CSC212 Midterm Exam Prep 2014
--D. Thiebaut (talk) 17:52, 7 October 2014 (EDT)
This is a sample of problems to get you ready for the midterm exam. The midterm will be closed-book, closed-computers, and on paper. You can see the answers to the questions by highlighting the white areas under each question.
Problem #1
- Fill in the spaces marked with ____ to complete the following Boolean expressions. Do not use the Boolean operator "!" in your answer. Write only in the spaces marked with ____.
- Assume that X, Y and Z are integer variables.
- Question 1
- Write the expression that is true if X is strictly the largest of the three variables X, Y and Z. For example, if X is 50, Y is 40 and Z is 45, the expression should be true, but if X is 50, Y is 40, and Z is 50, the expression should be false, since X is not strictly greater than Z.
(______) _____ (______)
(X > Y) && (X > Z)
Problem #2
- Assume that we have an array of ints, table, declared as follows:
int[] table = new int[] { 10, 20, 5, 15, 25, 0, 3 };
- Question 1
- Write the java code required to print all the elements of the array table.
for ( int i=0; i<table.length; i++ ) System.out.println( table[i] );
- Question 2
- write the java code required to find the largest element of table and print it on the screen.
int max=table[0];
for ( int i=1; i<table.length; i++ )
if (table[i]>max)
max = table[i];
System.out.println( max );
- Question 3
- write the java code required to replace all the 0 element of table with -1.
for ( int i=1; i<table.length; i++ )
if (table[i]==0) table[i] = -1;
Problem #3
Given this code, and assuming that the user enters the number 3 at the keyboard, followed by ENTER; what is the output of the program?
Scanner scan = new Scanner( System.in ); int n, k, max; max = scan.nextInt(); /* read value for max */ for (n = 0; n < max; n++) { for (k = 0; k < max; k++) { if (n > k) System.out.print(" G "); else if (n < k) System.out.print(" L "); else System.out.print(" E "); } System.out.println(); }
3
E L L
G E L
G G E
Problem #4
- Assume the ArrayList fibonacci is initialized as follows:
ArrayList fibonacci = new ArrayList(); fibonacci.add( 1 ); fibonacci.add( 1 );
- Question 1
- Write a for-loop that will compute 10 more fibonacci term and store them in the array.
for (int i=2; i<2+10; i++)
fibonacci.add( (int) fibonacci.get( i-1 ) + (int) fibonacci.get( i-2 ) );
- Question 2
- Same question, but using a LinkedList instead of an ArrayList.
LinkedList fibonacci = new LinkedList();
for (int i=2; i<2+10; i++)
fibonacci.add( (int) fibonacci.get( i-1 ) + (int) fibonacci.get( i-2 ) );
- ArrayList
- use add( Object o ) to add an element, and get( int index) to access an element at some location.
- LinkedList
- use add( Object o ) to add an element, and get( int index ) to access an element at some location.
Problem #5
- Question 1
- In a singly-linked list containing several thousands of items, do the remove-from-tail and the remove-from-front operations take the same amount of time to operate? Why or why not?
No, the remove from tail requires a loop to find the node that points to the last node in the list, so that the pointer tail can be moved to that one-before-last node. So the remove-from-tail requires looping thousands of time to get to the one-before-last node. Remove-from-front requires only a fixed number of operations.
Problem #6
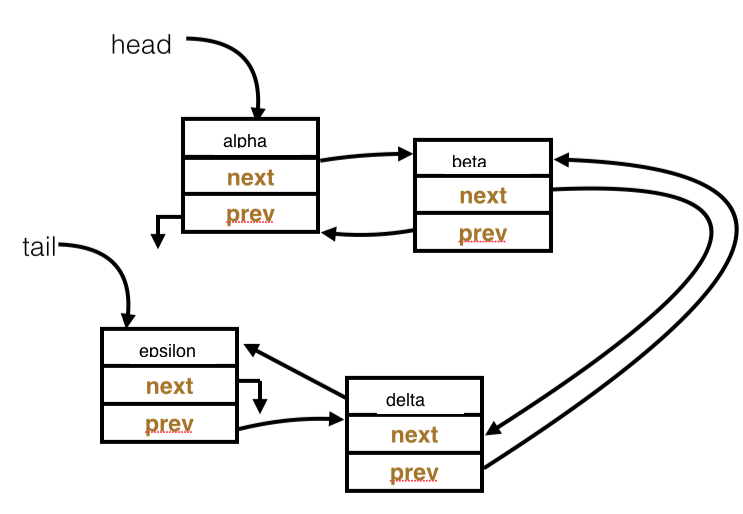
- Question 1
- Write the code necessary to remove the node containing the string "beta" from the list. The result should be a list containing the series "alpha", "delta", and "epsilon".
IntDLLNode temp = head.next;
head.next = temp.next;
temp.next.prev = head;
- Question 2
- Write the code that will print the contents of all the cells of a doubly-linked list, no matter how many nodes it contains.
IntDLLNode temp = head;
while ( temp != null ) {
System.out.println( temp.info );
temp = temp.next;
}
Problem #7
- Question 1
- What is a circular list?
See Section 3.3 in Drozdek
- Question 2
- What is a skip-list? What is its advantage?
See Section 3.4 in Drozdek