Difference between revisions of "CSC212 Homework 5 2014"
(→Problem #1) |
(→Problem #1) |
||
| Line 71: | Line 71: | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
::* Select your program in the list | ::* Select your program in the list | ||
| − | ::* | + | ::* Click on the '''Arguments''' tab, and enter N and the key in the window ("20 24" in this case). |
| + | ::* Run your program. From then on, whenever you press the run-icon it will use these two numbers for N and key. If you want to change them, go through the same above steps again. | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
Revision as of 15:35, 24 October 2014
--D. Thiebaut (talk) 23:24, 22 October 2014 (EDT)
This assignment is due Friday (note the different day) Oct. 31st, at 11:55 p.m.
Problem #1
- Write a recursive Java program called Hw5_1.java that implements a modified recursive binary search that, instead of returning the index where the key was found, returns an ArrayList of all the indexes where the key is located. By returning, I mean either return with a return statement, or an ArrayList that is passed as a parameter, or an ArrayList that is a member variable of the class.
- You must use this function to create a sorted array of dimension N:
private static int[] initSortedArray( int N ) {
if ( N<10 ) N = 10;
int[] array = new int[N];
array[0] = 3;
for ( int i=1; i<N; i++ )
array[ i ] = array[i-1] + (i*11)%7;
// duplicate some keys
for ( int i=1; i<4; i++ )
array[ N/3 + i] = array[N/3];
return array;
}
- This way the indexes for a given key will be known to the testing program in Moodle. For verification, this is the array created by the function for N = 20:
3 7 8 13 15 21 24 24 24 24 34 36 42 45 45 49 50 55 57 63
- If the array contains [3 7 8 13 15 21 24 24 24 24 34 36 42 45 45 49 50 55 57 63], and we are searching for key 24, then your program will output
6 7 8 9
- You cannot use an iterative method that is not recursive.
- Your program should get N, the dimension of the array, and the key from the command line. Here's the code you should use:
public static void main(String[] args) { if ( args.length == 0 ) { System.out.println( "Syntax: javac Hw5_1 N key" ); return; } int N = Integer.parseInt( args[0] ); int key = Integer.parseInt( args[1] ); }
- Note
-
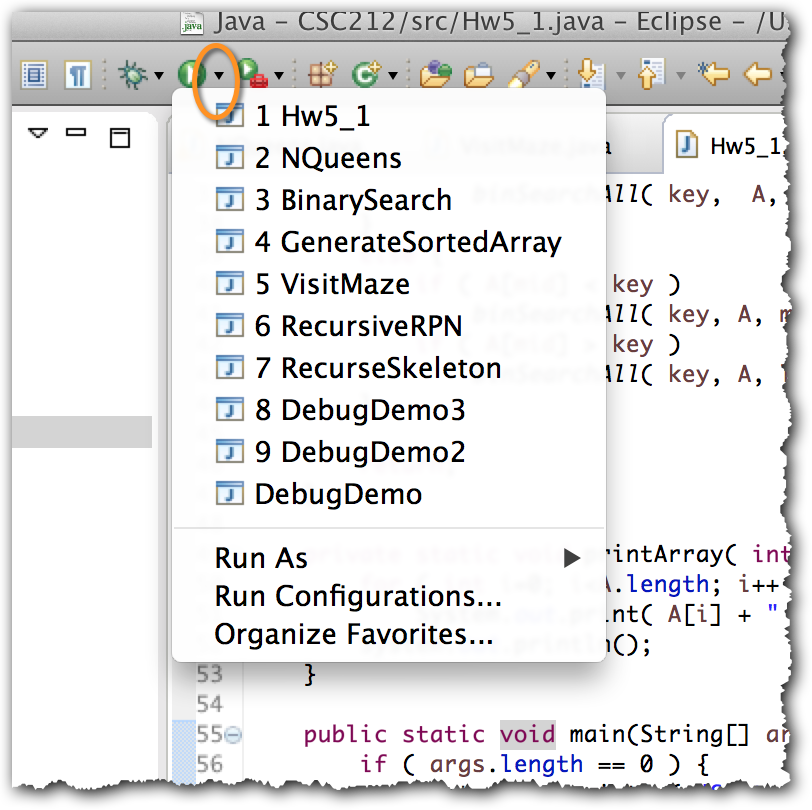
- If you are using Eclipse (which I hope you are), then passing parameters on the command line is a bit tricky, though totally possible. Here's how you do would do it. First click on the little black down arrow next to the Green Circle/White Triangle icon (Run icon) you click to run your programs.
- Select your program in the list
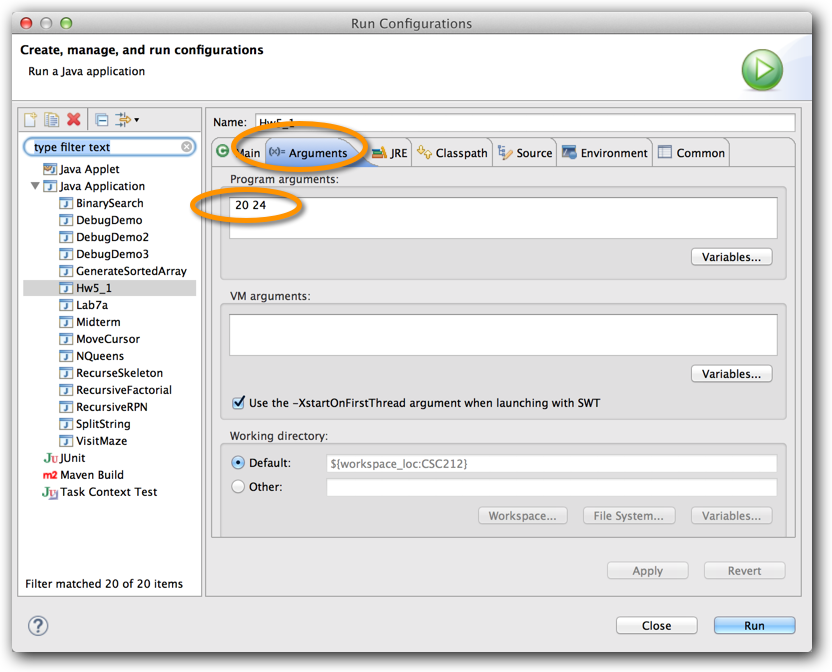
- Click on the Arguments tab, and enter N and the key in the window ("20 24" in this case).
- Run your program. From then on, whenever you press the run-icon it will use these two numbers for N and key. If you want to change them, go through the same above steps again.
- Your output should be sorted. To sort an ArrayList of integers, you can use the Collections library, as illustrated below:
import java.util.Collections; ... ArrayList<Integer> indexes = new ArrayList<Integers>(); // add some ints to the array ... // sort the ArrayList Collections.sort(indexes);
- Submit your program on Moodle, in the Homework 5, Problem 1 section.
Problem #2
- Modify the N-Queens problem seen in Lab #9 and make it compute the total number of different solutions existing for an NxN board. The program as we have seen in the lab stops when it finds a solution, but there might be many different possible ways of putting N queens on the NxN board. Make your program compute the total number of such solutions.
- Call your program Hw5_2.java.
- The output of your program should just be an integer number representing the number of solutions.
- Your program will get N from the command line, as in:
java Hw5_2 20
- which will compute the total number of different ways we can organize 20 queens on a 20x20 chessboard.