Difference between revisions of "CSC220 Homework 5 2010"
(→Assignment: Part 1) |
(→Assignment: Part 1) |
||
| Line 190: | Line 190: | ||
SELECT * FROM `Names` WHERE `Name` = 'Adder'; | SELECT * FROM `Names` WHERE `Name` = 'Adder'; | ||
| − | ;; Example 2 -- Select the records where the name starts with ''Algorithm'' (you should find 3 such records): | + | ;; Example 2 -- Select the records where the name starts with ''Algorithm'' |
| + | :: (you should find 3 such records): | ||
SELECT `Name` FROM `Names` WHERE `Name` LIKE 'Algorithm%'; | SELECT `Name` FROM `Names` WHERE `Name` LIKE 'Algorithm%'; | ||
| − | ;; Example 3 -- Select the records that contain the word ''computer'' inside the field '''Name''' ( | + | ;; Example 3 -- Select the records that contain the word ''computer'' inside the field '''Name''' |
| + | ::(Be careful that when there is a large number of returned records, phpmyadmin shows only a subset of them, and you have to go through several pages to see all the records): | ||
SELECT `Name` FROM `Names` WHERE `Name` LIKE '%computer%'; | SELECT `Name` FROM `Names` WHERE `Name` LIKE '%computer%'; | ||
Revision as of 15:50, 14 October 2010
--D. Thiebaut 20:04, 13 October 2010 (UTC)
This assignment is due on 10/20/10, at 11:59 p.m. + 1 minute. You can work on it in pairs.
Contents
Setup
- Your assignment is to write a collection of mysql queries that will be the answers to different questions.
- In order to test these queries easily, you will need to include all of them in a text file (test.sql) that will become a single SQL program. This is the file you will submit for the assignment.
- you will generate the different queries using phpmyadmin running on either hadoop101 or hadoop110.
- You can test the correctness of your test.sql program by testing it with the same php program I will use to grade the assignment. More about this at the end of this page.
Dry Run
This section is just to make sure you format your result file correctly. If you result file does not generate a good output with the setup explained here, it will not work well with the grading program, so pay close attention to details!
This section also assume that you have done Lab 5 and that you have 3 tables named users, items, and orders, with information in them.
- Login to your 220a-xx account on one of the Hadoop machines. (you can ssh to them remotely, no need to be in FH342.)
- Get a copy of the following php program which you will store in your regular main directory (no need to store it in your public_html directory): testSql.php.
- Locate the two lines in the php code that requires editing, and enter your own account and password (the password is the same one as your 220a-xx account on beowulf).
- create a new text file, in the same directory where you put testSql.php and call it test.sql. Store the following information in it:
SELECT * FROM `items`;
SELECT `itemName` FROM `items`;
SELECT `itemName` FROM `items`WHERE `itemId`=2;
SELECT * FROM `users` ORDER BY `userName` ASC;
SELECT * FROM `orders` WHERE `userId`=1;
SELECT `itemName` FROM `items` WHERE `itemId` IN ( 1, 2, 3 );
SELECT `itemName` FROM `items` WHERE `itemId` IN ( SELECT `itemId` FROM `orders` WHERE `userId`=1 );
SELECT `itemName` FROM `items` WHERE `itemId` IN (
SELECT `itemId` FROM `orders` WHERE `userId` IN (
SELECT `userId` FROM `users` WHERE `userName`='Marie') );
- You can now make your php program execute all the queries.
php testSql.php
- Verify that you get an output similar to this one (although your tables might contain different information):
==> Connected to database
=========================================================
query = SELECT * FROM `items`
---------------------------------------------------------
Result of query:
1 pencil 1
2 eraser 0.5
3 paper 5
4 ink 30
5 ruler 1.5
6 markers 2.5
=========================================================
query = SELECT `itemName` FROM `items`
---------------------------------------------------------
Result of query:
pencil
eraser
paper
ink
ruler
markers
=========================================================
query = SELECT `itemName` FROM `items`WHERE `itemId`=2
---------------------------------------------------------
Result of query:
eraser
=========================================================
query = SELECT * FROM `users` ORDER BY `userName` ASC
---------------------------------------------------------
Result of query:
6 Dominique
5 Elaine
2 John
3 Manon
1 Marie
4 Rob
=========================================================
query = SELECT * FROM `orders` WHERE `userId`=1
---------------------------------------------------------
Result of query:
1 1 1
2 1 2
3 1 3
4 1 4
=========================================================
query = SELECT `itemName` FROM `items` WHERE `itemId` IN ( 1, 2, 3 )
---------------------------------------------------------
Result of query:
pencil
eraser
paper
=========================================================
query = SELECT `itemName` FROM `items` WHERE `itemId` IN ( SELECT `itemId` FROM
`orders` WHERE `userId`=1 )
---------------------------------------------------------
Result of query:
pencil
eraser
paper
ink
=========================================================
query = SELECT `itemName` FROM `items` WHERE `itemId` IN ( SELECT
`itemId` FROM `orders` WHERE `userId` IN (
SELECT `userId` FROM `users` WHERE `userName`='Marie') )
---------------------------------------------------------
Result of query:
pencil
eraser
paper
ink
Preparation
- Read the page from the MySQL developer site documenting the SELECT command: http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.0/en/select.html.
- Read the whole page!
- The purpose is not for you to learn it by heart, but to be aware of the features available when you select information from tables.
Assignment: Part 1
- Take the contents of this SQL dump and store it in the file test.sql you created in the preparation section above. If you observe it closely you will notice that it is just a collection of queries. These queries were generated by phpmyadmin when I executed an export operation of one of my databases. Phpmyadmin saves a database by creating a series of queries that, if one were to run them, would recreate the contents of the database. This is a nice way to save a database for backup.
- Run the testSql.php program from the section above to run the queries stored in the dump file. These queries will create 2 tables in your database, called Names, and Connections2.
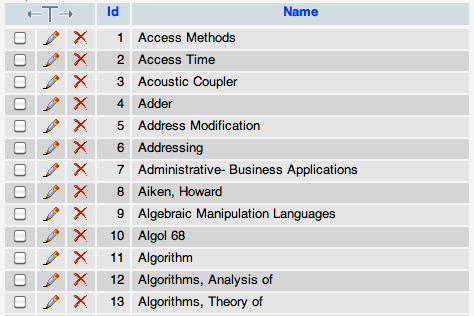
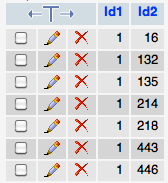
- Description of the tables:
- Each record in Names is an entry in an encyclopedia of computer science dating from 1976. The fields of interest to us are the Id and the Name of the entry. For example, Access Time has Id 2 in this database.
- Each record of Connections2 shows a relationship between two entries. For example, the first row indicates that Entry 1 in the encyclopedia, Access Methods, refers to Entry 16 in the encyclopedia, Application Programming. In otherword, if you were to read the page for Access Methods, you would find that it makes reference to Application Programming.
- When you deal with text, you can use the = (equal sign) to compare strings, but you have to make sure you can get an exact match. In general, though, use the LIKE SQL construct, and use the % (percent sign) character to indicate wild characters.
- Example 1 -- Select the record(s) for Adder
SELECT * FROM `Names` WHERE `Name` = 'Adder';
- Example 2 -- Select the records where the name starts with Algorithm
- (you should find 3 such records):
SELECT `Name` FROM `Names` WHERE `Name` LIKE 'Algorithm%';
- Example 3 -- Select the records that contain the word computer inside the field Name
- (Be careful that when there is a large number of returned records, phpmyadmin shows only a subset of them, and you have to go through several pages to see all the records):
SELECT `Name` FROM `Names` WHERE `Name` LIKE '%computer%';
Assignment: Part 2
- Querry 1
- Pick the name of one of the people you entered in your table users and generate the query that will return the list of the names and prices of all the items the person ordered. Make sure you have several items associated with this person
- Query 2
- Same as Query 1, but make this new query, Query 2, display the total cost of all the items returned by Query 1.
- Query-Group 3
- A good question in class had to do with inserting duplicate names in the users table. The table as created will not prevent this from happening. In order to modify the table (alter it), a query can be executed that specifies that some fields should contain only unique value:
ALTER TABLE `users` ADD UNIQUE `userName` ( `userName` )
- Generate a group of several queries (including the one above) that are necessary to strengthen the robustness of our series of 3 tables, so that duplicate entries cannot be entered by mistake.
- Generate a second group of queries that can be used to verify that duplicates are not allowed for the fields you have protected. Basically, write queries that attempt to insert record that will clash with existing records.
- Query 4 -- Optional and Extra Credit
- Use phpmyadmin and alter the orders table so that each order also lists a number of items ordered. You do not need to delete any information to do this. Just figure out a way to add the new field, then fill the empty cell with random quantities for each of the items ordered (Hints: look at the structure of the table...). Call this new field quantity.
- Generate a query that displays the items ordered by a person specified by name (say "Marie"), along with the cost of the items to this person, computed as the price of a given item multiplied by the quantity of items order.
Assignment: Part 2
...
