CSC111 Lab 12 2015
--D. Thiebaut (talk) 11:31, 19 April 2015 (EDT)
|
This lab deals with recursive functions. Programming recursive functions is a challenging concept to master. The best way to proceed is to write many different recursive solutions and observe the behavior of the functions as they perform their work. Eventually recursion will start making sense. It is normal to not fully understand it at first. Keep at it. Little by little, it will become natural thinking. |
Visualizing Recursive Factorial At Work
Create a copy of this simple example:
# factorial.py # Demonstrates a recursive factorial function def fact( n ): # stopping condition if n<=1: return 1 # recursive step y = fact( n-1 ) result = n * y return result def main(): n = int( input( "Enter a positive number: " ) ) x = fact( n ) print( "the factorial of %d is %d." % ( n , x ) ) main()
- Run your program
- It will prompt you for a number and will return its factorial.
- Verify that it computes the correct result. Below are some factorials numbers to compare your output to.
1! = 1 2! = 2 3! = 6 4! = 24 5! = 120 6! = 720 7! = 5040 8! = 40320 9! = 362880 10! = 3628800 11! = 39916800 12! = 479001600 13! = 6227020800 14! = 87178291200
Visualizing, Step 1
- Add print statements to your fact() function so that it will let you know exactly what it does. For example, before it tests to see if n is less than equal to 1, you could print:
print( "fact function started. Receives n =", n )
print( "testing if %d is >= 1" % (n) )
- Add print statements that will show the values of y and result.
- Run your program and observe its output. Can you see better how the function fact() recursively calls itself?
Visualizing, Step 2
- Create the more sophisticated program shown below. Observe it well first, and try to figure out what the indent variable does.
# factorialPrint.py # Demonstrates a recursive factorial function def fact2( n, indent ): print( indent, "fact2(%d) started" % n ) print( indent, "comparing %d to 1" % n ) if n<=1: print( indent, "%d is <= 1. Returning 1" % 1 ) return 1 print( indent, "%d is not <= 1. Calling fact2(%d) and storing it in y" % (n, n-1) ) y = fact2( n-1, indent + " " ) print( indent, "just received %d from fact2( %d )." % ( y, n-1 ) ) result = n * y print( indent, "multiplied %d by %d. It's %d. Returning %d to caller" % ( n, y, result, result ) ) return result def main(): n = input( "Enter a positive integer: " ) print( "Main calls fact( %d )" % n ) y = fact2( n, " " ) print( "Main receives result = ", y ) main()
- Run the program
- Explain the pattern made by the printed lines. Why this shape?
- Where does the stopping condition appear in the printed lines? In other words, where is the printed statement that indicates that fact() just received a value of n equal to 1? Why isn't this statement at the end of the printout?
Thinking Recursively
All the challenges below require you to put together a recursive function for a simple problem.
Thinking recursively is quite challenging and takes a while to master. So don't despair!
Here are points to remember when building a recursive function:
- First, figure out what the function will return to the main program. Will it return a boolean? An integer? A list? Then when the function calls itself recursively, that's what it should expect to receive back from a call to itself.
- What is the stopping condition? What is the smallest problem you can solve without recursion? That's the first thing you want to test for and do in your recursive function.
- If the stopping condition doesn't apply, and the function has to do some work, figure out how to make one or several recursive calls to the function, get some intermediate results back, combine them together and get the final answer. That's the recursive step.
- First, figure out what the function will return to the main program. Will it return a boolean? An integer? A list? Then when the function calls itself recursively, that's what it should expect to receive back from a call to itself.
Challenge 1: Recursive Sum |
- Given a number n, compute recursively the sum of all the numbers from 1 to n. For example, if you pass n = 5 to the solution function, it will return 15 (which is equal to 5+4+3+2+1)
Challenge 2: Recursive Even Sum |
- Given a number n, compute recursively the sum of all the positive even numbers less than or equal to n.
- This is trickier than it seems! Here is an example of running a loop and asking the recursive function to compute the sum of all the even numbers up to n when n ranges from 0 to 12.
n = 0 sumEven(0) returns 0 n = 1 sumEven(1) returns 0 n = 2 sumEven(2) returns 2 n = 3 sumEven(3) returns 2 n = 4 sumEven(4) returns 6 n = 5 sumEven(5) returns 6 n = 6 sumEven(6) returns 12 n = 7 sumEven(7) returns 12 n = 8 sumEven(8) returns 20 n = 9 sumEven(9) returns 20 n = 10 sumEven(10) returns 30 n = 11 sumEven(11) returns 30
Challenge 3: Recursive Max |
- Write a recursive function that returns the largest element of a list L using the following formula:
|
largest( L ) |
= L[0] |
if len( L ) == 1 |
|
|
= max( L[0], largest( L[1:] ) ) |
otherwise. We assume N=len(L) |
- Test your program on different lists of varying sizes. We assume that the lists will always have at least one element.
- Hints
- the function definition is simply def largest( L ):
- write the stopping condition first (if len(L)...)
- if the stopping condition is not met, compute the max() of L[0] and largest( L minus the first element )
def largest( A ):
if len( A )==1:
return A[0]
return max( A[0], largest( A[1:] ) )
Divide and Conquer Recursion
- We now take a slightly different approach. This time we take a list, divide it two halves, recursively process the two halves, and combine the result of the results obtained on both sides.
- As an example, assume we have to find the largest item in a list L. Here's a possible way to describe the recursive divide-and-conquer approach:
|
largest( L ) |
= L[0] |
if len( L ) == 1 |
|
|
= max( largest( L[0:N/2], largest( L[N/2:] ) ) |
otherwise. We assume N=len(L) |
The code equivalent to this definition is shown below:
def divideConquerLargest( L ): N = len( L ) if N==1: return L[0] return max( divideConquerLargest( L[0:N//2] ), divideConquerLargest( L[N//2: ] ) )
- Run this code, and verify that it returns the largest element of an unsorted list of integers.
L = [1, 2, 3, 0, 10, 20, 30, 3, -3, 5, 1, 100, 1] print( "divideConquerLargest( %s ) = %d" % (L, divideConquerLargest(L ) ) )
Challenge 4: Divide-and-Conquer Min |
- Write a recursive function that uses the divide and conquer approach to find the smallest element in a list L.
Challenge 5: Divide-and-Conquer Sum |
- Write a recursive function that uses the divide and conquer approach to compute the sum of all the elements in a list L.
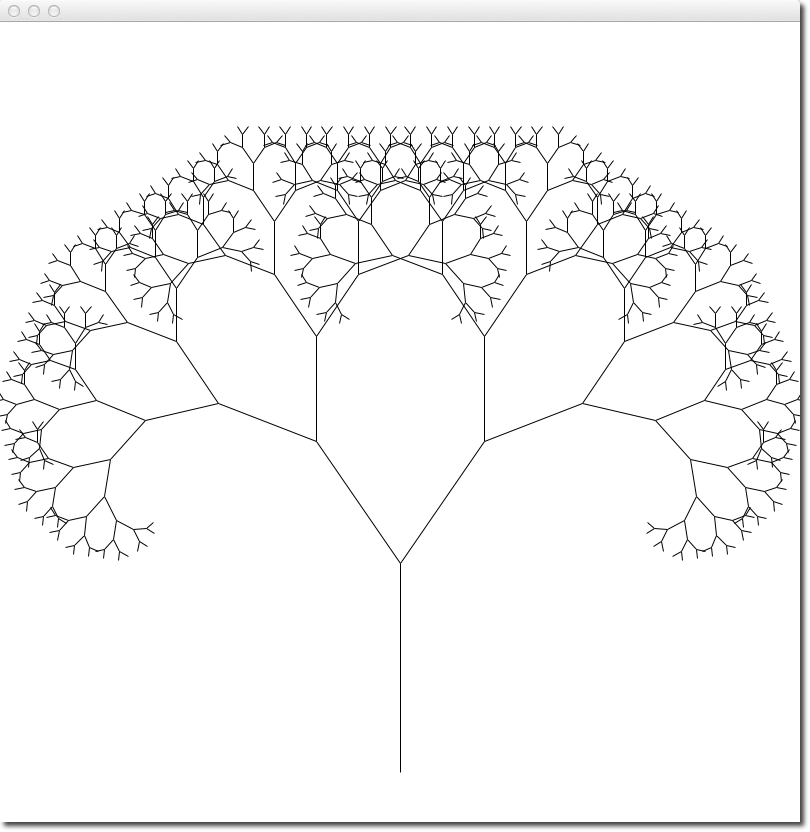
Fractal Trees
- This exercise is for you to explore recursion in the context of graphics.
- Create a new program with the code you'll find on this page, put it in the same directory where you store your graphics.py directory. You may want to call your program fractalTree.py.
- The program will generate a fractal tree. Fractals are self-similar objects: they look the same on a small scale as they do on a larger scale.
- Run the program first.
- Look at the code and see if you can figure out how the recursion works.
- To see how the different parameters influence the drawing of the fractal tree, modify the following parameters, one at a time, and give them different values:
- theta
- in the main program, change the angle theta which controls how much a branch will diverge from the direction of the branch that supports it. Try 0.4 first. Then try values between 0 and 0.8.
- level of recursion
- the main program passes 9 to the function as a starting level of recursion. Try passing smaller numbers first, then larger numbers (but less than 13 or so).
- trunk_ratio
- recursive function defines this as 0.29 and that represents the length of the trunk relative to its two branches. Try ratios between 0.1 (10%) and 0.9 (90%).
Exploration: Visiting a Maze
Here is an example of a complex problem that can be (relatively) easily solved using a recursive program.
- Go to this page, copy the program in the Python 3 section, and run it.
- Observe how the recursive visitMaze() function leaves "bread crumbs" behind the cells that it visits, and "v" characters in cells visited but known not to lead to an exit.
- Edit the program and switch the order in which the function visits cells in the 4 directions. Make the recursive function decide to go up first, then left, then right, and finally down.
- Run the program and see how this change influences the way the program explores the maze.
- Modify your program so that the maze is now a much simpler maze, in the spirit of the maze shown below:
mazeText = """
#########################
........................#
#.......................#
#.......................#
#...........#...........#
#...........#...........#
#############...........#
#...........#...........#
#.......................#
#........################
#........................
#.......................#
#.......................#
#########################
"""
- Predict the path that the program is going to take when visiting it.
- Repeat the same experiment as before and change the order in which the recursive function visits the different directions, and observe if this makes the function find the exit faster.
Treasures in the maze
- Let's change the rules of the game, and make your program find a path to a treasure, rather than a path to an exit. In our case the treasure will be a special character, say '&', inside the maze.
- Modify your the visitMaze() function so that it now returns true if it finds the treasure, and not an exit. Verify that your program displays at the end the path to the treasure.
<showafterdate after="20150424 12:00" before="20150601 00:00">
Solution Programs
# solution programs for Lab12 2015
#
#
from random import randrange
def fact( n ):
print( "fact function started. Received n =", n )
print( "testing if %d is >= 1" % (n) )
if n<=1:
print( "n == 1. Returning 1" )
return 1
print( "n > 1. Calling fact( %d )" % (n-1) )
y = fact( n-1 )
print( "setting y to %d" % y )
result = n * y
print( "returning result = %d * %d = %d" % (n, y, n*y) )
return result
def fact2( n, indent ):
print( indent, "fact2(%d) started" % n )
print( indent, "comparing %d to 1" % n )
if n<=1:
print( indent, "%d is <= 1. Returning 1" % 1 )
return 1
print( indent, "%d is not <= 1. Calling fact2(%d) and storing it in y" % (n, n-1) )
y = fact2( n-1, indent + " " )
print( indent, "just received %d from fact2( %d )." % ( y, n-1 ) )
result = n * y
print( indent, "multiplied %d by %d. It's %d. Returning %d to caller" % ( n, y, result, result ) )
return result
def sum1( n ):
if n==1:
return 1
return n + sum1( n-1 )
def evenSum1( n ):
if n <= 1:
return 0
if n%2 == 0:
return n + evenSum1( n-2 )
if n%2 == 1:
return evenSum1( n-1 )
def recurseMax( L ):
N = len( L )
if N==1:
return L[0]
return max( L[0], recurseMax( L[1:] ) )
def divideConquerLargest( L ):
N = len( L )
if N==1:
return L[0]
return max( divideConquerLargest( L[0:N//2] ),
divideConquerLargest( L[N//2: ] ) )
def divideConquerMin( L ):
N = len( L )
if N==1:
return L[0]
return min( divideConquerMin( L[0:N//2] ),
divideConquerMin( L[N//2: ] ) )
def divideConquerSum( L ):
N = len( L )
if N==1:
return L[0]
return divideConquerSum( L[0:N//2] ) + divideConquerSum( L[N//2: ] )
def divideConquerAbs( L ):
N = len( L )
if N==1:
L[0] = abs( L[0] )
return L
return divideConquerAbs( L[0:N//2] ) + divideConquerAbs( L[N//2: ] )
#------------------------------------------------------------------
def createArray( n ):
"""Creates a list of n random numbers in sorted order"""
A= []
for i in range( n ):
A.append( randrange( n * 10 ) )
A.sort()
return A
#------------------------------------------------------------------
def binsearch( A, low, high, key ):
"""a recursive function that searches the list A to see if
it contains the item key between the indexes "low" and "high".
returns the index where the key was found, or -1 otherwise
"""
print( "low=%10d high=%10d key=%10d" % (low, high, key) )
if low>high:
return -1
mid = ( low + high )//2
if A[mid]==key:
return mid
if key < A[mid]:
return binsearch( A, low, mid-1, key )
else:
return binsearch( A, mid+1, high, key )
def main():
# fact
"""
n = int( input( "Enter a positive number: " ) )
x = fact( n )
print( "the factorial of %d is %d." % ( n , x ) )
"""
# fact2
"""
n = int( input( "Enter a positive number: " ) )
x = fact2( n, " " )
print( "the factorial of %d is %d." % ( n , x ) )
"""
# sum1
"""
n = int( input( "Enter a positive number: " ) )
print( "sum of all numbers from 1 to %d = %d" % (n, sum1(n) ) )
"""
# evenSum1
"""
for n in range( 12 ):
print( " n = %d sumEven(%d) returns %d" % (n, n, evenSum1(n) ) )
"""
# recursive max
"""
L = [1, 2, 3, 0, 10, 20, 30, 3, -3, 5, 1, 100, 1]
print( "recurseMax( %s ) = %d" % ( L, recurseMax( L ) ) )
"""
# divideConquerLargest
"""
L = [1, 2, 3, 0, 10, 20, 30, 3, -3, 5, 1, 100, 1]
print( "divideConquerLargest( %s ) = %d" % (L, divideConquerLargest(L ) ) )
"""
# divideConquerMin
"""
L = [1, 2, 3, 0, 10, 20, 30, 3, -3, 5, 1, 100, 1]
print( "divideConquerMin( %s ) = %d" % (L, divideConquerMin(L ) ) )
"""
# divideConquerSum
"""
L = [1, 2, 3, 10, 101, 100, 100]
print( "divideConquerSum( %s ) = %d" % (L, divideConquerSum(L ) ) )
"""
# divideConquerAbs
"""
L = [1, 2, 3, -10, -101, 100, 100]
print( "divideConquerAbs( %s ) = %s" % (L, divideConquerAbs(L ) ) )
"""
# binSearch
#A = createArray( 20 )
#print( "A = ", A )
A = createArray( 1000000 )
print( A[100:110] )
while True:
print
key = int( input( "search for what number? " ) )
if key==-1: break
index = binsearch( A, 0, len( A )-1, key )
if index != -1:
print( "found %d at index %d" % ( key, index ) )
else:
print( "%d not in A" % key )
main()
</showafterdate>