Difference between revisions of "CSC111 Python Programs Fall 2015"
(→Random Dot Demo) |
(→Random Circles Demo) |
||
| Line 1,533: | Line 1,533: | ||
if addDotButton.isClicked( clickedPoint ): | if addDotButton.isClicked( clickedPoint ): | ||
addDot( win ) | addDot( win ) | ||
| + | |||
| + | # redraw the buttons, just in case a circle covers them. | ||
OkButton.undraw() | OkButton.undraw() | ||
OkButton.draw( win ) | OkButton.draw( win ) | ||
| Line 1,539: | Line 1,541: | ||
addDotButton.undraw() | addDotButton.undraw() | ||
addDotButton.draw( win ) | addDotButton.draw( win ) | ||
| + | |||
| + | # go back to top of loop and wait for another click from user... | ||
continue | continue | ||
| − | # if | + | # if we're here, it's because user |
# clicked on window, but not on buttons | # clicked on window, but not on buttons | ||
print( "clicked on window" ) | print( "clicked on window" ) | ||
Revision as of 12:19, 16 November 2015
--D. Thiebaut (talk) 10:34, 18 September 2015 (EDT)
Contents
Wed., 9/16/15
# displayWeek.py # D. Thiebaut # displays a schedule for the five days of the week length = eval( input( "Length of bar? " ) ) print( "-" * length ) for day in [ "Mo:", "Tu:", "We:", "Th:", "Fr:" ]: print( day ) #print( " :" * 2) print( " :" ) print( "-" * length )
Friday, 9/18/15
# displayGrade.py # D. Thiebaut # # prompts user for information and # grade. # display user's grade in graph, along with # class average (constant) # constant information classAvg = 80 # user input. Get info from user fName = "Al" lName = "K" Id = "990123456" final = 90 #--- Format information and display --- # create the bar bar = "+" + 48*"-" + "+" lenBar = len( bar ) # compute the number of dashes noSpaces = lenBar - len( fName ) -len(lName )-len(Id) - 6 spaces = " " * noSpaces # create the scale scale = " 00...10...20...30...40...50...60...70...80...90...100" # display the information print( bar ) print( "|" + fName, lName, spaces, Id, "|" ) print( bar ) print() print( scale ) # the length of the bar for the bar-graph, in number of characters # is 1/2 the actual grade. So divide the grade by half to get the # number of chars. We use // to get the integer part of the result print( "grade:", (final//2) * "#" ) print( "class:", (classAvg//2) * "#" )
Monday, 9/21/15
Version 1 of Teller Machine program
# tellerMachine.py # D. Thiebaut # A program that simulates a teller machine, where user enters an amount of # dollars, and program figures out the number of bills to return. # get the amount amount = eval( input( "Please enter amount: " ) ) amount = int( amount ) print() # break down into bills no20s = amount // 20 # how many 20s go into amount amount = amount % 20 # what is left over after giving out 20s go back into amount no10s = amount // 10 amount = amount % 10 no5s = amount //5 no1s = amount % 5 # display the results print( "Amount withdrawn = ", amount ) print( "Please lift your keyboard and find: " ) print( no20s, "$20-bill(s)" ) print( no10s, "$10-bill(s)" ) print( no5s, "$5-bill(s)" ) print( no1s, "$1-bill(s)" )
Version 2, submitted by Shirui Cheng, who figured out that it was a perfect opportunity to use a loop!
# Teller machine simulator # Shirui Cheng # get the input amount = eval(input ("How much money do you want to withdraw? ")) # break down in $20-, $10-, $5-, and $1-bills # and print the result at every step for bill in (20, 10, 5, 1): no = amount // bill amount = amount % bill print (no, "$", bill, "bill(s)")
Wednesday, 9/23/15
# averageAge.py # D. Thiebaut # # Example of how one would go about computing # the average value of a list of numbers. # def main(): # initialize variables sum = 0 count = 0 # loop through a list of ages and compute the total sum # of the ages, and the number of values in the list. for age in [20, 19, 21, 20, 21, 29, 17]: sum = sum + age count = count + 1 # compute the average, displays quantities of interest print( "-" * 30 ) print( "average = ", sum/count ) main()
Accumulating Strings
# stringPatterns.py # D. Thiebaut # print a string of 5 alternating patterns. def main(): # define 2 different patterns pat1 = "**" pat2 = "++" # create an empty string result = "" # loop 5 times (we want a string of 5 alternating patterns) for i in range( 5 ): # add a new pattern to the string result = result + pat1 # switch the patterns around pat1, pat2 = pat2, pat1 # done with the loop! Print string of patterns print( result ) main()
Friday, 9/25/15
# averageAge.py # D. Thiebaut # # Example of how one would go about debugging a simple # program and reveal how the loop works. # def main(): # initialize variables sum = 0 count = 0 print( "sum = {0:1} count = {1:1}".format( sum, count ) ) input() # loop through a list of ages and compute the total sum # of the ages, and the number of values in the list. for age in [20, 19, 21, 20, 21, 29, 17]: sum = sum + age count = count + 1 print( "age = {0:5} sum = {1:5} count = {2:5}".format( age, sum, count ) ) input() # compute the average, displays quantities of interest print( "-" * 30 ) print( "sum = ", sum ) print( "count = ", count ) print( "average = ", sum/count ) main()
Wed., 9/30/15
# exercises 9/30/15 def main(): # Exercise #1 fName = "SOPHIA" lName = "smith" fullName = fName + " " + lName print( fullName.title().center( 60 ) ) print( "\n", "-"*60, "\n\n", sep="" ) # Exercise #2 # Define the string with multiple lines book = """Ulysses James Joyce Stately, plump Buck Mulligan came from the stairhead, bearing a bowl of lather on which a mirror and a razor lay crossed. """ # split the book into a list of lines lines = book.splitlines() # assign different lines to variables bookTitle = lines[0] author = lines[1] sentence = lines[2] + lines[3] + lines[4] # this next statement is too sophisticated for now #sentence = " ".join( lines[2: ] ) # display the result print( bookTitle.upper().center( 60 ) ) print( author.title().center( 60 ) ) print( ) print( sentence ) main()
Fri., 10/2/15
# Using split() # ------------------------- poem = """Chocolate Chocolate is the first luxury. It has so many things wrapped up in it: Deliciousness in the moment, childhood memories, and that grin-inducing feeling of getting a reward for being good. --Mariska Hargitay""" # display each line centered in 60 spaces. # first line all uppercase. # last line right justified in 60 spaces. lines = poem.split( "\n" ) #print( lines ) # ----------------------------------------------------------------------- # (remove the triple double-quotes to energize the code section) print( lines[0].upper().center(60) ) for line in lines[1: ]: print( line.center( 60 ) ) # ----------------------------------------------------------------------- print( "-" * 60 ) lines[0] = lines[0].upper() for line in lines[0:3]+lines[4:]: print( line.center(60) )
Another Example
# ------------------------- # Another Example # ------------------------- def printBar(): print( 60 * '-' ) def sayHello(): print( ) print( "Hello, and welcome!" ) print( ) def main(): for i in range( 10 ): printBar() sayHello() printBar() main()
Happy Birthday
# ------------------------------------------ # Sing Happy Birthday to some Minions # ------------------------------------------ def singHappyBirthday( minion ): print( "Happy birthday to you\n" * 2, end="" ) print( "Happy birthday, dear", minion ) print( "Happy birthday to you" ) print() def main(): #singHappyBirthday( "Dave" ) #singHappyBirthday( "Stuart" ) minions = "Dave, Stuart, Jerry, Jorge, Tim, Mark, Phil, Kevin, Jon" minions = minions.split( ", " ) #print( minions ) for minion in minions: singHappyBirthday( minion.strip() ) main()
Mon. 10/5/15
Converting Temperatures
# F = C * 9 / 5 + 32
def convert( c ):
return int( c * 9/5 + 32 )
def main():
for C in [ 0, 32, 100 ] :
fahr = convert( C )
print( fahr )
main()
Transforming dates
def singHappyBirthday( minion ):
print( "minion = ", minion )
#print( "Happy birthday to you\n" * 2, end="" )
#print( "Happy birthday, dear", minion )
#print( "Happy birthday to you" )
#print()
def worker0( ):
return "clap " * 10
def worker1( num1 ):
return num1 * 2 + 1
def worker2( n ):
return n % 10
def worker3( p ):
p = worker1( p )
p = worker2( p )
return p
def dateConvert( date ):
"""converts a date in the form "2 Jan 2010" into
a date of the form 01022010"
"""
# split the string into day, month, and year
fields = date.split()
day = fields[0]
month = fields[1]
year = fields[2]
#print( day, month, year )
# if the day is less than 10, add a 0 in front of it
day = ( '0' + day )[-2: ]
#print( day, month, year )
# find where the month is located in a string of 3-letter
# months. If the string is "Jan", then the location will
# be 0. If the string is "Feb", then the location will be 3,
# etc.
months = "janfebmaraprmayjunjulaugsepoctnovdec"
index = months.find( month.lower() )
# divide by 3 to find the index in the form 0, 1, 2,... 11.
# and add 1 to make this 1, 2,... 12
monthDigit = index//3 + 1
# transform this digit into a string, with a 0 in front
# in case the digit is less than 10.
monthDigit = "{0:02}".format( monthDigit )
#print( day, month, year, monthDigit )
# return the formatted string
return "{0:1}{1:1}{2:1}".format( monthDigit, day, year )
def main():
for date in [ "1 Jan 2010", "2 Mar 1900", "31 Dec 2015" ]:
print( dateConvert( date ) )
main()
- Output:
01012010 03021900 12312015
Fri. 10/9/15
Once More: the Teller Machine program
def getAmount():
amount = eval( input( "Amount? " ) )
return abs( amount )
def breakDown( amount ):
no20s, amount = amount // 20, amount % 20
no10s, amount = amount // 10, amount % 10
no5s, amount = amount // 5, amount % 5
no1s = amount
return no20s, no10s, no5s, no1s
def display(orgAmount, No20s, No10s, No5s, No1s ):
print( orgAmount, No20s, No10s, No5s, No1s )
return
def main():
# get amount from user
amount = getAmount( )
orgAmount = amount # keep value of original amount
# get Number of $20-, $10, $5-, and $1-bills
No20s, No10s, No5s, No1s = breakDown( amount )
# display result
display( orgAmount, No20s, No10s, No5s, No1s )
main()
Flipping DNA
def getSentence( ):
sentence = input( "Enter a list of words: " )
words = sentence.split( )
for i in range( len( words ) ):
#print( "i = ", i, "words = ", words )
#print( "words[i] = ", words[i] )
#print( "words[i].capitalize() = ", words[i].capitalize() )
words[i] = words[i].capitalize()
#print( "i = ", i, "words = ", words )
#print()
return words
def flip( DNA ):
newDNA = DNA.replace( "A", "t" ).replace( "T", "a" )
newDNA = newDNA.replace( "G", 'c' ).replace( "C", 'g' )
return newDNA.upper()
def main():
listWords = getSentence( )
print( "list = ", listWords )
print( "AAACGTTTAG", flip( "AAACGTTTAG" ), sep="\n" )
main()
Wed 10/14/15
dempolls.raw
<html>
<head>
<title>
Democratic Polls
</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Results</h1>
<data />
</body>
</html>
dempolls.data
Biden 19.1 Chafee 0.6 Clinton 44.4 Lessig 0.0 O'Malley 1.0 Sanders 25.1 Webb 1.2
createDynamicWebPage.py
# createDynamicWebPage.py # D. Thiebaut # create dynamic Web page import datetime # get a library that will allow # us to print today's date. # getTextFrom(): given a file name, opens the # file, gets its contents as a string, and return # it. def getTextFrom( fileName ): file = open( fileName, "r" ) text = file.read() file.close() return text def main(): # get the raw html file html = getTextFrom( "dempolls.raw" ) # get the raw data file candidates = getTextFrom( "dempolls.data" ) # replace <data /> tag with the data just # read in the raw html file. today = datetime.datetime.today().strftime("%m/%d/%Y") newString = today + "<br />" + candidates html = html.replace( "<data />", newString ) # store new html to file file = open( "dempolls.html", "w" ) file.write( html ) file.close() # tell the user that process is over print( "File dempolls.html created, and in your directory!" ) main()
Wed. 10/21/15
graphicsDemo.py
# graphicsDemo.py # D. thiebaut # A demo program using the graphics library to make a ball # move on the graphic window. from graphics import * from random import * def main(): # open the graphic window win = GraphWin("My Circle", 600, 600) # put some text in the middle of the window label = Text( Point( 300, 300 ), "CSC111 Graphics Demo" ) label.draw( win ) # draw a circle x = 50 y = 50 r = 20 c = Circle( Point( x, y ), r ) red = randint( 0, 255 ) green = randint( 0, 255 ) blue = randint( 0, 255 ) color = color_rgb( red, green, blue ) c.setFill( color ) c.draw( win ) dx = 3 dy = 0 for i in range( 1000 ): # pick random color red = randint( 0, 255 ) green = randint( 0, 255 ) blue = randint( 0, 255 ) color = color_rgb( red, green, blue ) c.setFill( color ) # move c.move( dx, dy ) # see if bounce off walls center = c.getCenter() x = center.getX() if x > 600-r or x < 0+r: dx = -dx #win.getMouse() # move label label.move( 1, -1 ) # wait for user to click in window win.getMouse() # close the window win.close() main()
Mon. 11/2/15
Exception, Version 1
# getInput: returns an integer larger # than 0. Expected to be robust… def getInput(): while True: x = int( input( "Enter a positive int: " ) ) if x >= 0: return x print( "invalid input. Please reenter" ) def main(): num = getInput() print( "you entered", num ) main()
Exception, Version 2
# getInput: returns an integer larger # than 0. Expected to be robust… def getInput(): while True: try: x = int( input( "Enter a positive int: " ) ) except ValueError: print( "Invalid number. Please reenter" ) continue if x >= 0: return x print( "invalid input. Please reenter" ) def main(): num = getInput() print( "you entered", num ) main()
Quadratic Equation with Exceptions
import math def ZelleExample(): print( "solution to quadratic equation" ) try: a, b, c = eval( input( "Enter 3 coefficients (a, b, c): " ) ) disc = math.sqrt( b*b - 4*a*c ) root1 = (-b + disc )/ (2*a) root2 = (-b - disc )/ (2*a) print( "solutions: ", root1, roo2 ) except NameError: print( "You didn't enter 3 numbers!" ) except TypeError: print( "Your input contained invalid numbers" ) except SyntaxError: print( "Forgot a comma between the numbers? " ) except ValueError: print( "No real roots, negative discriminant" ) except: print( "Something went wrong..." ) def main(): ZelleExample() main()
Dice: Definining Classes
# DiceExample.py # D. Thiebaut # our first program where we define a class. # # The class implement a die, with some number # of sides, and a way to "roll" and show a new # number (value) up top. # libraries import random # a class for a die class Die: def __init__( self, n ): self.noSides = n self.value = 1 def roll( self ): self.value = random.randrange( 1, self.noSides+1 ) def getValue( self ): return self.value def main(): # Create 2 dice, one with 6 sides, one with 8 d1 = Die( 6 ) d2 = Die( 8 ) # Roll both dice d1.roll( ) d2.roll( ) # display their value print( "Die 1: ", d1.getValue() ) print( "Die 2: ", d2.getValue() ) main()
A program with a class to implement Cat objects
# cats1.py # D. Thiebaut # Our first built-from scratch program involving # classes and objects. # In this program we read a CSV file containing # the definitions of cats, one cat per line. # We extract the name, vaccinated status, breed, # and age of the cat, and save them in a cat # object. the Cat class is used to define how # a cat object behaves. class Cat: def __init__( self, na, vac, bre, ag ): self.name= na self.vaccinated = vac self.breed = bre self.age = ag def isVaccinated( self ): #if self.vaccinated == True: # return True #else: # return False return self.vaccinated def getName( self ): return self.name def main(): # Minou, 3, vac, stray text = """Minou, 3, vac, stray Max, 1, not-vac, Burmese Gizmo, 2, vac, Bengal Garfield, 4, not-vac, Orange Tabby""" catList = [] for line in text.split( "\n" ): words = line.split( "," ) if words[2].find( "not" ) != -1: vac = False else: vac = True age = int( words[1].strip() ) cat = Cat( words[0], vac, words[3], age ) catList.append( cat ) #cat1 = Cat( "Minou", True, "stray", 3 ) for cat in catList: if cat.isVaccinated(): print( cat.name, "is vaccinated" ) else: print( cat.getName(), "is not vaccinated" ) main()
Cats1.csv File
Max, 1, vaccinated, not tattooed, stray Black, 3, not vaccinated, tattooed, stray Gizmo, 2, vaccinated, not tattooed, Bengal Winston, 2, vaccinated, tattooed, Bengal Garfield, 3, vaccinated, not tattooed, Burmese Bob, 4, not vaccinated, tattooed, Orange Tabby Minou, 1, vaccinated, tattooed, stray Silky, 3, not vaccinated, tattooed, Siamese
Wed. 11/04/15
cats1.py
# cats1.py # D. Thiebaut # Our first built-from scratch program involving # classes and objects. # In this program we read a CSV file containing # the definitions of cats, one cat per line. # We extract the name, vaccinated status, breed, # and age of the cat, and save them in a cat # object. the Cat class is used to define how # a cat object behaves. class Cat: def __init__( self, na, vac, bre, ag ): self.name= na self.vaccinated = vac self.breed = bre self.age = ag def isVaccinated( self ): #if self.vaccinated == True: # return True #else: # return False return self.vaccinated def getBreed( self ): return self.breed def getName( self ): return self.name def __str__( self ): if self.vaccinated == True: vacc = "vaccinated" else: vacc = "not vaccinated" return "{0:1}: {1:1} {2:1} {3:1} yrs old".format( self.name, vacc, self.breed, self.age ) def getCatList( fileName ): """parses a collection of lines and creates a list of cat objects.""" file = open( fileName, "r" ) text = file.read() file.close() catList = [] for line in text.split( "\n" ): words = line.split( "," ) if len( words ) != 4: continue if words[2].find( "not" ) != -1: vac = False else: vac = True age = int( words[1].strip() ) cat = Cat( words[0].strip(), vac, words[3].strip(), age ) catList.append( cat ) return catList def main(): fileName = input( "File name? " ) catList = getCatList( fileName ) for cat in catList: print( cat ) for cat in catList: if not cat.isVaccinated() and cat.getBreed()=="stray": print( cat ) return main()
cats2.csv
Minou, 3, vac, stray Max, 1, not-vac, Burmese Gizmo, 2, vac, Bengal Garfield, 4, not-vac, Orange Tabby Smudges, 10, not-vac, stray Minique, 5, vac, French Tabby
Fri. 11/06/15
Wheel1.py
The beginning of a car...
# Graphics with Objects. # Demo program illustrating how we are going to # build a car. # from graphics import * #define global geometry of window WIDTH = 800 HEIGHT = 600 def main(): global WIDTH, HEIGHT win = GraphWin( "Wheel Demo", WIDTH, HEIGHT ) c1 = Circle( Point( WIDTH//2, HEIGHT//2 ), 30 ) c1.draw( win ) win.getMouse() win.close() main()
Car1.py
# Graphics with Objects. # Demo program illustrating how we are going to # build a car. # from graphics import * #define global geometry of window WIDTH = 800 HEIGHT = 600 class Wheel: def __init__( self, center, radius ): self.c1 = Circle( center, radius ) self.c2 = Circle( center, radius//2 ) self.c1.setFill( "black" ) self.c2.setFill( "white" ) def draw( self, win ): self.c1.draw( win ) self.c2.draw( win ) def move( self, dx, dy ): self.c1.move( dx, dy ) self.c2.move( dx, dy ) class Car: def __init__( self, refPoint ): x1 = refPoint.getX() y1 = refPoint.getY() x2 = x1 + 180 y2 = y1 + 60 self.body = Rectangle( Point( x1 , y1 ), Point( x2 , y2 ) ) self.w1 = Wheel( Point( x1+40, y1+60 ), 20 ) self.w2 = Wheel( Point( x1+140, y1+60 ), 20 ) self.body.setFill( "yellow" ) def draw( self, win ): self.body.draw( win ) self.w1.draw( win ) self.w2.draw( win ) def move( self, dx, dy ): self.body.move( dx, dy ) self.w1.move( dx, dy ) self.w2.move( dx, dy ) def main(): """Open a graphic window and puts graphic object(s) on it. Wait for user to click mouse to close. """ global WIDTH, HEIGHT # open window win = GraphWin( "Wheel Demo", WIDTH, HEIGHT ) # Create a list of 10 cars cars = [] # empty list for i in range( 10 ): # create a new car c1 = Car( Point( i*10, i*90 ) ) # draw the car just created c1.draw( win ) # add car just created to the list cars.append( c1 ) dx = 3 # x-direction for movement of cars dy = 0 # y-direction for movement of cars # animation loop while True: # move all the cars in the list for c1 in cars: c1.move( dx, dy ) # if user clicks the mouse, change the # direction of movement. if win.checkMouse() != None: dx = -dx # wait for user to click the mouse to close window win.getMouse() win.close() main()
Mon. 11/9/15
Images to Play With
catGlasses.gif
imageProcessing.py
# imageProcessingSkel.py # D. Thiebaut # A skeleton program to start doing image processing # in Python from graphics import * # image geometry = 424x18 # make the window the same geometry WIDTH = 424 HEIGHT = 418 def main(): # open the window win = GraphWin( "CSC111 Image Viewer", WIDTH, HEIGHT ) # get the file name from the user fileName = "catGlasses.gif" #input( "Image name? " ) print() # open the cat image cat = Image( Point(WIDTH//2, HEIGHT//2), fileName ) cat.draw( win ) # wait for user to click the mouse... win.getMouse() # and close the window win.close() main()
pixelProcessing.py
# pixelProcessingSkel.py # D. Thiebaut # Simple skeleton program for processing # the pixels of an image from graphics import * WIDTH = 424 HEIGHT = 418 IMAGEFILENAME = "catGlasses.gif" def makeRed( img, win ): """ set the red component of all the pixels to 255, the maximum value. """ global WIDTH, HEIGHT for y in range( HEIGHT ): win.update() # refresh the window after each inner loop for x in range( WIDTH ): red, green, blue = img.getPixel( x, y ) green, blue, red = red, green, blue red = 255 img.setPixel( x, y, color_rgb(red, green, blue ) ) def main(): win = GraphWin( "CSC111 Image Viewer", WIDTH, HEIGHT ) img = Image( Point(WIDTH//2, HEIGHT//2), IMAGEFILENAME ) img.draw( win ) makeRed( img, win ) win.getMouse() win.close() main()
Wed. 11/11/15
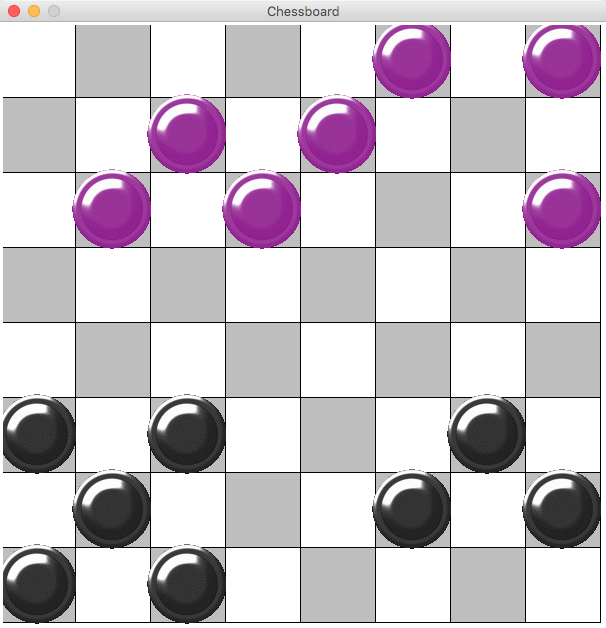
chessboard0.py
# chessboard0,py # D. Thiebaut # Displays an 8x8 chessboard. from graphics import * WIDTH = 600 HEIGHT = 600 def displayBoard( win ): """display an 8x8 chessboard in the square window defined by WIDTH and HEIGHT""" global WIDTH, HEIGHT # compute size of square side = WIDTH//8 # display 8 columns and 8 rows of squares for i in range( 0, 8 ): for j in range( 0, 8 ): # create a rectangle r = Rectangle( Point( i*side, j*side ), Point( i*side+side, j*side+side ) ) # figure out if it should be black or white if (i+j) % 2 != 0: r.setFill( "grey" ) else: r.setFill( "white" ) # draw it r.draw( win ) def main(): global WIDTH, HEIGHT # open a graphics window. win = GraphWin( "Chessboard", WIDTH, HEIGHT ) # display the board. displayBoard( win ) # wait for use to click window, and close up. win.getMouse() win.close() main()
Gifs for the game of Checkers
- piece.gif
- piece2.gif
Interactive Checkers
# Interactive game of checkers. # This program creates an 8x8 board, with # alternating white and dark cells. It then positions # 3 rows of white pieces, and 3 rows of black pieces at # the top and bottom of the board, respectively. # It then allows the user to click on various pieces to make them # disappear. from graphics import * WIDTH = 600 HEIGHT = 600 class CheckersPiece: """ a class defining a checkers piece. It uses gif images for each piece.""" def __init__(self, color, i, j ): global WIDTH, HEIGHT side = WIDTH // 8 x = i * side y = j * side centerPoint = Point( x+side//2, y+side//2 ) if color=="white": self.img = Image( centerPoint, "piece2.gif" ) else: self.img = Image( centerPoint, "piece.gif" ) def draw( self, win ): self.img.draw( win ) def undraw( self ): self.img.undraw() def getCoords( self ): global WIDTH, HEIGHT side = WIDTH // 8 x = self.img.getAnchor().getX() y = self.img.getAnchor().getY() return x-side//2, y-side//2, x+side//2, y+side//2 def isWhite( i, j ): if (i+j)%2==0: return True return False def displayBoard( win ): """this function displays the 8x8 board, with alternating colors.""" global WIDTH, HEIGHT side = WIDTH//8 for i in range( 0, 8 ): for j in range( 0, 8 ): r = Rectangle( Point( i*side, j*side ), Point( i*side+side, j*side+side ) ) if not isWhite( i, j ): r.setFill( "grey" ) else: r.setFill( "white" ) r.draw( win ) def createDisplayPieces( win ): """create 3 rows of white pieces at the top, and 3 rows of black pieces at the bottom. Put them only on dark squares.""" whites = [] blacks = [] for i in range( 8 ): for j in range( 3 ): if isWhite( i, j ): continue c = CheckersPiece( "white", i, j ) c.draw( win ) whites.append( c ) for j in range( 5, 8 ): if isWhite( i, j ): continue c = CheckersPiece( "black", i, j ) c.draw( win ) blacks.append( c ) return whites, blacks def findClickedPiece( p, whites, blacks ): """loop through all the pieces and see if the point that the user clicked (p) is inside the square that corresponds to where the piece is.""" for c in whites + blacks: x1, y1, x2, y2 = c.getCoords() if x1 <= p.getX() <= x2 and y1 <= p.getY() <= y2: return c return None def main(): global WIDTH, HEIGHT win = GraphWin( "Chessboard", WIDTH, HEIGHT ) displayBoard( win ) whites, blacks = createDisplayPieces( win ) # animation loop while True: p = win.getMouse() c = findClickedPiece( p, whites, blacks ) if c != None: c.undraw( ) win.getMouse() win.close() main()
Mon, 11/16/15
Button Demo
# buttonDemo.py # D. Thiebaut from graphics import * WIDTH = 600 HEIGHT = 600 class Button: """Implements a button, which contains a label (text), is rectangular (frame), and can be clicked (True) or not clicked.""" def __init__(self, x1, y1, w, h, text ): """constructor: pass (x,y) of top left corner, and width and height. Pass the text displayed in button.""" p1 = Point( x1, y1 ) p2 = Point( x1+w, y1+h ) self.frame = Rectangle( p1, p2 ) self.frame.setFill( "white" ) self.label = Text(Point( x1+w//2, y1+h//2 ), text ) self.clicked = False def draw( self, win ): """display button on window.""" self.frame.draw( win ) self.label.draw( win ) def isClicked( self, p ): """Checks if p is inside the frame of the button. Returns True if p inside frame, False otherwise. If p inside, button changes state and color.""" x1, y1 = self.frame.getP1().getX(), self.frame.getP1().getY() x2, y2 = self.frame.getP2().getX(), self.frame.getP2().getY() if x1 <= p.getX() <= x2 and y1 <= p.getY() <= y2: self.clicked = not self.clicked if self.clicked: self.frame.setFill( "yellow" ) else: self.frame.setFill( "white" ) return True else: return False def main(): global WIDTH, HEIGHT win = GraphWin( "Pushbutton Demo", WIDTH, HEIGHT ) button1 = Button( 10, 10, 60, 30, "OK" ) button1.draw( win ) while True: clickPoint = win.getMouse() if button1.isClicked( clickPoint ): print( "button clicked!" ) win.close() main()
Random Circles Demo
# randomDotDemo.py # D. Thiebaut from graphics import * from random import * WIDTH = 600 HEIGHT = 600 class Button: """Implements a button, which contains a label (text), is rectangular (frame), and can be clicked (True) or not clicked.""" def __init__(self, x1, y1, w, h, text ): """constructor: pass (x,y) of top left corner, and width and height. Pass the text displayed in button.""" p1 = Point( x1, y1 ) p2 = Point( x1+w, y1+h ) self.frame = Rectangle( p1, p2 ) self.frame.setFill( "white" ) self.label = Text(Point( x1+w//2, y1+h//2 ), text ) self.clicked = False def draw( self, win ): """display button on window.""" self.frame.draw( win ) self.label.draw( win ) def undraw( self ): self.frame.undraw( ) self.label.undraw( ) def isClicked( self, p ): """Checks if p is inside the frame of the button. Returns True if p inside frame, False otherwise. If p inside, button changes state and color.""" x1, y1 = self.frame.getP1().getX(), self.frame.getP1().getY() x2, y2 = self.frame.getP2().getX(), self.frame.getP2().getY() if x1 <= p.getX() <= x2 and y1 <= p.getY() <= y2: self.clicked = not self.clicked if self.clicked: self.frame.setFill( "yellow" ) else: self.frame.setFill( "white" ) return True else: return False def addDot( win ): x = randint( 100, 500 ) y = randint( 100, 500 ) center = Point( x, y ) radius = randint( 10, 600 ) c = Circle( center, radius ) r = randint( 0, 255 ) g = randint( 0, 255 ) b = randint( 0, 255 ) c.setFill( color_rgb( r, g, b ) ) c.draw( win ) def main(): global WIDTH, HEIGHT win = GraphWin( "Pushbutton Demo", WIDTH, HEIGHT ) # create UI OkButton = Button( 10, 10, 60, 30, "Ok" ) OkButton.draw( win ) quitButton = Button( 80, 10, 60, 30, "Quit" ) quitButton.draw( win ) addDotButton = Button( 150, 10, 60, 30, "Add Dot" ) addDotButton.draw( win ) # animation loop while True: clickedPoint = win.getMouse() if quitButton.isClicked( clickedPoint ): break if OkButton.isClicked( clickedPoint ): print( "button clicked!" ) continue if addDotButton.isClicked( clickedPoint ): addDot( win ) # redraw the buttons, just in case a circle covers them. OkButton.undraw() OkButton.draw( win ) quitButton.undraw() quitButton.draw( win ) addDotButton.undraw() addDotButton.draw( win ) # go back to top of loop and wait for another click from user... continue # if we're here, it's because user # clicked on window, but not on buttons print( "clicked on window" ) win.close() main()
Polygon Demo
# buttonDemo.py # polygon demo. A triangle # and a start are drawn # D. Thiebaut from graphics import * from random import * WIDTH = 300 HEIGHT = 300 def main(): global WIDTH, HEIGHT win = GraphWin( "Pushbutton Demo", WIDTH, HEIGHT ) # draw a triangle points = [ Point( 100, 100 ), Point( 150, 100 ), Point( 175, 150 ) ] poly1 = Polygon( points ) poly1.setFill( "orange" ) poly1.draw( win ) # draw a star points = [ Point( 35, 120 ), Point( 37.9,129.1), Point( 46.9,129.1), Point( 39.7,134.5), Point( 42.3, 143.1 ), Point( 35, 139 ), Point( 27.7, 143.1 ), Point( 30.3, 134.5 ), Point( 23.1, 129.1 ), Point( 32.1, 129.1 ) ] poly2 = Polygon( points ) poly2.setFill( "lightgreen" ) poly2.draw( win ) # wait for user to click mouse to close window win.getMouse() win.close() main()
Create Polygon With Mouse Demo: Skeleton Program
# recordShapeIntoPolygon.py # D. Thiebaut # Brings up a gif image in the window # and creates 2 buttons. # User can click on buttons to 1) start # Recording a shape, and 2) stop recording # it and displaying it as light-blue polygon. # WARNING: the program, as is, is not safe and will crash # if the user start the program and clicks on a point that is not # inside a button... The problem is with pointList... from graphics import * WIDTH = 400 HEIGHT = 400 class Button: """Implements a button, which contains a label (text), is rectangular (frame), and can be clicked (True) or not clicked.""" def __init__(self, x1, y1, w, h, text ): """constructor: pass (x,y) of top left corner, and width and height. Pass the text displayed in button.""" p1 = Point( x1, y1 ) p2 = Point( x1+w, y1+h ) self.frame = Rectangle( p1, p2 ) self.frame.setFill( "white" ) self.label = Text(Point( x1+w//2, y1+h//2 ), text ) self.clicked = False def draw( self, win ): """display button on window.""" self.frame.draw( win ) self.label.draw( win ) def isClicked( self, p ): """Checks if p is inside the frame of the button. Returns True if p inside frame, False otherwise. If p inside, button changes state and color.""" x1, y1 = self.frame.getP1().getX(), self.frame.getP1().getY() x2, y2 = self.frame.getP2().getX(), self.frame.getP2().getY() if x1 <= p.getX() <= x2 and y1 <= p.getY() <= y2: self.clicked = not self.clicked if self.clicked: self.frame.setFill( "yellow" ) else: self.frame.setFill( "white" ) return True else: return False def main(): global WIDTH, HEIGHT # create a graphic window win = GraphWin( "Record Polygon", WIDTH, HEIGHT ) # put a logo of Smith in the middle of the window img = Image( Point(WIDTH//2, HEIGHT//2), "smithLogo.gif" ) img.draw( win ) # create 2 buttons startB = Button( 10, 10, 60, 30, "Start" ) startB.draw( win ) stopB = Button( 80, 10, 60, 30, "Stop" ) stopB.draw( win ) # animation loop while True: clickedPoint = win.getMouse() # quit? if exitB.isClicked( clickedPoint ): break # start recording polygon? if startB.isClicked( clickedPoint ): pointList = [] continue # stop recording polygon? if stopB.isClicked( clickedPoint): poly = Polygon( pointList ) poly.setFill( "cyan" ) poly.draw( win ) continue # if we're here, it's because # the user clicked somewhere outside # the buttons pointList.append( clickedPoint ) win.getMouse() win.close() main()