Difference between revisions of "CSC103 Lab 2"
(→Part 2: Loading a constant in the Accumulator) |
(→Part 2: Loading a constant in the Accumulator) |
||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
=Part 2: Loading a constant in the Accumulator= | =Part 2: Loading a constant in the Accumulator= | ||
| − | Let's write a 1-instruction program: | + | * First, make sure the top right box displays '''Instructions''' as the format of the data in memory. |
| + | |||
| + | * Let's write a 1-instruction program: | ||
0 LOD-C 57 | 0 LOD-C 57 | ||
1 HLT | 1 HLT | ||
| − | '''Enter''' 0 in the '''addr:''' box, and '''LOD-C 57''' in the '''data:''' box. Press '''Enter''' to store these values in memory. | + | * '''Enter''' 0 in the '''addr:''' box, and '''LOD-C 57''' in the '''data:''' box. Press '''Enter''' to store these values in memory. |
| − | '''Enter''' 1 (if it isn't already there) in the '''addr:''' box, and '''HLT''' in the '''data:''' box. Press '''Enter''' to store these values in memory. | + | * '''Enter''' 1 (if it isn't already there) in the '''addr:''' box, and '''HLT''' in the '''data:''' box. Press '''Enter''' to store these values in memory. |
| − | '''Run''' your program by clicking on the '''Cycle''' a few times. | + | * '''Run''' your program by clicking on the '''Cycle''' a few times. |
| − | '''Verify''' that you get the right number in the ''accumulator'' register. | + | * '''Verify''' that you get the right number in the ''accumulator'' register. |
<center> | <center> | ||
[[Image:CSC103_Assembly_1.png]] | [[Image:CSC103_Assembly_1.png]] | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
Revision as of 15:49, 30 September 2008
<meta name="keywords" content="computer science, How Computers Work, Dominique Thiebaut, smith college" /> <meta name="description" content="Dominique Thiebaut's Web Page" /> <meta name="title" content="Dominique Thiebaut -- Computer Science" /> <meta name="abstract" content="Dominique Thiebaut's Computer Science Web pages" /> <meta name="author" content="thiebaut at cs.smith.edu" /> <meta name="distribution" content="Global" /> <meta name="revisit-after" content="10 days" /> <meta name="copyright" content="(c) D. Thiebaut 2000, 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004, 2005, 2006, 2007,2008" /> <meta name="robots" content="FOLLOW,INDEX" />
In this lab you will program at the lowest level of programmation: at the assembly language level. You will write small programs in assembly, and see how the programs correspond to numbers that are stored in memory. Some numbers represent instructions, some numbers represent data. But everything in memory is a number! That's a very important concept of CSC103!
Part 1: Starting the simulator
- Go to the applet page for the class. Click on
- The processor simulator will pop up.
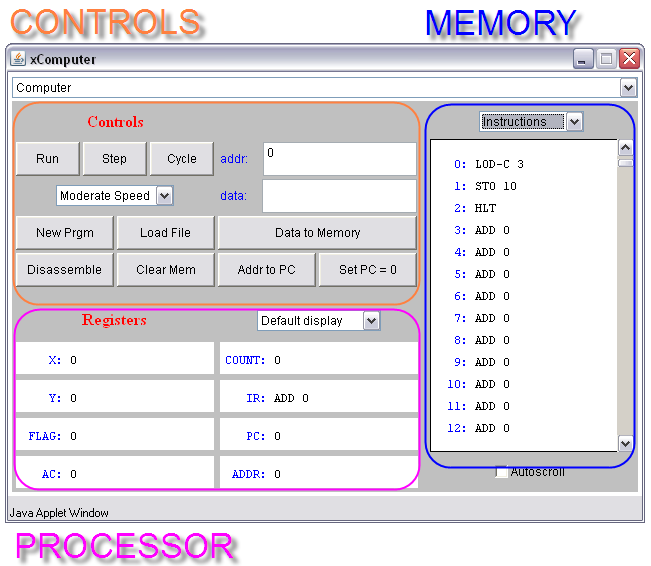
The purple part represents what is inside the processor, while the blue part represents the memory. Remember what they look like from the recent lab:
| Processor | Memory | |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Part 2: Loading a constant in the Accumulator
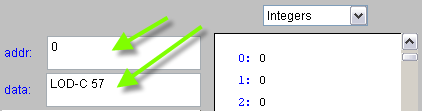
- First, make sure the top right box displays Instructions as the format of the data in memory.
- Let's write a 1-instruction program:
0 LOD-C 57 1 HLT
- Enter 0 in the addr: box, and LOD-C 57 in the data: box. Press Enter to store these values in memory.
- Enter 1 (if it isn't already there) in the addr: box, and HLT in the data: box. Press Enter to store these values in memory.
- Run your program by clicking on the Cycle a few times.
- Verify that you get the right number in the accumulator register.