Difference between revisions of "CSC111 Homework 4 2011"
(→Generating random circles) |
(→Generating random circles) |
||
| Line 98: | Line 98: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | * Here's | + | * Here's an example of the output of the program: |
<center> | <center> | ||
Revision as of 15:05, 4 October 2011
--D. Thiebaut 12:42, 4 October 2011 (EDT)
Contents
Mondrian
Piet Mondrian is famous for his very geometric paintings with simple colors with mostly white, red, yellow and blue rectangles between black lines. This style has been applied to many different articles, as shown below.
This assignment is inspired by this style and asks you to write a graphics program that will display 1000 random rectangles filled with random colors.
First, let's explore the Python random module
Picking an item at random in a list
- The random module is a standard module in Python. It is part of the language and can be used to generate randomness. Actually, pseudo-randomness, because all randomness generated by programs cannot be purely random, since it is always based on some mathematical algorithm.
- Visit the official python.org documentation on the random module, and in particular scroll down to the Examples and Recipes section. It shows many different ways to get random information.
- For example. If I wanted to pick a random color out of a set of colors, here's a way we could do it:
import random
def main():
colors = ["blue", "red" ]
for i in range( 10 ):
print( random.choice( colors ) )
main()
- I have used a for-loop just to test the choice() function several times, and verify that it picks a random color every time.
- By the way, a list of the color names that are recognized by the graphics module is available here.
- Add a few more colors to your list and run your program again. See that it picks them at random?
Generating a random number
- The Examples and Recipes section of the documentation of the random module also shows that you can also pick a random number in a range. For example, if you want an even random number between 0 and 100, included, you can do this:
random.randrange(0, 101, 2) # Even integer from 0 to 100
- Try it by typing in the program below and running it a few times:
import random
def main():
# generate 10 random even numbers between 0 and 100:
for i in range( 10 ):
x = random.randrange( 0, 101, 2 )
print( "x = ", x )
main()
Generating random circles
- Let's generate 5 circles on a line (like a music notes on a score), and pick their placement at random.
def main2():
# define the width and height of our window (so that we can easily
# change the geometry if needed)
width = 800
height = 600
# open a graphics window
win = GraphWin( "Circles", width, height )
# draw a line
line =Line( Point( 10, height/2 ), Point( width-10, height/2 ) )
line.setFill( "black" )
line.setWidth( 5 )
line.draw( win )
# draw 5 circles placed at random x positions on the line
for i in range( 5 ):
radius = 20
x = random.randrange( 0+radius, width-radius )
c = Circle( Point( x, height/2 ), radius )
c.setFill( "black" )
c.draw( win )
win.getMouse()
win.close()
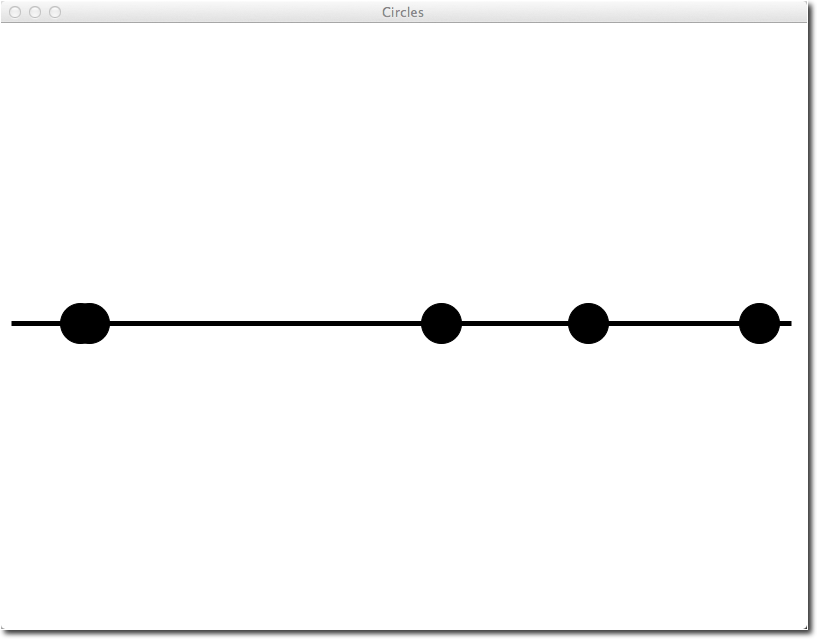
- Here's an example of the output of the program:
- Two of the circles overlap, but that's fine for our purpose.