Tutorial: Introduction to the Arduino
--D. Thiebaut 15:18, 20 April 2011 (EDT)
Contents
Misc. Information Before You Start |
Good Reference Pages
Good Tutorials on the Web
Notes for Mac Users
- You may have to install special drivers for your Mac to see the Arduino through the USB Port. Look here for more info: http://www.ftdichip.com/Drivers/VCP.htm
Arduino-Laptop Setup |
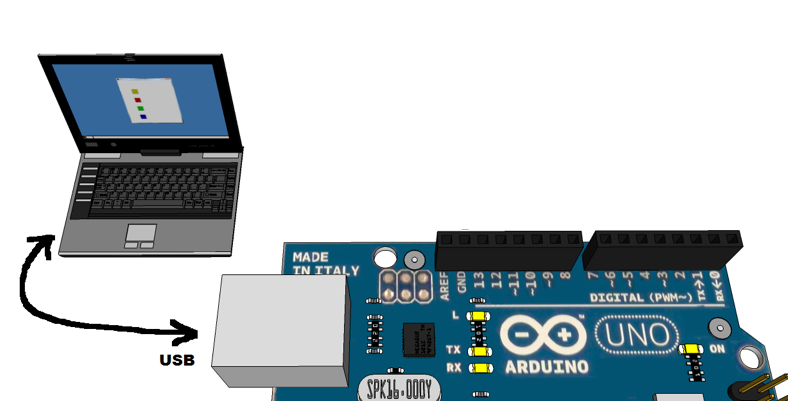
- Programs are written on the laptop
- Programs are compiled on the laptop
- Programs are downloaded to the Arduino
- Programs run on the Arduino
- Programs output information via the USB cable, and this information is captured by the IDE which shows it in the Serial Monitor.
- The Arduino inputs information that the User types in the Serial Monitor. This information is sent via the USB cable to the Arduino.
An Introduction to C in the Arduino Context |
Comments
// this is a comment
/* and so is this */
/* and
this
as
well */
Setup() and Loop()
Output
Output strings from the Arduino to Laptop
- Done with the Serial library
- Use Serial.begin() to set the baud rate (# of bits per second)
- Then output strings with Serial.println( ... ) or Serial.print( ... )
void setup() {
Serial.begin( 38400 );
Serial.println( "Hello there!" );
}
void loop() {
delay(1000); // wait for a second
Serial.println( "hello again!" );
}
Output numbers
- Taken from http://arduino.cc/en/Serial/Print
- Serial.print(78) gives "78"
- Serial.print(1.23456) gives "1.23"
- Serial.print(byte(78)) gives "N" (whose ASCII value is 78)
- Serial.print('N') gives "N"
- Serial.print("Hello world.") gives "Hello world."
- An optional second parameter specifies the base (format) to use; permitted values are BYTE, BIN (binary, or base 2), OCT (octal, or base 8), DEC (decimal, or base 10), HEX (hexadecimal, or base 16). For floating point numbers, this parameter specifies the number of decimal places to use. For example:
- Serial.print(78, BYTE) gives "N"
- Serial.print(78, BIN) gives "1001110"
- Serial.print(78, OCT) gives "116"
- Serial.print(78, DEC) gives "78"
- Serial.print(78, HEX) gives "4E"
- Serial.println(1.23456, 0) gives "1"
- Serial.println(1.23456, 2) gives "1.23"
- Serial.println(1.23456, 4) gives "1.2346"
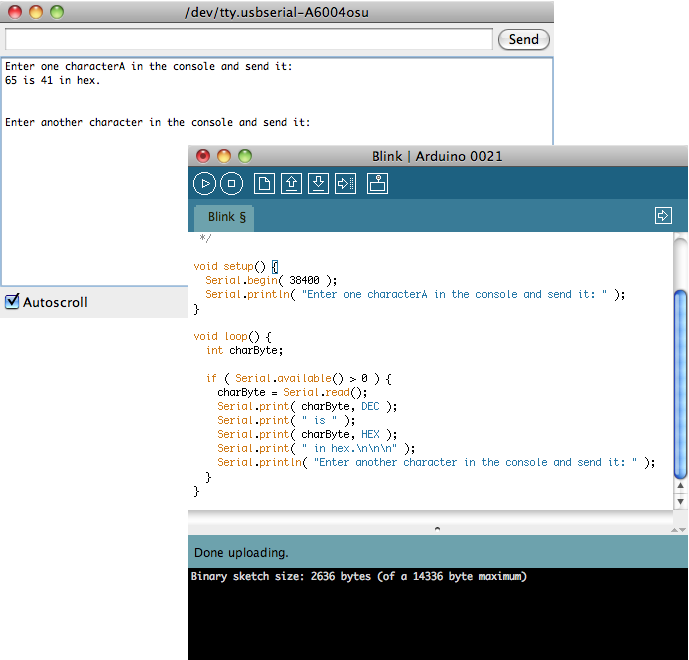
Inputting characters
- Use Serial.read() and Serial.available(), as illustrated below
void setup() {
Serial.begin( 38400 );
Serial.println( "Enter one characterA in the console and send it: " );
}
void loop() {
int charByte;
if ( Serial.available() > 0 ) {
charByte = Serial.read();
Serial.print( charByte, DEC );
Serial.print( " is " );
Serial.print( charByte, HEX );
Serial.print( " in hex.\n\n\n" );
Serial.println( "Enter another character in the console and send it: " );
}
}
Statements
statement;
statement;
statement;
// comment
statement;
compound-statement {
statement;
statement;
}
Control Statements
IF
if ( condition equal to 0 or different from 0 ) {
// Action A
}
else {
// Action B
}
FOR
- same syntax and structure as in Java.
- you can declare the variable in the loop.
- the variable is undefined outside the loop.
for ( int i = 0; i < 100; i++ ) {
statement;
statement;
}
SWITCH
- works with countable variables (not floats).
switch (var) {
case 1:
//do something when var equals 1
break;
case 2:
//do something when var equals 2
break;
default:
// if nothing else matches, do the default
// default is optional
}
WHILE
while (expression evaluating to 0 or something different from 0 ) {
statement;
statement;
statement;
}
BREAK/CONTINUE
- break: break out of the most inner loop it is located in.
- continue: skips the remainder of the current loop and returns to the closest for or while statement.
Variables and Data Types
- void
- boolean
- char
- unsigned char
- byte
- int
- unsigned int
- word
- long
- unsigned long
- float
- double
- string (array of chars)
- String (object)
- array
- Exercise
- Create a sketch based on the Blink sketch (in File/Examples/1. Basics) that outputs alternatively "hello" one second, then your name the next second, in an endless loop.