03
0002 04
0003 01
0004 07
0005 00 sum FCB 0
;--- code section ---
ORG 0010
0010 CE 00 00 START: LDX #0000 ; IX = 0, address of 1st byte of array
0013 A6 00 LDAA 0,X ; ACCA = mem[0]
0015 AB 01 ADDA 1,X ; ACCA = ACCA + mem[1]
0017 AB 02 ADDA 2,X ; ACCA = ACCA + mem[2]
0019 AB 03 ADDA 3,X ; ACCA = ACCA + mem[3]
001B AB 04 ADDA 4,X ; ACCA = ACCA + mem[4]
001D 97 05 STAA 05 ; sum = ACCA
001F 7E FC 00 JMP FC00 ; Restart the monitor (OS)
- The instruction "LDAA 0,X" is the one of interest here. The "0,X" part indicates that the addressing mode is indexed and that an offset of 0 is used. In other words, "0,X" means "load into ACCA the contents of Mem[X+0]".
- "1,X" would have meant "of Mem[X+1]."
- Note that the 6811 does not allow negative offsets, so "-1,X" is not allowed.
- Assemble your program by hand, enter it in the Kit's RAM, and verify that the program computes correctly the first 5 fibonacci numbers. Make sure you demonstrate this to your instructor!
Your assignment for next lab
Write a small program as an endless loop that reads a byte from memory address 0, increments it by 1, and stores the result back at that address. Assemble the program by hand and come back to next lab with its listing. Try to make it as short a program as possible.
We will need it to observe in real time how the processor executes your program (we'll use the oscilloscope to capture the signals).
