CSC352 MapReduce/Hadoop Class Notes
Contents
Outline
- History
- Based on Functional Programming
- Infrastructure, Streaming
- Submitting a Job
- Smith Cluster
- Example 1: Java
- Example 2: Python (streaming)
- Useful Commands
History
- Introduced in 2004 [1]
- MapReduce is a patented software framework introduced by Google to support distributed computing on large data sets on clusters of computers [1]
- 2010 first conference: The First International Workshop on MapReduce and its Applications (MAPREDUCE'10). [2] Interesting tidbit: nobody from Google on planning committee. Mostly INRIA
MapReduce Sibblings, and Related Projects
- Hadoop, open source. Written in Java, with a few routines in C. Wins Terabyte sorting competition in 2008 [3]
- Apache Hadoop Wins Terabyte Sort Benchmark
One of Yahoo's Hadoop clusters sorted 1 terabyte of data in 209 seconds, which beat the previous record of 297 seconds in the annual general purpose (daytona) terabyte sort benchmark. The sort benchmark, which was created in 1998 by Jim Gray, specifies the input data (10 billion 100 byte records), which must be completely sorted and written to disk. This is the first time that either a Java or an open source program has won. Yahoo is both the largest user of Hadoop with 13,000+ nodes running hundreds of thousands of jobs a month and the largest contributor, although non-Yahoo usage and contributions are increasing rapidly. - Their implementation provided also to be highly scalable, and last year placed first place in the Terabyte Sort Benchmark. In order to do so, they used 910 nodes, each with 2 cores (a total of 1820 cores), and were able to keep the data entirely in memory across the nodes. With this many machines and their open-source MapReduce implementation, they were able to sort one terabyte of data in 209 seconds, in contrast to the previous record of 297 seconds. Not one to be left behind, Google showed that they were still quite ahead, claiming they could do the same with their closed-source implementation in only 68 seconds. The only details they note are that they use 1000 nodes, but since it’s not verifiable or mentioned on the official Sort Benchmark Home Page, it may not be worthwhile to discuss it further.
- Apache Hadoop Wins Terabyte Sort Benchmark
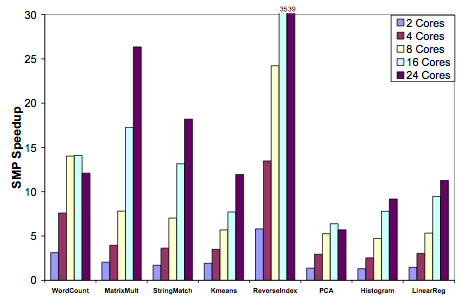
- Phoenix [4] Another implementation of MapReduce, named Phoenix [2], has been created to facilitate optimal use of multi-core and multiprocessor systems. Written in C++, they sought to use the MapReduce programming paradigm to perform dense integer matrix multiplication as well as performing linear regression and principal components analysis on a matrix (amongst other applications). The following graph shows the speedup they achieve over varying number of cores:
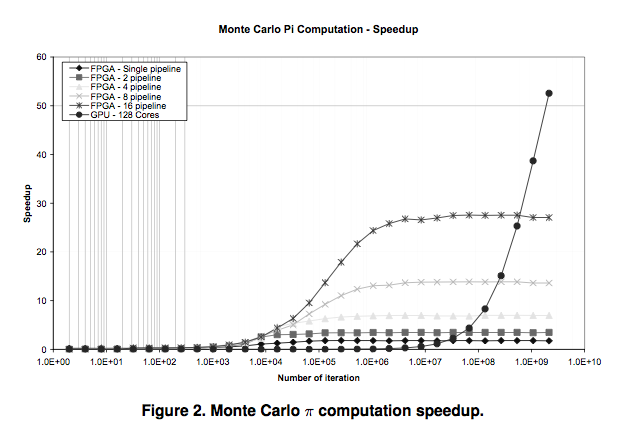
- GPU/FPGA and MapReduce [5]
MapReduce Based on Functional Programming Concepts
From [6]
- Operations do not modify the data structures. New data created. The data are immutable.
- Original data unmodified
- Data flows are implicit in program design
- order of operations does not matter
Motivation
- Grand scale: data > TB, # servers > 1000.
- Automatic parallelization
- Fault Tolerant
- Simple and clean to program
Infrastructure
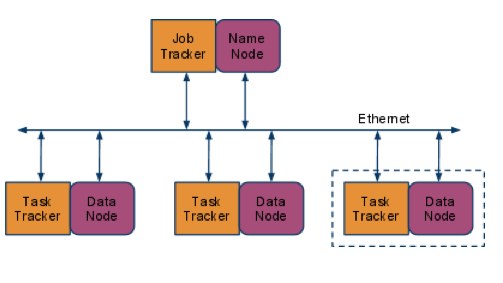
The Block Diagram
The Data is stored in the HDFS
- The data is held in a distributed file system, the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS)
- The goal of a DFS [7]
- A distributed file system is designed to hold a large amount of data and provide access to this data to many clients distributed across a network. There are a number of distributed file systems that solve this problem in different ways.
- HDFS is designed to store a very large amount of information (terabytes or petabytes). This requires spreading the data across a large number of machines. It also supports much larger file sizes than NFS.
- HDFS should store data reliably. If individual machines in the cluster malfunction, data should still be available.
- HDFS should provide fast, scalable access to this information.
- HDFS should integrate well with Hadoop MapReduce, allowing data to be read and computed upon locally when possible.
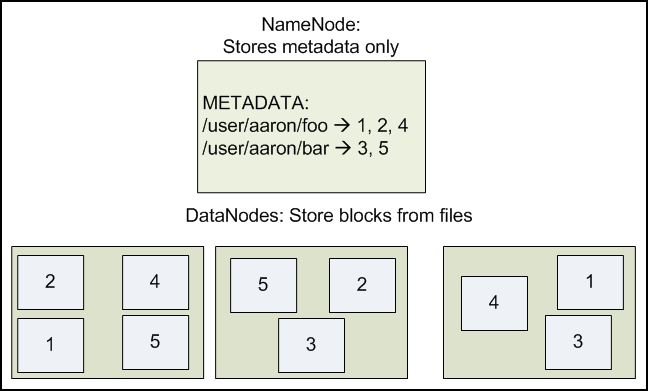
Figure 2.1: DataNodes holding blocks of multiple files with a replication factor of 2.
The NameNode maps the filenames onto the block ids.[7]
The Computation
The images in this section are mostly taken from the excellent Yahoo tutorial (Module 4) on MapReduce [8]
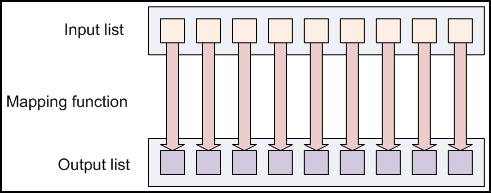
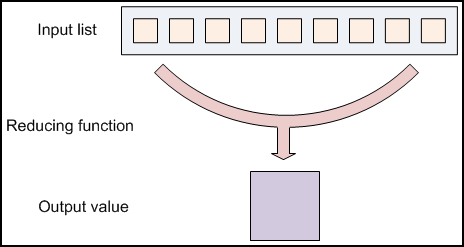
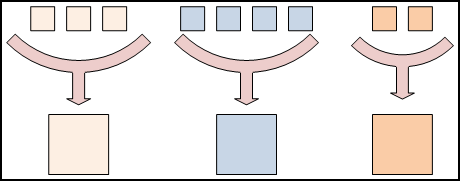
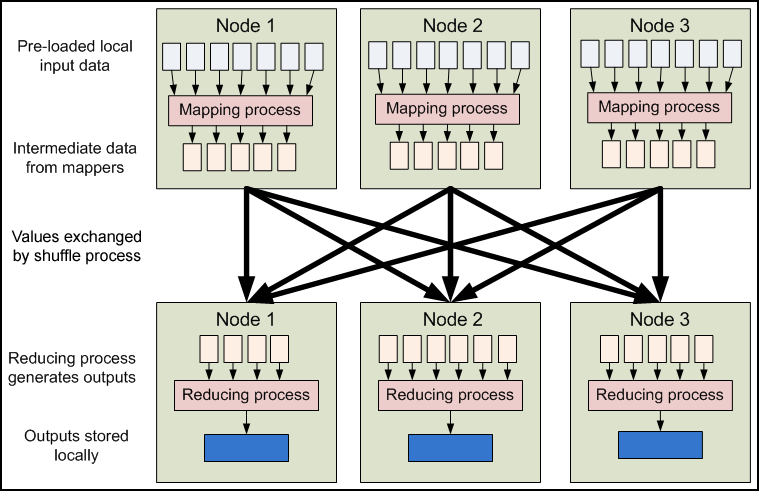
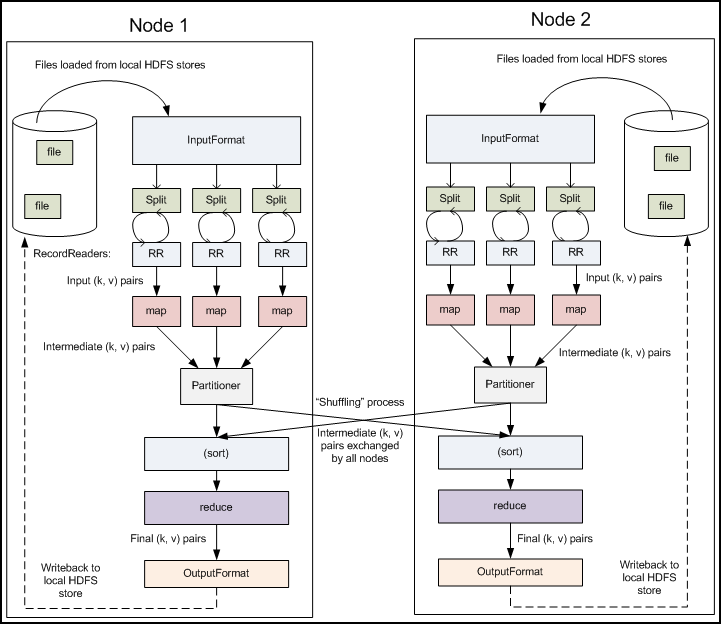
Programming Model
Material also taken from [8].
The WordCount Program (example)
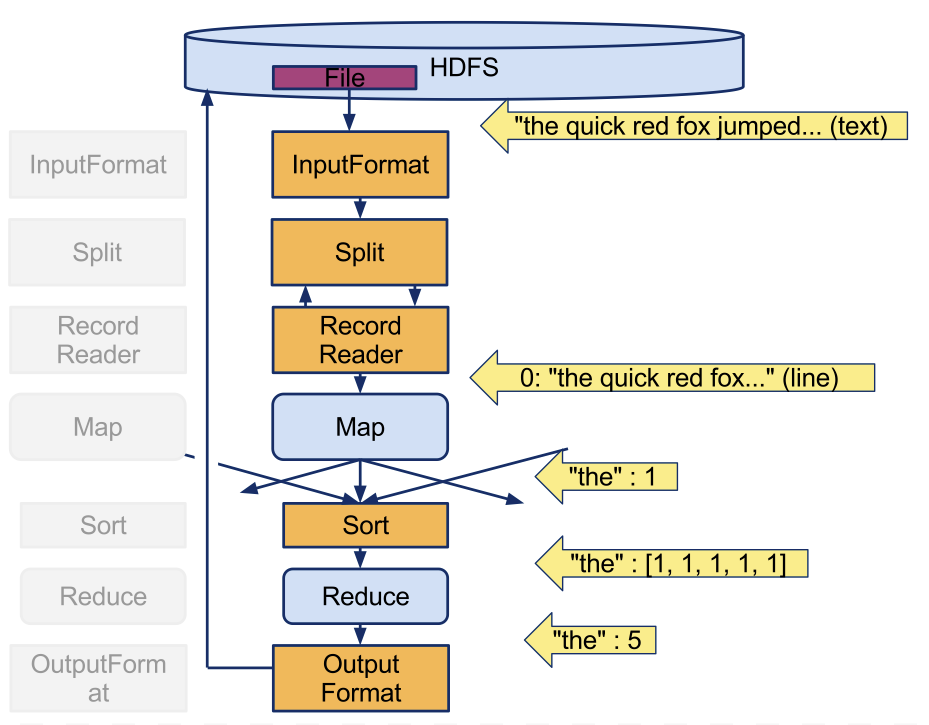
The Map Function, simplified
mapper (filename, file-contents):
for each word in file-contents:
emit (word, 1)
The Reduce Function, simplified
reducer (word, values):
sum = 0
for each value in values:
sum = sum + value
emit (word, sum)
The Map and Reduce Java Blocks
public static class MapClass extends MapReduceBase
implements Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable> {
private final static IntWritable one = new IntWritable(1);
private Text word = new Text();
public void map(LongWritable key, Text value,
OutputCollector<Text, IntWritable> output,
Reporter reporter) throws IOException {
String line = value.toString();
StringTokenizer itr = new StringTokenizer(line);
while (itr.hasMoreTokens()) {
word.set(itr.nextToken());
output.collect(word, one);
}
}
}
/**
* A reducer class that just emits the sum of the input values.
*/
public static class Reduce extends MapReduceBase
implements Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> {
public void reduce(Text key, Iterator<IntWritable> values,
OutputCollector<Text, IntWritable> output,
Reporter reporter) throws IOException {
int sum = 0;
while (values.hasNext()) {
sum += values.next().get();
}
output.collect(key, new IntWritable(sum));
}
}
 |  | |
| ||
 |  |
Test: Running WordCound on 1, 2, 4, 8, and 16 identical files
- Setup: create 5 directories, one with 1 file, the other with 2 copies of the same file (with different names), one with 4 copies of the file, one with 8 copies, and 1 with 16 copies.
- the file contains "the quick red fox jumped over the lazy brown sleeping dog." which is 10 words long, and 60 bytes in size.
- The command to run hadoop on these directories is:
hadoop jar /home/hadoop/352/dft/wordcount.jar org.myorg.WordCount dft_16fox dft_16fox-output
| Output Log | 1 file | 2 files | 4 files | 8 files | 16 files | comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MapReduce
- ↑ MapReduce 2010: http://graal.ens-lyon.fr/mapreduce/
- ↑ Apache Hadoop wins Terabyte Sort Benchmark, http://developer.yahoo.net/blogs/hadoop/2008/07/apache_hadoop_wins_terabyte_sort_benchmark.html
- ↑ Evaluating MapReduce for Multi-core and Multiprocessor Systems Colby Ranger, Ramanan Raghuraman, Arun Penmetsa, Gary Bradski, Christos Kozyrakis∗ Computer Systems Laboratory, Stanford University, http://csl.stanford.edu/~christos/publications/2007.cmp_mapreduce.hpca.pdf
- ↑ Map-reduce as a Programming Model for Custom Computing Machines, Jackson H.C. Yeung, C.C. Tsang, K.H. Tsoi, Bill S.H. Kwan, Chris C.C. Cheung, Anthony P.C. Chan, Philip H.W. Leong, Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Shatin NT, Hong Kong, and Cluster Technology Limited, Hong Kong Science and Technology Park, NT, Hong Kong. http://mesl.ucsd.edu/gupta/cse291-fpga/Readings/mr_fccm08.pdf
- ↑ Google tutorials on MapReduce, http://code.google.com/edu/submissions/mapreduce-minilecture/listing.html
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Yahoo Hadoop Tutorial, Module 2, http://developer.yahoo.com/hadoop/tutorial/module2.html
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Yahoo Tutorial, Module 4, MapReduce Basics http://developer.yahoo.com/hadoop/tutorial/module4.html