CSC212 Lab 13 2014
--D. Thiebaut (talk) 11:19, 17 November 2014 (EST)
Contents
Problem #1: DFS
- Create a new program called Graph1.java and copy the code from this page.
- Implement the DFS function, with the main function calling a recursive helper function.
- Question 1
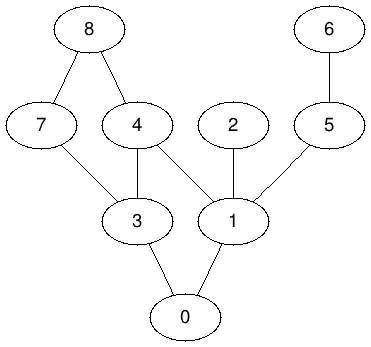
- Make your new DFS start with a vertex of your choice, and display all the vertices it visits. Below is an example of the output for G.DFS( 0 ).
DFS starting on 0: 0, 1, 2, 4, 3, 7, 8, 5, 6,
- Question 2
- Same question, but this time make DFS print the edges of the graph it visits. Below is an example of the output for G.DFS(0).
DFS starting on 0: visiting Edge (0)---(1) visiting Edge (1)---(2) visiting Edge (1)---(4) visiting Edge (4)---(3) visiting Edge (3)---(7) visiting Edge (7)---(8) visiting Edge (1)---(5) visiting Edge (5)---(6)
Problem #2: Connected Components
- A graph is connected if there is a path from any vertex to any other vertex in the graph.
- Create a new method called isConnected( ) that is based on DFS, and that returns true if the graph is connected, and false otherwise.
- The graph created by the init1() method is connected. You will need to add a new method called, say, init2() that initializes the graph with several disconnected components. (Hints: You can probably remove some edges from the graph generated by init1() to get a graph with several components!)
Problem #3: GraphViz & Dot
- Add a method to your graph that will print the graph in dot language, as we did with trees a while back.
- Here's the dot version of the graph generated by init1():
|
Problem 4
7-degrees of separation
Problem #3
All-Pairs Shortest Paths