CSC111 Lab 7 2014
--D. Thiebaut (talk) 12:45, 10 March 2014 (EDT)
This lab presents image-processing operations in Python using JES. You will need to submit the last working version of your program by the end of the lab.
Contents
References
- A very good reference can be found here.
- A list of all the JES functions that apply to image processing can be found here.
Images
- It turns out that the new version of JES also works on JPG images as well at BMP images, so for this lab you can use the cat and baby with red eyes we saw in class, or pictures of your own choosing. One recommendation, though: the larger the image you pick, the more time you'll have to wait for your programs to process your image.
JES and Image Processing
Skeleton Program
The program you need to submit at the end of this lab will be called lab7.py.
Below is a program you should copy/paste to your JES window.
# JES Picture processing
# D. Thiebaut
# A demo of some of the functions available in JES for manipulating
# the pixels of an image.
# changeColor( image ).
# Changes the amount of red, green and blue that is in an image
def doNotChangeColor( image ):
for x in range(0,getWidth(image)):
for y in range(0,getHeight(image)):
pixel = getPixel (image, x, y)
red = getRed(pixel)
green = getGreen(pixel)
blue = getBlue(pixel)
# the line below replaces the pixel with its original color. Change
# the amount of red, green and blue to see some change in the colors
newColor = makeColor( red, green, blue )
setColor( pixel, newColor )
return image
# ==================================================================
# MAIN PROGRAM
# ==================================================================
file = pickAFile()
image = makePicture( file )
show( image )
image = changeColor( image )
repaint( image )
- Run it to verify that it displays your image. Right now the program doesn't modify any pixel, so do not expect anything different from the original.
Problem 1: Andy Warhol Cat
Copy the doNotChangeColor() function and create a new one that looks just the same, but change its name to something like andyWarhol(). Make this new function modify the red, green and blue components of each pixel. Here are different modifications you can try (be imaginative and try others too). Don't limit to just one color component: apply the modification to all 3!
blue = blue // 2
|
make blue component darker |
blue = blue + (255-blue)//2
|
make blue component lighter |
if blue <125 :
blue = 0
else:
blue = 255
|
Andy Warhol transform |
blue = ( blue + red ) // 2
red = ( red + green ) // 2
green = ( green + blue ) // 2
|
shift colors and average out pairs of components. |
- Can you reproduce the (Andy Warhol-type) image on the right?
Problem 2: black and white
- Make your image black and white by storing the same value in the green, red, and blue component of a pixel. In a first step, pick the amount of red of the pixel and store that number in the other two components. (green = red, blue = red).
- Next take the average amount of red, green and blue and store that value (store it in a variable called grey for example), in all three components.
- Better: initialize the grey variable as follows:
grey = int( 0.3 * red +0.6 * green +0.11 * blue )
Problem 3: Controlling the Sweep Through the Pixels
- Copy paste this function that contains a call to repaint( image ) inside the for x in range(...) loop.
def sweep( image ):
for x in range(0,getWidth(image)):
repaint( image )
for y in range(0,getHeight(image)):
pixel = getPixel (image, x, y)
red = getRed(pixel)
green = getGreen(pixel)
blue = getBlue(pixel)
# the line below replaces the pixel with its original color. Change
# the amount of red, green and blue to see some change in the colors
if red < 125:
red = green = blue = 0
else:
red = 255
newColor = makeColor( red, green, blue )
setColor( pixel, newColor )
return image
- Make your main program call sweep( image ) instead of the previous function it was calling.
- Run your program.
- Notice how it "sweeps" through the image as it processes it.
Challenge 1 |
- Modify the function so that the sweep goes from right to left.
Challenge 2 |
- Modify the function so that the sweep goes from top to bottom
Challenge 3 |
- Modify the function so that the sweep goes from bottom to top
Problem 4: Sideways
Pick one of the functions you have written for the problems above and make a new copy of it under a different name.
Replace the nested for-loop with this loop:
for x in range( getWidth( image ) ):
maxY = min( x, getHeight( image ) )
for y in range( maxY ):
...
- Look at the code. See if you can accurately predict the way the image is going to be transformed by these nested for-loops. Then run it!
- Modify your new function so that the transformation affects another side of the image.
Problem 5: Borders
- Write a new function called addBorder( image, borderWidth ) that will put a red border around the image.
- Do it one step at a time. First put a border at the top of the image. At the beginning make it just 10 pixels wide.
- Modify the program and ask the user to pick a color first, then pass this color to the function addBorder( image, borderWidth, color ) which will put a border all around the image.
- Modify the program so that it also asks the user for the width of the border, as well as the color (two dialogs will open, one after the other).
Challenge 4 |
- B&W image with Colored Border
- Make your program output a version of your colored image that will be black and white with a colored border around it.
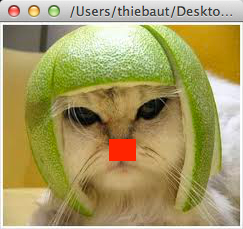
Problem 6: Cat with a Red Nose
- Add a new function that will draw a red square over the cat nose. Don't worry if it doesn't match perfectly. Just a big square over the nose will do.
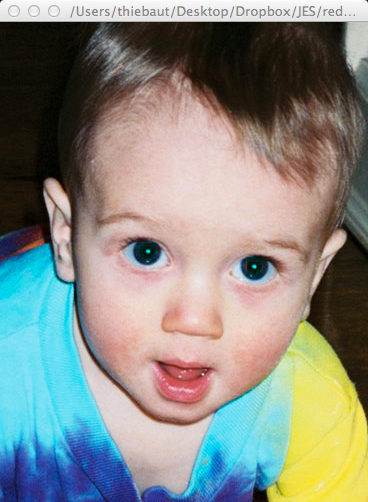
- Add a new function that will remove the red from the eyes of the little boy. For this you will need to
- Figure out the coordinates of two squares around the red pupils of the little boy (use the Media Tool)
- Write a function that will modify all the pixels inside these two squares and remove their red component while leaving the green and blue untouched.
Problem 7: Diagonal
- Go back to one of the transformations that affects all the pixels in the image. Replace the nested for-loops by this single loop like this:
for x in range(0,getWidth(image)):
y = min( x, getHeight( image )-1 )
pixel = getPixel (image, x, y)
newColor = makeColor( 255, 0, 0 )
setColor( pixel, newColor )
- What do you get?
- Modify your function so that it puts a red diagonal cross over the image.
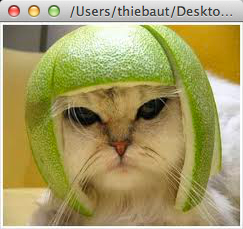
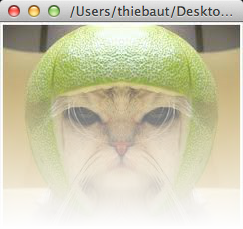
Challenge of the Day: Symmetrical Cat in Fog |
- Write a JES program that takes our original cat image (shown on the left below) and produces this new one (on the right) where the cat now has a symmetrical head and is in the fog...
Note that the colors at the top of the new image are the original colors, but that the color of all the pixels on the bottom line is white...
Submission
Submit the last JES program that works here
Saving your Images
If you want to save your processed image, you need to figure out what your Desktop path is and save to that path. On a Mac saving to a file called "MyFile.bmp" would be done as follows (replace thiebaut by your user name):
writePictureTo( image, "/Users/thiebaut/Desktop/MyFile.bmp" )
With Windows, the same code might read:
writePictureTo( image, "C:\\Users\\thiebaut\\Desktop\\MyFile.bmp" )