CSC111 Lab 3 2015
--D. Thiebaut (talk) 21:22, 9 February 2015 (EST)
Contents
- 1 Teller Machine Program
- 1.1 Reviewing the Division Operators, // and %
- 1.2 Beginning Program
- 1.3 Define original amount
- 1.4 Compute the number of $20s to give out
- 1.5 Computing the Left-Over Amount
- 1.6 Computing the Remaining Quantities
- 1.7 Using Constants
- 1.8 Flexibility and Adaptability
- 1.9 Challenge #1: A Change Machine
- 2 Python Functions: abs(), int(), str(), len()
- 3 The input() Function
- 4 Submission
Teller Machine Program
This section will get you to write a program similar (though not necessarily the same) to the program we wrote in class on Monday. The program takes an integer (without a decimal part) amount of dollars and figures out how to break it down into the least number of 20-, 10-, 5-, and 1-bills.
Reviewing the Division Operators, // and %
Use the Python shell, and try to predict the result of the following operations.
>>> 21 // 5 >>> 21 % 5 >>> 9 // 2 >>> 9 % 2 >>> 13 // 3 >>> 13 % 3 >>> 139 // 20 >>> 139 % 20
Beginning Program
- Write a program that contains
- a short header with the program name (lab3.py, for example),
- your name,
- the date, and
- A short description of the program.
- Create 3 different comment lines that will create an outline of your program.
# lab3.py # yourName # date # blah blah blah blah blah blah... # # get the initial amount # compute number of bills # output number of bills to give out
- Save and Run the program, just to make sure you do not have a syntax error.
Define original amount
- Under the #get the initial amount comment, create a variable called amount and initialize it with a value of your choice. Pick a value that is not a multiple of 5.
- Add a print() statement under the #output number of bills comment, and make it print the amount the user wants to withdraw.
- Verify that your program works.
Compute the number of $20s to give out
- Using the right operator (//, /, or %), make your program compute the number of $20 and store that value in a new variable, called no20s. Add this code under the # compute number of bills.
- Make your program output the no20s variable in the output section.
- Verify that your program works.
Computing the Left-Over Amount
- Go back to the computation of the number of $20s, and compute the amount of money left over once the $20s are taken out of the amount. You have several ways of doing this. You can do it using the % modulo operator, or using multiplication and subtraction. Whichever method you use is fine for today.
- Make your program output the left-over amount, just to make sure that value is computed correctly.
- Verify that your program works fine.
Computing the Remaining Quantities
- Now that you have the structure for your program, add enough Python code to make your code display
- The total amount
- The number of $20-bills
- The number of $10-bills
- The number of $5-bills
- The number of $1-bills
- Verify that your program works. Below is a typical output you should try to emulate:
Amount to withdraw = 97 Please lift keyboard and find: 4 $20-bill(s) 1 $10-bill(s) 1 $5-bill(s) 2 $1-bill(s)
Using Constants
- You probably have statements like these in your program
no20 = amount // 20
leftover = amount % 20
- Instead of using the literals 20, 10, 5, and 1 in the program, we can use variables to hold them. It adds to the complexity a tiny bit, but makes the program more useful. You'll see how.
- Modify your program and add these variables near the top of the program:
DENOM1 = 20
DENOM2 = 10
DENOM3 = 5
DENOM4 = 1
- and where you compute the number of $20-bills, replace 20 by DENOM1. You should get something like this:
noBills = amount // DENOM1
leftover = amount % DENOM1
print( noBills, "$", DENOM1, "bill(s)" )
- Run your program. Make sure it still outputs the correct result after this modification. If not, fix the error(s)!
- Replace 10, 5, and 1 by DENOM2, DENOM3, DENOM4 in the remaining part of your program.
- Run your program and make sure it sill outputs the correct result.
Flexibility and Adaptability
Imagine that your program will be used in an area where the bills do not come in 20, 10, 5 or 1 denominations, but in 100, 50, 10, and 1.
Figure out a way to make the least amount of change to your program so that it now outputs the correct break down for any amount, but in $100-, $50-, $10- and $1-bills.
Make sure your program works! Below is the output of the program if the amount is set to $97:
Amount to withdraw = $ 97 Please lift keyboard and find: 0 $ 100 bill(s) 1 $ 50 bill(s) 4 $ 10 bill(s) 7 $ 1 bill(s)
Challenge #1: A Change Machine |
- Using a similar approach, write a program that, given some number of pennies, will output the correct number of quarters, dimes, nickels, and pennies. You should initialize the amount of pennies with an integer, like this:
pennies = 84
- Here is an example of what your program should output for 84 pennies:
Amount to withdraw = 84 penny or pennies Please lift keyboard and find: 3 quarter(s) 0 dime(s) 1 nickel(s) 4 penny or pennies
Python Functions: abs(), int(), str(), len()
Python supports many functions. A very good way to understand how they work is to try them in the Console window of Idle, i.e. the window where programs output their result.
Below is a series of statements you should type in the console, and as you see how Python interprets these statements, this should help you figure out how the functions work.
>>> a = 10.34
>>> a
>>> int( a )
>>> a = -10.34
>>> abs( a )
>>> abs( a * 100 )
>>> str( 10.34 )
>>> 'hello' + 10.34
>>> 'hello' + str( 10.34 )
>>> amount = 123.45
>>> int( amount )
>>> int( amount * 10 )
>>> int( amount / 10 )
>>> amount = 1234
>>> 1234 // 10
>>> 1234 // 100
>>> 1234 % 100
>>> 1234.0 % 100
>>> int( 1234.0 ) % 100
>>> 'a' * '5'
>>> 'a' * 5
>>> '3' * 5
>>> 3 * 5
>>> str( 3 ) + str( 5 )
>>> str( 3 ) * 5
>>> print( 5, "apples" )
>>> print( 5 + "apples" )
>>> print( str( 5 ) + "apples" )
>>> dog = "Pluto"
>>> len( dog )
>>> dog = "+ " + dog + " +"
>>> dog
>>> len( dog )
>>> "-" * len( dog )
Challenge #2: Cleaning Up the Output |
Using what you just learned, modify your ATM program (the one that outputs the number of bills), and make the output look neat.
In particular, change the output that looks like this:
4 $ 20 bill(s) 1 $ 10 bill(s) 1 $ 5 bill(s) 2 $ 1 bill(s)
and make it look like this:
4 $20 bill(s) 1 $10 bill(s) 1 $5 bill(s) 2 $1 bill(s)
Challenge #3: an ATM that delivers bills and coins |
Combine the two program sections, the one that delivers bills and the one that delivers coins and create a program that would allow an amount of the form 123.47 to be withdrawn from the machine. In this case the output of your program should be:
6 $20 bill(s) 0 $10 bill(s) 0 $5 bill(s) 3 $1 bill(s) 1 quarter(s) 2 dime(s) 0 nickel(s) 2 penny or pennies
The input() Function
Try the following statements in the console window. Again, some of these might generate errors. It is important for you to understand why these errors occur.
>>> firstName = input( "Enter your first name: " )
>>> firstName
>>> lastName = input( "Enter your last name: " )
>>> lastName
>>> print( firstName, lastName )
>>> x = input( "enter a number: " )
>>> x
>>> x + 5
>>> x = input( "Enter a number: " )
>>> x
>>> x = int( answer )
>>> x
>>> y = int( "314.56789" )
>>> y
Challenge #4: Gathering student information |
Write a python program that asks the user for her name, box number, 99-Id number, and phone number, and that outputs it back on the screen nicely formatted.
Example (the information entered by the user is in boldface):
your first name? Allie your last name? Gator your box number? 1234 your phone number? 413 456 7890 your Smith Id? 990123456 Name: Allie Gator (990123456) box #: 1234 phone: 413 456 7890
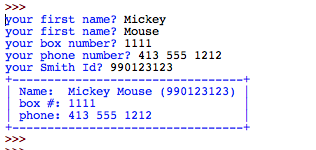
Challenge #5: (Challenging) Printing the student information it in a box |
Same idea as with the previous challenge but after inputing the information from the user, the program outputs it in a box!
Example:
Challenge #6: Programmable ATM Machine |
Modify your last ATM program so that it prompts the user for an amount of money to withdraw, and then it breaks it down into number of bills of different denominations.
Here is an example with the user input in boldface:
Please enter the amount you want to withdraw: 231.50 Please lift you keyboard and find: ...
Challenge #7: Seconds to Days, Hours, Minutes, Second converter |
Write a program that prompts the user for a time expressed as a number of seconds. The program then outputs the equivalent number of days, hours, minutes, and seconds.
Make the program output the result in a box, similar to the one shown below (the user input is in boldface):
Please enter a time expressed in seconds: 3662 +--------------------------------------------+ | 0 day(s) 1 hour(s) 1 minute(s) 2 second(s) | +--------------------------------------------+
Submission
- Store the last program that you were able to run without errors in a file called lab2.py.
- Write down your name at the top of the program, in a comment, and add your 2-letter Id (the list of 2-letter Ids is available here). Follow this example
# lab2.py # Mickey Mouse (aa) # Solution program for Challenge 3
- If you worked on this lab with a partner, add the two names in the program header.
# lab2.py # Mickey Mouse (aa) # Donald Duck (cc) # Solution program for Challenge 7
- Submit your program here.








