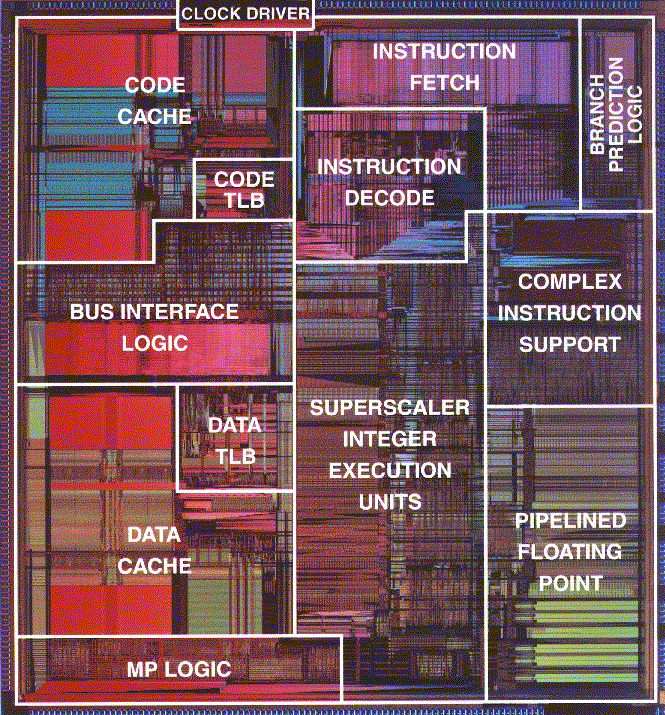
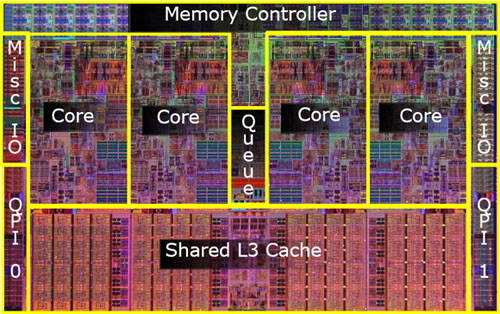
|
|
| Line 155: |
Line 155: |
| | ---- | | ---- |
| | * | | * |
| − | ||
| |
| − | =Weekly Schedule=
| |
| − |
| |
| − | {| style="width:100%" border="1"
| |
| − | |- style="background:#ffdead;"
| |
| − | |'''Week''' || '''Topics''' || '''Reading'''
| |
| − | |-valign="top"
| |
| − |
| |
| − | |width="15%"| Week 1 <br /> 9/05
| |
| − | |width="60%"|
| |
| − | * [[CSC231_First_Program | first program]]
| |
| − | * assembling programs
| |
| − | * first look at Pentium processor. [http://www.intel.com/pressroom/archive/photos/p4_photos.htm?iid=ipp_850echpst+relate_pr& Photos].
| |
| − | * Outputing text in assembly
| |
| − | * memory map of a program
| |
| − | * [[CSC231_skeleton_program | skeleton program]]
| |
| − | * [[media:CSC231_Bare_and_Skeleton_version.pdf | Bare versus Skeleton versions]]
| |
| − | * A [[CSC231_Hello_World_on_Mac | hello-world program]] for the Mac OSX. More info on Mac OS X system calls can be found [http://www.freebsd.org/doc/en_US.ISO8859-1/books/developers-handbook/x86-system-calls.html here ][[CSC231 Final Exam 12/08|.]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ----
| |
| − |
| |
| − | * '''Mini lab''': [[CSC231_Lab_1 | Lab #1 ]]
| |
| − | || Chapter 1 in the [http://cs.smith.edu/~thiebaut/ArtOfAssembly/artofasm.html Art of Assembly].
| |
| − | Also Chapter 3, Sections 0 to 3.1.2.
| |
| − | Sections 1.3.1, 1.3.2, 1.3.3, 1.3.4, and 1.3.5 in Carter's [http://cs.smith.edu/~thiebaut/classes/231_0405/doc/pcasm-book.pdf PC Assembly Language].
| |
| − |
| |
| − | |- style="background:#eeeeff" valign="top"
| |
| − | | Week 2 <br /> 9/08
| |
| − | ||
| |
| − | * First introduction to the Pentium processor. Registers, ALU, Control Unit, Busses, Memory
| |
| − | * [[CSC231_Exercises_Binary_Hexadecimal | Exercises]] on binary, decimal, hexadecimal system
| |
| − | * [http://www.willamette.edu/~gorr/classes/cs130/lectures/BinaryConversion/convert.html Bin/Dec/Hex converter]
| |
| − | * [[CSC231_listing_file | Listing file]] with assembly and opcodes
| |
| − | * [[media:CSC231_StepByStepInstruction.pdf | Step by Step]] execution of instructions
| |
| − | * [[CSC231_ReverseEngineering.lst | Exercise]] on reverse engineering. [[CSC231_ReverseEngineeringSol.asm | Solution]]
| |
| − | * The '''mov''' instruction. Syntax. Operands
| |
| − | * Units of storage: nybble, byte, word, double-word
| |
| − | * The '''add''' instruction.
| |
| − | * Using the '''ddd''' debugger
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ----
| |
| − |
| |
| − | * [[CSC231_Homework_1 | Homework #1]] and [[CSC231_Homework_1_Solution | Solution ]]
| |
| − | * [[CSC231_Lab_2 | Lab #2]]
| |
| − | ||
| |
| − | *[http://maven.smith.edu/~thiebaut/ArtOfAssembly/CH03/CH03-1.html Basic computer organization], Sections 3.0, 3.1, 3.3.1
| |
| − | *[http://webster.cs.ucr.edu/AoA/Linux/HTML/DataRepresentation.html#998846 Review of data representation]
| |
| − | *[http://webster.cs.ucr.edu/AoA/Linux/HTML/DataRepresentation2.html#998917 Bits, nybbles, bytes]
| |
| − | *[http://webster.cs.ucr.edu/AoA/Linux/HTML/DataRepresentation3.html#1012324 The hex system]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | |- valign="top"
| |
| − | | Week 3 <br /> 9/15
| |
| − | ||
| |
| − | * Review of last lab
| |
| − | ** [[CSC231_Add5.asm | add5.asm]]
| |
| − | ** [[CSC231_ComputeFib7.asm | computeFib7.asm]]
| |
| − | * new instructions
| |
| − | ** add, sub, inc, dec, loop
| |
| − | ** [[CSC231_Loop_Exercises | Exercises]]
| |
| − | * Binary adders, [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Boolean_algebra_(introduction) Boolean Algebra], and the ALU
| |
| − | * Signed and unsigned numbers
| |
| − | ----
| |
| − |
| |
| − | * [[CSC231_Homework_2 | Homework #2]] and its [[CSC231_Homework_2_Solution | Solution]]
| |
| − | * [[CSC231_Lab_3 | Lab #3]]
| |
| − | ||
| |
| − | Signed and unsigned numbers are covered in
| |
| − | [http://maven.smith.edu/~thiebaut/ArtOfAssembly/CH01/CH01-2.html#HEADING2-96 Sections 1.7 and 1.8] and
| |
| − | [http://maven.smith.edu/~thiebaut/classes/231_0607/doc/pcasm-book.pdf Chap. 2]
| |
| − | [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Boolean_algebra_(introduction) Boolean Algebra]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | |- style="background:#eeeeff" valign="top"
| |
| − | | Week 4 <br /> 9/22
| |
| − | ||
| |
| − | * A [[CSC231_OverFlow_C_Program | C program]] that overflows
| |
| − | * A [[CSC231_OverFlow_Python_Program | Python program]] that overflows (or does it?)
| |
| − | * How do we represent signed numbers?
| |
| − | * What formats are available?
| |
| − | ** Signed magnitude
| |
| − | ** 1's complement
| |
| − | ** 2's complement
| |
| − | * Why the binary adder dictates what we choose
| |
| − | * [[CSC231_Mystery_C_Program_with_signed_numbers | Mystery C Program]]
| |
| − | *[http://www.mathsisfun.com/binary-decimal-hexadecimal-converter.html Hex/Bin/Decimal converter]
| |
| − | * <font color="purple">'''Project starts!'''</font> (on Friday)
| |
| − | ----
| |
| − | * [[CSC231_Homework_3 | Homework #3]] and its [[CSC231_Homework_3_Solution | Solution]]
| |
| − | * [[CSC231_Lab_4 | Lab #4]]
| |
| | || | | || |
| | *The signed and unsigned representations of numbers are covered in [http://maven.smith.edu/~thiebaut/ArtOfAssembly/CH01/CH01-2.html#HEADING2-96 Sections 1.7 and 1.8] of The Art of Assembly, and in [http://maven.smith.edu/~thiebaut/classes/231_0607/doc/pcasm-book.pdf Chapter 2] of Carter's PC Assembly Language. | | *The signed and unsigned representations of numbers are covered in [http://maven.smith.edu/~thiebaut/ArtOfAssembly/CH01/CH01-2.html#HEADING2-96 Sections 1.7 and 1.8] of The Art of Assembly, and in [http://maven.smith.edu/~thiebaut/classes/231_0607/doc/pcasm-book.pdf Chapter 2] of Carter's PC Assembly Language. |