Tutorial: C + MySQL + MPI
--D. Thiebaut (talk) 16:30, 13 October 2013 (EDT)
The purpose of this tutorial/lab is to generate an MPI program written in C that walks a directory containing image files, gets their geometry in the form of a width and height, and enters this information in a MySQL database.
Contents
The Main Idea of this Tutorial
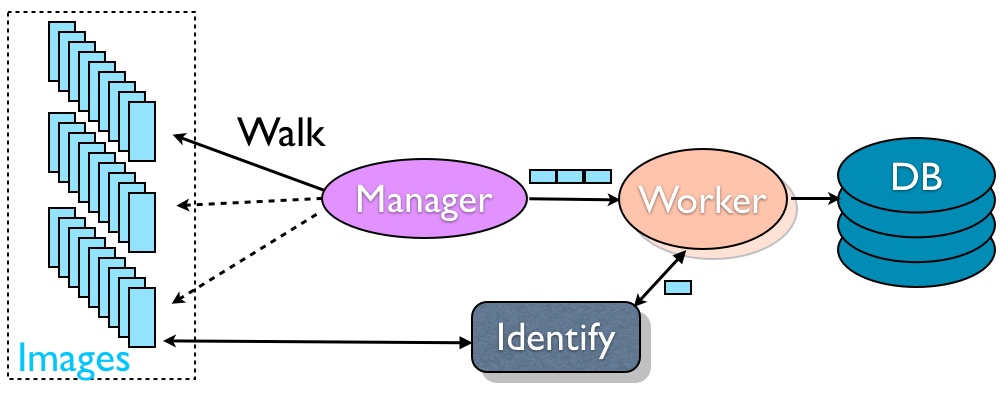
Above is a possible solution for the following situation.
- A large collection of images exist in a hierarchical directory structure. The paths are of the form
- /media/dominique/3TB/mediawiki/images/wikipedia/en/0
- /media/dominique/3TB/mediawiki/images/wikipedia/en/0/00
- /media/dominique/3TB/mediawiki/images/wikipedia/en/0/01
- /media/dominique/3TB/mediawiki/images/wikipedia/en/0/02
- ...
- /media/dominique/3TB/mediawiki/images/wikipedia/en/0/0f
- /media/dominique/3TB/mediawiki/images/wikipedia/en/1/10
- ...
- /media/dominique/3TB/mediawiki/images/wikipedia/en/1/1f
- ...
- /media/dominique/3TB/mediawiki/images/wikipedia/en/f/ff
- Each image name should be entered in a database along with its short path (e.g. 0/10), and its size, expressed as an integer width and an integer height.
- The number of files is approximately 3 million.
- ImageMagick provides a quick and efficient way to find the size of an image in its utility identify
- We are looking for a solution that uses MPI to parallelize the processing of the 3 million files.
Quick Timing Experiment
To get an idea of how long it takes to identify an image on the AMD server, we run a simple few commands:
time for i in `ls /media/dominique/3TB/mediawiki/images/wikipedia/en/1/10/E*` ; do
identify -format "%w %h" $i
done | wc
87 174 705
real 0m1.758s
user 0m0.284s
sys 0m0.392s
The command above takes all the images whose name starts with E in the 1/10 subdirectory of images, and identifies each one. The | wc counts the number of lines output by the command, which is close to the number of images processed, and time computes the real time, i.e. the time we have to wait for the command to be done.
It takes 1.7 seconds to the server to identify 87 files, or 20 ms per file. This represents 16 hours for 3 million images. Our goal is to diminish this time by close to a factor of 8 or more, since we have 8 cores, and since the database server can operate in parallel. 2 hours or better (can we do better?) is our target!
References
A good reference on combining MySQL and C programming:
Verify that MPI works
- test your installation with the classic hello world program.
Source
// mpi_hello.c
#include <mpi.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main (int argc, char* argv[])
{
int rank, size;
MPI_Init (&argc, &argv); /* starts MPI */
MPI_Comm_rank (MPI_COMM_WORLD, &rank); /* get current process id */
MPI_Comm_size (MPI_COMM_WORLD, &size); /* get number of processes */
printf( "Hello world from process %d of %d\n", rank, size );
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}
Compile & Run
mpicc -o hello mpi_hello.c mpirun -np 2 ./hello Hello world from process 0 of 2 Hello world from process 1 of 2
Verify that the MySQL API works
Using the example and tricks provided at http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/linux-unix-connect-mysql-c-api-program.html, we can easily test whether we can access a MySQL database from our program:
Source
// mysqlTest.c
// Taken from http://www.cyberciti.biz
// Lists all the tables found in a MySQL database whose name is stored
// in the char[] database variable.
#include <mysql.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
main() {
MYSQL *conn;
MYSQL_RES *res;
MYSQL_ROW row;
char *server = "localhost";
char *user = "352a";
char *password = "xxxxxx";
char *database = "enwiki_images";
conn = mysql_init(NULL);
/* Connect to database */
if (!mysql_real_connect(conn, server,
user, password, database, 0, NULL, 0)) {
fprintf(stderr, "%s\n", mysql_error(conn));
exit(1);
}
/* send SQL query */
if (mysql_query(conn, "show tables")) {
fprintf(stderr, "%s\n", mysql_error(conn));
exit(1);
}
res = mysql_use_result(conn);
/* output table name */
printf("MySQL Tables in mysql database:\n");
while ((row = mysql_fetch_row(res)) != NULL)
printf("%s \n", row[0]);
/* close connection */
mysql_free_result(res);
mysql_close(conn);
}
Compile & Run
On Server Hadoop0
- Once you have installed mysql_config on your system, you can easily get the library switches and compiler switches corresponding to your installation. They are given by
- mysql_config --cflags
- mysql_config --libs
mysql_config --cflags -I/usr/include/mysql -DBIG_JOINS=1 -fno-strict-aliasing -g -DNDEBUG mysql_config --libs -L/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu -lmysqlclient -lpthread -lz -lm -ldl
To compile, simply pass on the output of the mysql_config commands, or substitute their output in the compile line:
gcc -o mysqlTest $(mysql_config --cflags) mysqlTest.c $(mysql_config --libs)
To run:
./mysqlTest images <--- the only table was images
On Server Beowulf
- After changing the host from localhost to the address of our beowulf server, and using different credentials (user/password), we get this series of commands/responses in the Terminal window.
[352a@beowulf mysql]$ gcc -o mysqlTest $(mysql_config --cflags) mysqlTest.c $(mysql_config --libs)
In file included from /usr/include/sys/types.h:26:0,
from /usr/include/mysql/mysql.h:47,
from mysqlTest.c:6:
/usr/include/features.h:314:4: warning: #warning _FORTIFY_SOURCE requires compiling with optimization (-O) [-Wcpp]
[352a@beowulf mysql]$ gcc -O -o mysqlTest $(mysql_config --cflags) mysqlTest.c $(mysql_config --libs)
[352a@beowulf mysql]$ ./mysqlTest
MySQL Tables in mysql database:
Colleges
Graduated
Names
Nums
Note that the first attempt to compile yields a warning, which we read, and adopt its suggested solution of using the optimization switch -O when compiling the program. The second attempt, with -O is error/warning free.
Calling System Applications from C
In our application we need to process a large collection of images and get their geometry information. To get the width and height of images, we simply call imageMagick from the C program and grab the width and height from the command.
Source
// getImageInfo.c
// D. Thiebaut
// Syntax:
// getImageInfo imageFileName
//
// Takes the image file and get identify (part of the ImageMagick tools) to
// get the image width and height in pixels.
//
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main( int argc, char *argv[] ) {
FILE* fp;
char command[100];
char buffer[1000];
int width, height;
//--- display syntax info if user does not specify image name---
if ( argc <= 1 ) {
fprintf( stderr, "Syntax: getImageInfo imageFilename\n\n" );
exit( 1 );
}
//--- create the command with the file name (passed in argv) ---
strcpy( command, "/usr/bin/identify -format \"%w %h\" " );
strcat( command, argv[1] );
//--- open a pipe, make the command run, and return the information ---
//--- in the pipe. ---
if ( ( fp = popen( command, "r" ) ) != NULL ) {
while ( fgets( buffer, 1000, fp ) != NULL ) {
printf( "%s", buffer );
char *p = buffer;
while ( *p != ' ' ) p++;
*p = '\0';
//printf( "width = %s height = %s\n", buffer, p );
width = atoi( buffer );
height = atoi( p+1 );
printf( "width = %d height = %d\n", width, height );
}
}
//--- close pipe ---
pclose( fp );
return 0;
}
Compile & Run
gcc -o getImageInfo getImageInfo.c ./getImageInfo bunny.jpg 1280 800 width = 1280 height = 800
Walking a Directory in C
This program is for running through our tree of directories containing images and to take all the images in one directory and
process them.
Source
// walk.c
// D. Thiebaut
// Taken from http://stackoverflow.com/questions/612097/
// how-can-i-get-a-list-of-files-in-a-directory-using-c-or-c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <dirent.h>
int main( int argc, char **argv) {
DIR *dir;
char path[] = "/media/dominique/3TB/mediawiki/images/wikipedia/en/0/01";
int count = 0;
struct dirent *ent;
if ( argc < 2 ) {
fprintf( stderr, "Syntax: ./walk path" );
exit( 0 );
}
if ((dir = opendir ( path )) != NULL) {
//-- print all the files and directories within directory
while ((ent = readdir (dir)) != NULL) {
printf ( "%s\n", ent->d_name);
//if ( count++ > 10 )
// break;
}
closedir (dir);
return( 0 );
}
else {
/* could not open directory */
perror ("");
exit( 1 );
}
}
Compile and Run
gcc -o walk walk.c ./walk /media/dominique/3TB/mediawiki/images/wikipedia/en/0/01 . .. Keep_the_Home_Fires_Burning_-_Frederick_Wheeler.ogg Voyage_of_the_Jerle_Shannara.jpg Picw.jpg ... The_Constructicons.jpg StarFeathers.jpg Brickell_district,_Miami.jpg One_Tree_Hill_-_Season_2_-_DVD.JPG Silent_All_These_Years_(Single).png
Full Hierarchical Walk
This page presents a solution that will walk a full hierarchical directory set.
Serial Walk-Images-Store-Database Version
The version below is a serial version that walks the directory and enters the image file names into the database.
Source Program
// walkGetSizeAddMySQL.c
// D. Thiebaut
//
// See http://cs.smith.edu/dftwiki/index.php?title=Tutorial:_C_%2B_MySQL_%2B_MPI for
// more information.
//
// to Compile and Run:
// gcc -o walkGetSizeAddMySQL $(mysql_config --cflags) walkGetSizeAddMySQL.c $(mysql_config --libs)
// ./walkGetSizeAddMySQL path n/nn
//
// where "path" is the path to the root directory containing subdirectories of the form 0/00, 0/01, 0/02... a/af, each one
// containing a flat list of image files. The n/nn is one of the subdirectories, for example 0/0a.
//
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <mysql.h>
//--- a simple structure to create a pair of ints ---
typedef struct {
int width;
int height;
} Pair;
//--- Globals refering to the MySql database ---
MYSQL *conn;
MYSQL_RES *res;
MYSQL_ROW row;
char *server = "localhost";
char *user = "352a";
char *password = "xxxxxxx"; // MySql password
char *database = "enwiki_images";
int debug = 0; // use to debug the application
//-----------------------------------------------------
// getPrintTableNames: opens the database, and gets the
// names of the table(s) located in the database
// Taken from
// http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/linux-unix-connect-mysql-c-api-program.html
//
void getPrintTableNames() {
conn = mysql_init(NULL);
/* Connect to database */
if (!mysql_real_connect(conn, server,
user, password, database, 0, NULL, 0)) {
fprintf(stderr, "%s\n", mysql_error(conn));
exit(1);
}
/* send SQL query */
if (mysql_query(conn, "show tables")) {
fprintf(stderr, "%s\n", mysql_error(conn));
exit(1);
}
res = mysql_use_result(conn);
/* output table name */
printf("MySQL Tables in mysql database:\n");
while ((row = mysql_fetch_row(res)) != NULL)
printf("%s \n", row[0]);
/* close connection */
mysql_free_result(res);
mysql_close(conn);
}
//-----------------------------------------------------
// insertFileInDatabase: inserts the name of the image
// file, its path (as in "0/01", its width and height,
// and its scale in the database ase
void insertFileInDatabase( char* filename, char* path, int width, int height, float scale ) {
char query[200];
char escapedFileName[300];
mysql_real_escape_string( conn, escapedFileName, filename, strlen( filename ) );
sprintf( query, "INSERT INTO images2 (name, path, width, height, scale1) VALUES ( '%s', '%s', %d, %d, %f )",
escapedFileName, path, width, height, scale );
// printf( "Query = %s\n", query );
int retCode = mysql_query( conn, query );
if ( retCode ) {
fprintf( stderr, "%s\n", mysql_error( conn ) );
exit( 1 );
}
}
//-----------------------------------------------------
// openDatabase: opens a connection to the database that
// is kept in the global conn variable.
void openDatabase() {
conn = mysql_init( NULL );
/* Connect to database */
if ( !mysql_real_connect( conn, server,
user, password, database, 0, NULL, 0 ) ) {
fprintf( stderr, "%s\n", mysql_error(conn) );
exit(1);
}
}
//-----------------------------------------------------
// closeDatabase: closes the connection.
void closeDatabase() {
mysql_close( conn );
}
//-----------------------------------------------------
// getFileGeometry. Calls the system 'identify' command
// to get the geometry of the file, expressed as its
// width and height.
Pair getFileGeometry( char* fileName ) {
char command[100];
char buffer[1000];
FILE* fp;
Pair pair;
pair.width = 0;
pair.height = 0;
//--- create the command and put " around the file name ---
strcpy( command, "/usr/bin/identify -format \"%w %h\" \"" );
strcat( command, fileName );
strcat( command, "\"" );
//--- open a pipe to get the output of identify ---
if ( ( fp = popen( command, "r" ) ) != NULL ) {
while ( fgets( buffer, 1000, fp ) != NULL ) {
//--- split the width and height into two strings ---
char *p = buffer;
while ( *p != ' ' )
p++;
*p = '\0';
//--- convert them both to ints ---
pair.width = atoi( buffer );
pair.height = atoi( p+1 );
}
}
pclose( fp );
//--- return them in a structure ---
return pair;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------
// getExtension. returns a pointer to the extension of
// the image file, e.g. "jpg"
const char *getExtension(const char *filename) {
const char *dot = strrchr(filename, '.');
if ( !dot || dot == filename )
return "";
return dot + 1;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------
// escapeString: puts \ chars in front of special characters
// that might be in the image file-name, so that it can be
// passed to the "identify" command and not cause the shell
// to misunderstand the name for some shell syntax.
void escapeString( char* name, char* escapedName ) {
char *p = name, *q = escapedName;
while ( *p != '\0' ) {
if ( *p == '\'' || *p == ';' || *p == '"' || *p == '(' || *p == ')'
|| *p == ' ' || *p == ',' || *p == ':' || *p == '&' ) {
*(q++) = '\\';
}
*(q++) = *(p++);
}
*q = '\0';
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// M A I N
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
int main( int argc, char **argv) {
DIR *dir;
char path[100];
char shortPath[10];
int count = 0;
struct dirent *ent;
Pair pair;
char pathAndFileName[1000];
char escapedFileName[1000];
int noEntries = 0;
if ( argc < 3 ) {
fprintf( stderr, "Syntax: ./walkGetSizeAddMySql path n/nn" );
fprintf( stderr, "where path is the rooted path of where the image\n" );
fprintf( stderr, "resides, and n/nn is the directory-pair that is\n" );
fprintf( stderr, "md5 hash of the file name. Typically 0/01, or a/0a" );
exit( 0 );
}
//--- put the arguments into variables ---
strcpy( path, argv[1] );
strcpy( shortPath, argv[2] );
if ( path[ strlen( path )-1 ] != '/' )
strcat( path, "/" );
strcat( path, argv[2] );
//--- open connection to database ---
openDatabase();
//--- start walking the image repository ---
if ((dir = opendir ( path )) != NULL) {
//-- go recursively ---
while ((ent = readdir (dir)) != NULL) {
char* fileName = ent->d_name;
char extension[10];
//--- get file extension ---
strcpy( extension, getExtension( fileName ) );
//--- skip . and .. file names ---
if ( !strcmp( fileName, "." ) || !strcmp( fileName, ".." ) )
continue;
//--- skip some format that "identify" cannot recognize ---
if ( !strcmp( extension, "ogg" ) ) continue;
if ( !strcmp( extension, "OGG" ) ) continue;
if ( !strcmp( extension, "svg" ) ) continue;
if ( !strcmp( extension, "SVG" ) ) continue;
if ( !strcmp( extension, "mid" ) ) continue;
if ( !strcmp( extension, "MID" ) ) continue;
//--- escape special characters for identify ---
escapeString( fileName, escapedFileName );
//--- create the full path of the image file name ---
strcpy( pathAndFileName, "\"" );
strcat( pathAndFileName, path );
strcat( pathAndFileName, "/" );
strcat( pathAndFileName, escapedFileName );
strcat( pathAndFileName, "\"" );
//--- get the geometry as read by "identify" ---
pair = getFileGeometry( pathAndFileName );
//--- keep track of how many files we process ---
noEntries++;
if ( debug )
printf ( "%s\t\t%s\t%d %d\n",getExtension( fileName ), fileName,
pair.width, pair.height );
//--- add file and its geometry to database ---
insertFileInDatabase( fileName, shortPath, pair.width, pair.height, 1.0 );
}
//--- done! Close everything ---
closedir(dir);
closeDatabase();
printf( "%d images processed\n\n", noEntries );
return( 0 );
}
//--- if we're here, there was an error reading the root directory ---
else {
/* could not open directory */
perror ("");
exit( 1 );
}
}
To Compile and Run
gcc -o walkGetSizeAddMySQL $(mysql_config --cflags) walkGetSizeAddMySQL.c $(mysql_config --libs) ./walkGetSizeAddMySQL path n/nn
The MPI Version
The parallel version of this program is written using MPI as the parallel application and can run on multi-core systems as well as a cluster of distributed machines.
The first goal of writing such a parallel application is to take care of the protocol first. A good approach is to adopt the Manager/Worker paradigm, where the manager walks the directory, passes the files in blocks to each worker, which gets the geometry for each one and inserts the tuplet of file-name, path, geometry in the MySQL database.
Challenge 1 |
Given that there will be 1 manager and several workers, the first action item is to figure out who is walking the directory, who is identifying the files with ImageMagick, and who is inserting the files and geometry in the database.
Figure out a good strategy for the roles to be played by the manager and its workers.
Challenge 2 |
Figure out what needs to be exchanged between the manager and the workers. This will be a packet of information. Define exactly how this packet will be organized. Is it an array of ints, an array of chars, and array of something else? If it's an array of chars, are the strings somehow grouped as tuples? For example, if you decide that the manager does the walking and sends a group of file names to a worker, it might have to send the path for each file. Is it sent as a whole string, or as a collection of (path, short-path, filename)? What separator will you use if you are sending arrays of chars?
Will workers ever need to send something back to the manager?
Challenge 3 |
Once you've figured out what will be sent between the two types of players (manager, workers), how will the manager finish the communication with the workers? Define this part of the protocol.
Challenge 4 |
Now that you have a fairly complete protocol, write a skeleton MPI program that will support 1 manager and several workers, and where the protocol will be similar (although on a smaller scale) to the protocol you've defined above.
Test the program and run it.
Make sure it works if you have less data available than the number of workers created. In other words, make sure that if there are more workers than needed given the work, the manager will still be able to tell them to shut down at the right time.
Solution Protocol
The protocol we have chosen here is the following:
- The manager walks the directory and sends blocks of file names to each worker
- Each file name is actually a tuple, defined as
- a full path, e.g. /media/dominique/3TB/mediawiki/images/wikipedia/commons/
- a short path, e.g. 0/0a
- a file name, e.g. someImage.png
- Each tuple is separated from the previous tuple by a '\n' character
- Each entry in a tuple is separated from the next entry by a '\t' character (tab)
- There is a \n and a \0 at the end of a block.
- A worker gets a block of N tuples from the manager. N is given by the user on the command line.
- With each tuple, the worker creates a full path of the image file, and calls identify to get the geometry as a width and a height
- It then inserts the information in the MySQL database: filename, short-path, width, height, scale
- The scale is currently 1.0 for all images.
Solution Source
Solution For 1 Manager + 1 Worker
// walkGetSizeAddMySql_Parallel_2nodes.c
// D. Thiebaut
// The background for this program can be found here:
// http://cs.smith.edu/dftwiki/index.php/Tutorial:_C_%2B_MySQL_%2B_MPI
//
// An MPI manager and n workers take a large number of images (3 million for
// the English wikipedia), computes their geometry with ImageMagick's
// identify utility, and enters the information in a table in a MySQL
// database.
//
// to Compile and Run:
//
// mpicc -o walkGetSizeAddMySql_Parallel_2nodes \
// $(mysql_config --cflags) walkGetSizeAddMySql_Parallel_2nodes.c \
// $(mysql_config --libs)
//
// mpirun -np 2 ./walkGetSizeAddMySql_Parallel_2nodes \
// /media/dominique/3TB/mediawiki/images/wikipedia/en/ 0/05 10
//
// 2 represents 1 manager + 1 worker.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <mysql.h>
#include <mpi.h>
#define MANAGER 0
#define WORKER 1
//--- Pair structure to pass width and height of image ---
typedef struct {
int width;
int height;
} Pair;
MYSQL *conn;
MYSQL_RES *res;
MYSQL_ROW row;
char *server = "localhost";
char *user = "352a";
char *password = "xxxxxxxxx";
char *database = "enwiki_images";
char *buffer;
int noFilesPerBlock = 1;
int debug = 1; // set to 1 to enter debugging mode
//--- Prototypes ---
void doManager( int N, char** argv );
void doWorker();
// getPrintTableNames: gets the name of the tables from the database
// Use for quick check.
void getPrintTableNames() {
conn = mysql_init(NULL);
//--- Connect to database ---
if (!mysql_real_connect(conn, server,
user, password, database, 0, NULL, 0)) {
fprintf(stderr, "mysql_real_connect error: %s\n", mysql_error(conn));
exit(1);
}
//--- send SQL query ---
if (mysql_query(conn, "show tables")) {
fprintf(stderr, "%s\n", mysql_error(conn));
exit(1);
}
res = mysql_use_result(conn);
//--- output table name ---
printf("MySQL Tables in mysql database:\n");
while ((row = mysql_fetch_row(res)) != NULL)
printf("%s \n", row[0]);
//--- close connection ---
mysql_free_result(res);
mysql_close(conn);
}
// insertFileInDatabase: insert file, path and geometry in the table
void insertFileInDatabase( char* filename, char* path, int width, int height, float scale ) {
char query[200];
char escapedFileName[300];
mysql_real_escape_string( conn, escapedFileName, filename, strlen( filename ) );
sprintf( query, "INSERT INTO images2 (name, path, width, height, scale1) VALUES ( '%s', '%s', %d, %d, %f )",
escapedFileName, path, width, height, scale );
int retCode = mysql_query( conn, query );
if ( retCode ) {
fprintf( stderr, "%s\n", mysql_error( conn ) );
exit( 1 );
}
}
// openDatabase: opens connection to database or exit in case of errors
void openDatabase() {
conn = mysql_init( NULL );
//--- Connect to database ---
if ( !mysql_real_connect( conn, server,
user, password, database, 0, NULL, 0 ) ) {
fprintf( stderr, "%s\n", mysql_error(conn) );
exit(1);
}
}
// closeDatabase: closes connection. No more queries after this call!
void closeDatabase() {
mysql_close( conn );
}
// getFileGeometry: uses ImageMagick to get the file geomery.
Pair getFileGeometry( char* fileName ) {
char command[100];
char buffer[1000];
FILE* fp;
Pair pair;
pair.width = 0;
pair.height = 0;
//--- create the command to issue ---
strcpy( command, "/usr/bin/identify -format \"%w %h\" \"" );
strcat( command, fileName );
strcat( command, "\"" );
//--- run the command and open a pipe to its output ---
if ( ( fp = popen( command, "r" ) ) != NULL ) {
while ( fgets( buffer, 1000, fp ) != NULL ) {
char *p = buffer;
while ( *p != ' ' )
p++;
*p = '\0';
//--- get the width and height ---
pair.width = atoi( buffer );
pair.height = atoi( p+1 );
}
}
pclose( fp );
return pair;
}
// getExtension: returns a pointer to the extension of the given file
const char *getExtension(const char *filename) {
const char *dot = strrchr(filename, '.');
if ( !dot || dot == filename )
return "";
return dot + 1;
}
// escapeString: escape special characters with a \ so that the name will
// be understood by the shell when executing the "identify" application.
void escapeString( char* name, char* escapedName ) {
char *p = name, *q = escapedName;
while ( *p != '\0' ) {
if ( *p == '\'' || *p == ';' || *p == '"' || *p == '(' || *p == ')'
|| *p == ' ' || *p == ',' || *p == ':' || *p == '&' ) {
//*(q++) = '\\';
//*(q++) = '\\';
*(q++) = '\\';
}
*(q++) = *(p++);
}
*q = '\0';
}
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// M A I N
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
int main( int argc, char **argv) {
int myId;
int noProcs;
if ( argc < 4 ) {
fprintf( stderr, "Syntax: ./walk path n/nn noFilesPerBlock" );
exit( 0 );
}
//--- start MPI ---
MPI_Init( &argc, &argv);
MPI_Comm_rank( MPI_COMM_WORLD, &myId );
MPI_Comm_size( MPI_COMM_WORLD, &noProcs );
//MPI_Get_processor_name( procName, &nameLen );
//--- get command line arguments, in particular block size ---
noFilesPerBlock = atoi( argv[3] );
buffer = (char *) malloc( noFilesPerBlock * 500 * sizeof( char ) );
if ( myId == MANAGER )
doManager( noFilesPerBlock, argv );
else
doWorker();
//--- close up MPI ---
MPI_Finalize();
free( buffer );
return 0;
}
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// doManager:
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void doManager( int N, char* argv[] ) {
DIR *dir;
char path[100];
char shortPath[10];
struct dirent *ent;
Pair pair;
char pathAndFileName[1000];
char escapedFileName[1000];
int count = 0;
int noEntries = 0;
int noChars;
int fileCount = 0;
//--- get command line arguments ---
strcpy( path, argv[1] );
strcpy( shortPath, argv[2] );
if ( path[ strlen( path )-1 ] != '/' )
strcat( path, "/" );
strcat( path, argv[2] );
//--- clear send buffer ---
buffer[0] = '\0';
//--- walk the directory ---
if ((dir = opendir ( path )) != NULL) {
//-- print all the files and directories within directory
while ((ent = readdir (dir)) != NULL) {
char* fileName = ent->d_name;
char extension[10];
strcpy( extension, getExtension( fileName ) );
//--- skip parent and current dirs ---
if ( !strcmp( fileName, "." ) || !strcmp( fileName, ".." ) )
continue;
//--- skip files that identify can't process ---
if ( !strcmp( extension, "ogg" ) ) continue;
if ( !strcmp( extension, "OGG" ) ) continue;
if ( !strcmp( extension, "svg" ) ) continue;
if ( !strcmp( extension, "SVG" ) ) continue;
if ( !strcmp( extension, "mid" ) ) continue;
if ( !strcmp( extension, "MID" ) ) continue;
//--- make file name safe for identify ---
escapeString( fileName, escapedFileName );
//--- create full path for image file ---
strcpy( pathAndFileName, "\"" );
strcat( pathAndFileName, path );
strcat( pathAndFileName, "/" );
strcat( pathAndFileName, escapedFileName );
strcat( pathAndFileName, "\"" );
noEntries++;
//--- add file, path, and short path to send buffer ---
strcat( buffer, pathAndFileName );
strcat( buffer, "\t" );
strcat( buffer, shortPath );
strcat( buffer, "\t" );
strcat( buffer, fileName );
strcat( buffer, "\n" );
//--- if the buffer is full, send it to the worker ---
fileCount++;
if ( fileCount >= noFilesPerBlock ) {
noChars = strlen( buffer ) + 1; // +1 to send the \0
MPI_Send( &noChars, 1, MPI_INT, WORKER, 123, MPI_COMM_WORLD );
MPI_Send( buffer, noChars, MPI_CHAR, WORKER, 123, MPI_COMM_WORLD );
buffer[0] = '\0';
fileCount = 0;
if ( debug )
break;
}
}
//--- send last buffer, which may not be full ---
if ( strlen( buffer ) > 1 ) {
noChars = strlen( buffer ) + 1; // +1 to send the \0
MPI_Send( &noChars, 1, MPI_INT, WORKER, 123, MPI_COMM_WORLD );
MPI_Send( buffer, noChars, MPI_CHAR, WORKER, 123, MPI_COMM_WORLD );
buffer[0] = '\0';
}
//--- send empty buffer ---
noChars = 1;
MPI_Send( &noChars, 1, MPI_INT, WORKER, 123, MPI_COMM_WORLD );
MPI_Send( buffer, noChars, MPI_CHAR, WORKER, 123, MPI_COMM_WORLD );
closedir(dir);
closeDatabase();
}
else {
//--- could not open directory ---
free( buffer );
perror ("");
exit( 1 );
}
printf( "Manager sent %d file(s) to worker(s)\n\n", noEntries );
}
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// doWorker
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void doWorker() {
char *p, // points to long path with file name
*q, // points to short path, e.g. 0/01
*r, // points to file name, e.g. aloa.png
*s; // points to \0 at end of record
MPI_Status status;
Pair pair;
char pathAndFileName[1000];
char shortPath[20];
char fileName[400];
int noChars;
//--- open access to database at beginning of work ---
openDatabase();
//--- forever, get a buffer, and process it ---
while ( 1 ) {
MPI_Recv( &noChars, 1, MPI_INT, MPI_ANY_SOURCE, 123, MPI_COMM_WORLD, &status );
MPI_Recv( buffer, noChars, MPI_CHAR, MPI_ANY_SOURCE, 123, MPI_COMM_WORLD, &status );
//--- stop if buffer is empty ---
if ( noChars <= 1 )
break;
p = buffer;
//--- scan the buffer and get each entry delimited by \n ---
while ( (s = strchr( p, '\n')) != NULL ) {
*s = '\0';
q = strchr( p, '\t' );
*q = '\0';
r = strchr( q+1, '\t' );
*r = '\0';
strcpy( pathAndFileName, p );
strcpy( shortPath, q+1 );
strcpy( fileName, r+1 );
if ( debug )
printf( "Worker: pathAnFileName: %s shortPath: %s fileName: %s\n",
pathAndFileName, shortPath, fileName );
pair = getFileGeometry( pathAndFileName );
if ( debug )
printf ( "Worker: %s\t\t\t%d %d\n", pathAndFileName, pair.width, pair.height );
//--- add info in database ---
insertFileInDatabase( fileName, shortPath, pair.width, pair.height, 1.0 );
p = s+1;
}
}
//--- close database ---
closeDatabase();
printf( "Worker done!\n" );
}
Solution for 1 Manager + (N-1) Workers
// walkGetSizeAddMySql_Parallel_Nnodes.c
// D. Thiebaut
// The background for this program can be found here:
// http://cs.smith.edu/dftwiki/index.php/Tutorial:_C_%2B_MySQL_%2B_MPI
//
// An MPI manager and n workers take a large number of images (3 million for
// the English wikipedia), computes their geometry with ImageMagick's
// identify utility, and enters the information in a table in a MySQL
// database.
//
// to Compile and Run:
//
// mpicc -o walkGetSizeAddMySql_Parallel_Nnodes \
// $(mysql_config --cflags) walkGetSizeAddMySql_Parallel_Nnodes.c \
// $(mysql_config --libs)
//
// mpirun -np 3 ./walkGetSizeAddMySql_Parallel_Nnodes \
// /media/dominique/3TB/mediawiki/images/wikipedia/en/ 0/05 10
//
// 3 represents 1 manager + 2 workers. Change to suit your needs.
//
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <mysql.h>
#include <mpi.h>
#define MANAGER 0 // the Id of the manager
//--- a data structure to implement a pair of ints ---
typedef struct {
int width;
int height;
} Pair;
//--- globals ---
int debug = 1; // if set to 1 the manager only
// sends 1 block of files to each worker
MYSQL *conn;
MYSQL_RES *res;
MYSQL_ROW row;
char *server = "localhost"; // mysql server and user info
char *user = "352a";
char *password = "xxxxx";
char *database = "enwiki_images";
char *myTable = "pics1"; // the table to use
char *buffer; // the buffer for exchanging data between
// manager and workers
int noFilesPerBlock; // number of files exchanged per block
int noProcs; // will be set by MPI to # of processes (manager + workers)
int myId; // the Id of the running process
//-------------- PROTOTYPES ------------------
void doManager( int N, char** argv );
void doWorker();
//------------------------------------------------------------------------
// insertFileInDatabase: takes the file name, its short path, its geometry and scale
// (which is normally 1) and inserts all this in 1 row of the table of the database.
void insertFileInDatabase( char* filename, char* path, int width, int height, float scale ) {
char query[200];
char escapedFileName[300];
mysql_real_escape_string( conn, escapedFileName, filename, strlen( filename ) );
sprintf( query, "INSERT INTO %s (name, path, width, height, scale1) VALUES ( '%s', '%s', %d, %d, %f )",
myTable, escapedFileName, path, width, height, scale );
int retCode = mysql_query( conn, query );
if ( retCode ) {
fprintf( stderr, "%s\n", mysql_error( conn ) );
exit( 1 );
}
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------
// openDatabase: what the name says!
void openDatabase() {
conn = mysql_init( NULL );
/* Connect to database */
if ( !mysql_real_connect( conn, server,
user, password, database, 0, NULL, 0 ) ) {
fprintf( stderr, "%s\n", mysql_error(conn) );
exit(1);
}
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------
// closeDatabase: what the name says!
void closeDatabase() {
mysql_close( conn );
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------
// getFileGeometry: runs the "identify" command that is part of ImageMagick
// and passes it the file name and path. Identify returns 2 numbers
// representing the width and height of the image in pixels. A pair
// containing (width, height) is returned.
Pair getFileGeometry( char* fileName ) {
char command[100];
char buffer[1000];
FILE* fp;
Pair pair;
pair.width = 0;
pair.height = 0;
strcpy( command, "/usr/bin/identify -format \"%w %h\" \"" );
strcat( command, fileName );
strcat( command, "\"" );
if ( ( fp = popen( command, "r" ) ) != NULL ) {
while ( fgets( buffer, 1000, fp ) != NULL ) {
//printf( "%s", buffer );
char *p = buffer;
while ( *p != ' ' )
p++;
*p = '\0';
pair.width = atoi( buffer );
pair.height = atoi( p+1 );
}
}
pclose( fp );
return pair;
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------
// getExtension: returns a pointer to the extension of the file.
const char *getExtension(const char *filename) {
const char *dot = strrchr(filename, '.');
if ( !dot || dot == filename )
return "";
return dot + 1;
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------
// escapeString: takes a string representing an image file name and
// escapes all the special characters (quotes, colons, parentheses, etc)
// by putting a backslash \ in front of them. The escaped name is copied
// in escapedName.
void escapeString( char* name, char* escapedName ) {
char *p = name, *q = escapedName;
while ( *p != '\0' ) {
if ( *p == '\'' || *p == ';' || *p == '"' || *p == '(' || *p == ')'
|| *p == ' ' || *p == ',' || *p == ':' || *p == '&' )
*(q++) = '\\';
*(q++) = *(p++);
}
*q = '\0'; // terminate string
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------
// badExtension: returns 1 if extension is not supported by identify.
int badExtension( char *extension ) {
if ( !strcmp( extension, "ogg" ) ) return 1;
if ( !strcmp( extension, "OGG" ) ) return 1;
if ( !strcmp( extension, "svg" ) ) return 1;
if ( !strcmp( extension, "SVG" ) ) return 1;
if ( !strcmp( extension, "mid" ) ) return 1;
if ( !strcmp( extension, "MID" ) ) return 1;
return 0;
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------
// M A I N
//------------------------------------------------------------------------
int main( int argc, char **argv) {
//--- check number of parameters passed on command line ---
if ( argc < 4 ) {
fprintf( stderr, "Syntax: ./walk path n/nn noFilesPerBlock" );
exit( 0 );
}
//--- start MPI ---
MPI_Init( &argc, &argv);
MPI_Comm_rank( MPI_COMM_WORLD, &myId );
MPI_Comm_size( MPI_COMM_WORLD, &noProcs );
//--- get parameters from command line ---
noFilesPerBlock = atoi( argv[3] );
//--- allocate a buffer big enough for all the files we need to send
//--- in each block
buffer = (char *) malloc( noFilesPerBlock * 500 * sizeof( char ) );
//--- split execution: manager or worker ---
if ( myId == MANAGER )
doManager( noFilesPerBlock, argv );
else
doWorker();
//--- close up MPI and release dynamic variables---
MPI_Finalize();
free( buffer );
return 0;
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------
// doManager: the manager walks the directory structure and passes blocks
// of file names to its workers. When done it sends an empty block to
// each worker to indicate the end of the parallel computation.
void doManager( int N, char* argv[] ) {
DIR *dir; // the directory to walk
char path[100]; // holds the path to the images
char shortPath[10]; // holds short paths of the form 0/0a
struct dirent *ent; // pointer to internal structure
Pair pair;
char pathAndFileName[1000]; // holds full path with file name
char escapedFileName[1000]; // holds escaped and shell-safe path
int count = 0; // counter
int totalNoFilesSent = 0; // number of files processed
int noChars; // number of chars in buffer sent to workers
int filesInBuffer = 0; // file counter
int currentWorker = 1; // Id of worker currently targetted
//--- generate full path from command line arguments ---
strcpy( path, argv[1] );
strcpy( shortPath, argv[2] );
if ( path[ strlen( path )-1 ] != '/' )
strcat( path, "/" );
strcat( path, argv[2] );
//--- clear buffer ---
buffer[0] = '\0';
//--- walk the directory defined by path ---
if ((dir = opendir ( path )) != NULL) {
while ((ent = readdir (dir)) != NULL) {
char* fileName = ent->d_name; // the image file name
char extension[10]; // its extension
//--- get file extension ---
strcpy( extension, getExtension( fileName ) );
//--- skip . and .. subdirs ---
if ( !strcmp( fileName, "." ) || !strcmp( fileName, ".." ) )
continue;
//--- skip files we know identify can't process ---
if ( badExtension( extension ) )
continue;
//--- copy fileName into escapedFileName and escape special chars ---
escapeString( fileName, escapedFileName );
//--- create full path with escaped file name for identify ---
strcpy( pathAndFileName, "\"" );
strcat( pathAndFileName, path );
strcat( pathAndFileName, "/" );
strcat( pathAndFileName, escapedFileName );
strcat( pathAndFileName, "\"" );
//--- total number of files processed ---
totalNoFilesSent++;
//-- copy path, short path, and file name in buffer for worker ---
strcat( buffer, pathAndFileName );
strcat( buffer, "\t" );
strcat( buffer, shortPath );
strcat( buffer, "\t" );
strcat( buffer, fileName );
strcat( buffer, "\n" );
//--- total number of files put in buffer ---
filesInBuffer++;
//--- time to send a block of files to worker? ---
if ( filesInBuffer >= noFilesPerBlock ) {
noChars = strlen( buffer ) + 1; // +1 to send the \0
//--- send buffer to current worker ---
MPI_Send( &noChars, 1, MPI_INT, currentWorker, 123, MPI_COMM_WORLD );
MPI_Send( buffer, noChars, MPI_CHAR, currentWorker, 123, MPI_COMM_WORLD );
//--- clear buffer and file counter ---
buffer[0] = '\0';
filesInBuffer = 0;
//--- rotate through all the workers ---
if ( ++currentWorker >= noProcs ) {
currentWorker = 1;
//--- if we're in debug mode we stop after having sent ---
//--- a buffer to each workier ---
if ( debug )
break;
}
}
}
//--- if there are a few files in buffer, send last buffer ---
if ( strlen( buffer ) > 1 ) {
noChars = strlen( buffer ) + 1; // +1 to send the \0
MPI_Send( &noChars, 1, MPI_INT, currentWorker, 123, MPI_COMM_WORLD );
MPI_Send( buffer, noChars, MPI_CHAR, currentWorker, 123, MPI_COMM_WORLD );
//printf( "Manager sent %d chars (last buffer) to worker %d\n", noChars, currentWorker );
buffer[0] = '\0';
}
//--- send empty buffer to all workers ---
for ( currentWorker = 1; currentWorker < noProcs; currentWorker++ ) {
noChars = 1;
MPI_Send( &noChars, 1, MPI_INT, currentWorker, 123, MPI_COMM_WORLD );
MPI_Send( buffer, noChars, MPI_CHAR, currentWorker, 123, MPI_COMM_WORLD );
//printf( "Manager sent %d chars (empty buffer) to worker %d\n", noChars, currentWorker );
}
closedir(dir);
}
else {
// could not open directory
perror ( "Aborting. Manager Could not open directory\n\n" );
}
printf( "Manager sent %d file(s) to worker(s)\n\n", totalNoFilesSent );
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------
// doWorker: gets buffers of image file names and paths from manager.
// take each one and identify it to get the geometry, then insert the
// resulting information in the MySQL database.
void doWorker() {
char *p, // points to long path with file name
*q, // points to short path, e.g. 0/01
*r, // points to file name, e.g. aloa.png
*s; // points to \0 at end of record
MPI_Status status;
Pair pair;
char pathAndFileName[1000];
char shortPath[20];
char fileName[400];
int noChars;
//--- open the database ---
openDatabase();
//--- keep on receiving buffers until we get an empty buffer ---
while ( 1 ) {
MPI_Recv( &noChars, 1, MPI_INT, MPI_ANY_SOURCE, 123, MPI_COMM_WORLD, &status );
MPI_Recv( buffer, noChars, MPI_CHAR, MPI_ANY_SOURCE, 123, MPI_COMM_WORLD, &status );
//--- if noChars is 1 then buffer contains only '\0', and it's time to stop ---
if ( noChars <= 1 )
break;
//--- put a pointer at front of buffer ---
p = buffer;
//--- buffer format is
// pathname \t short path \t file name \n
// pathname \t short path \t file name \n
// pathname \t short path \t file name \n
// ... \0
// we cut each triplet into individual strings and work with that ---
while ( (s = strchr( p, '\n')) != NULL ) {
*s = '\0';
q = strchr( p, '\t' );
*q = '\0';
r = strchr( q+1, '\t' );
*r = '\0';
strcpy( pathAndFileName, p );
strcpy( shortPath, q+1 );
strcpy( fileName, r+1 );
//--- get identify to recognize the file and get its geometry ---
pair = getFileGeometry( pathAndFileName );
//--- insert information in database ---
insertFileInDatabase( fileName, shortPath, pair.width, pair.height, 1.0 );
//--- point to next record in buffer ---
p = s+1;
}
}
//--- we're done! ---
//--- close database ---
closeDatabase();
printf( "Worker %d done!\n", myId );
}
Compile and Run
mpicc -o walkGetSizeAddMySql_Parallel_Nnodes $(mysql_config --cflags) \
walkGetSizeAddMySql_Parallel_Nnodes.c $(mysql_config --libs)
time mpirun -np 9 ./walkGetSizeAddMySql_Parallel_Nnodes \
/media/dominique/3TB/mediawiki/images/wikipedia/en/ \
0/05 25
Timing
Timing the effect of the parallelism provided by MPI on an 8-core AMD 3.0 GHz processor yields this data:
| # workers | block size (# files/block) |
real time | user time |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
512 |
1m3.438s |
0m59.860s |
|
2 |
256 |
0m32.077s |
0m31.064s |
|
4 |
128 |
0m17.145s |
0m17.012s |
|
8 |
64 |
0m7.781s |
0m8.256s |
|
16 |
32 |
0m5.022s |
0m7.176s |
Note that there is speedup as the number of workers increase, with a definite lower return on parallelism as soon as we pass 8 workers (which makes sense as we have only 8 cores).
The bash script used to generate the data is shown above:
#! /bin/bash
noWorkers=( 1 2 4 8 16 )
blockSize=( 512 256 128 64 32 )
dim=${#noWorkers[*]}
lastIndex=$(( $dim - 1 ))
for i in $(seq 0 $lastIndex) ; do
echo "$i noWorkers = ${noWorkers[i]} blockSize = ${blockSize[i]}"
n=${noWorkers[i]}
noNodes=$(( $n + 1 ))
time mpirun -np $noNodes \
./walkGetSizeAddMySql_Parallel_Nnodes /media/dominique/3TB/mediawiki/images/wikipedia/en/ \
0/05 ${blockSize[i]}
done



