CSC231 Logic Design Lab 2014
--D. Thiebaut (talk) 10:35, 19 November 2014 (EST)
Contents
Logic Design LAB
EXPERIMENT #1: INVESTIGATING THE KIT
Overview of the Kit

The main tools for us today are the switches, the LEDs, the +5 and GND wiring plots, and the breadboard area. You will put Integrated Circuits (ICs) on the breadboard area.
Exploration
For this part, concentrate only on the flatter part of the Digital Kit, not the vertical circuit board that is upright, facing you. Please follow the steps below.
- Power OFF. Always turn OFF the power when you are wiring circuits. This will prevent shorts and extend the life of your circuits.
- Connect a wire between the Logic Indicator L4 and the Logic Switch A.
- Power ON
- Activate Switch A, and observe the LED (Light Emitting Diode) turn ON and OFF.
- Power OFF
- Switch the wire from A to A-Bar, turn the power back ON, and see how the LED reacts .
- Same experiment, but this time replace the Logic Switch by one of the Data Switches.
- Power OFF.
- Connect one of the Logic Indicators to the Clock signal. Connect a second wire from another Logic Indicator to the Clock-bar signal. Make sure the sliding switch is on the 1Hz mark.
- Power UP. What do you observe?
- Slide the switch to 1KHz. What happens? Why? Is there any difference in the brightness of the LED? Why?
EXPERIMENT #2: INTEGRATED CIRCUITS AND LOGIC GATES
Below are the simplified data sheets for the Integrated Circuits you will use today.
|
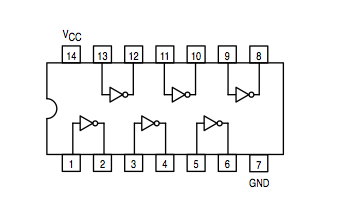
Inverter: 74LS04 | |
|
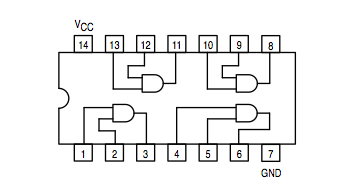
AND gate: 74LS08 | |
|
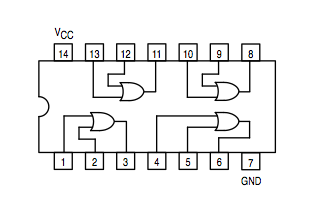
OR gate: 74LS32 | |
|
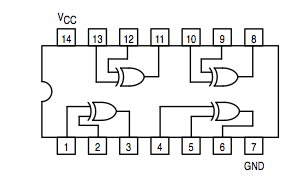
Exclusive OR: 74LS86 |
Note: The XOR is not a universal gate, but its function is encountered enough times in the real world that manufacturers have built a circuit just for this function. The equation for a XOR b is ( a and not b ) or ( not a and b), which can be implemented using the simple AND, OR, and NOT.
Testing
- Power OFF
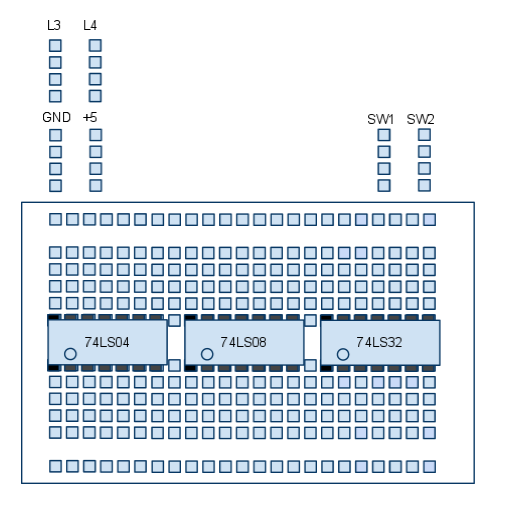
- Put a 74LS08 on the breadboard.
- Rule 1
- Always make sure the notch on the circuit is facing left. This way the circuit matches the diagram on the datasheets.
- Connect its pin 14 to +5V.
- Connect its pin 7 to GND.
- Rule 2
- Always make sure that the circuit is connected to +5V through its pin 14, and to GND via its pin 7.
- Connect Pin 1 to a data switch.
- Connect the Data Switch you just used to one of the Logic Indicators.
- Connect Pin 2 to a data switch.
- Connect the Data Switch you just used to another the Logic Indicators.
- Connect Pin 3 to a third Logic Indicator.
- Power ON
- Activate the different data switches.
- Verify that your circuit implements an AND boolean operator.
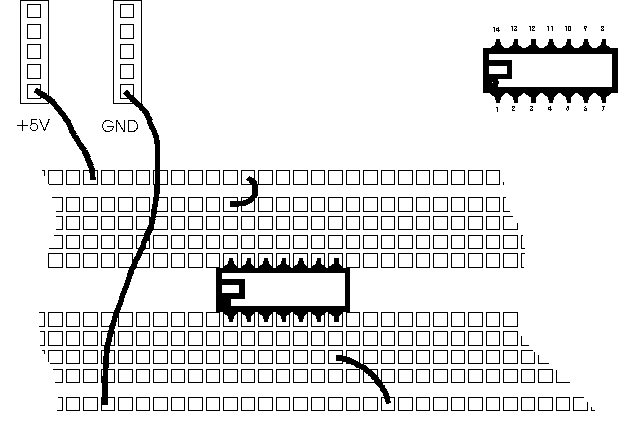
Figure 1:Wiring of an IC on the breadboard. Always identify pin 1 of the IC which is on the left (or below) the notch or circle embossed on the top of the chip
You may find the tables below useful for keeping notes of what is going on.
| Input 1 | Input 2 | Output |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
| 0 | 0 | |
| 0 | 1 | |
| 1 | 0 | |
| 1 | 1 |
| Input 1 | Input 2 | Output |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
| 0 | 0 | |
| 0 | 1 | |
| 1 | 0 | |
| 1 | 1 |
| Input 1 | Input 2 | Output |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
| 0 | 0 | |
| 0 | 1 | |
| 1 | 0 | |
| 1 | 1 |
2-Bit Adder
- We'll explore in class how to verify the property, both theoretically, on paper, and practically, using digital electronic circuits. The diagram below needs to be completed in class before wiring and testing.
Useful Boolean Axioms
- You may find these axioms useful in simplifying functions (taken from Wikipedia)
a OR (b OR c) = (a OR b) OR c a AND (b AND c) = (a AND b) AND c Associativity a OR b = b OR a a AND b = b AND a Commutativity a OR (a AND b) = a a AND (a OR b) = a Absorption a OR (b AND c) = (a OR b) AND (a OR c) a AND (b OR c) = (a AND b) OR (a AND c) Distributivity a OR NOT a = 1 a AND NOT a = 0 Complements
- Figure out how to test each axiom
- Divide the work to be done into tasks and assign each task to a group or to an individual
- Demonstrate to the class that the gates found in the integrated circuits used in the lab verify the axioms of the Boolean Algebra.