CSC270 Homework 3
© D. Thiebaut, 2009
Back to Weekly Schedule
This assignment is due on Wednesday evening, at the beginning of Lab 4.
Exercise 1
Assume that we have a boolean function f(a, b, c, d) = Σ( 5, 7, 15 ).
What is its minimal form, as given by a Karnaugh map?
Assume furthermore we know that the the signals a and b are never both equal to 1 at the same time, and that c and d are never both equal to 00 at the same time. So, for example, the signals a, b, c, d will never be in the state 1 1 0 1, because that would require a, and b to be 1. Similarly, the condition a = 0, b=1, c=0, d=0 will never occur either, because c and d are 0 in this case.
How can we use this information to our advantage, as logic designers?
Exercise 2
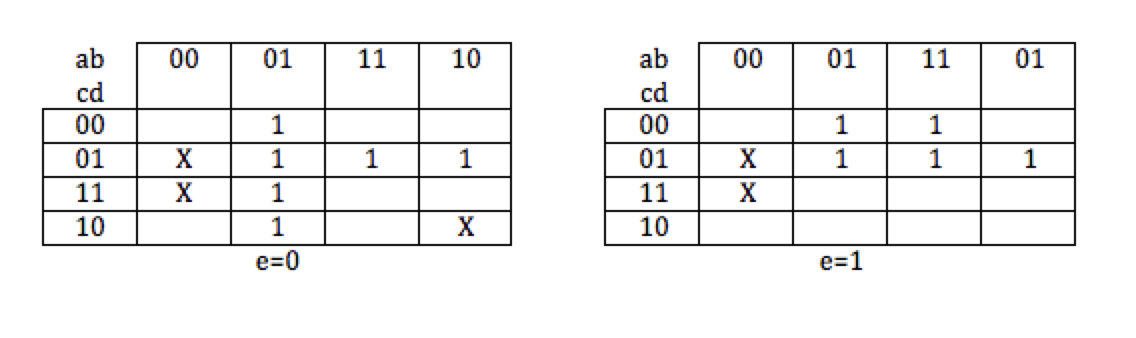
What is the simplified expression of the function g(a, b, c, d, e) expressed by the Karnaugh map above?
Exercise 3
Draw the logic diagram for the functions h() and k() below with 4-to-1 multiplexers:
- h( a, b, c, d ) = Σ( 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12, 14 )
- k( a, b, c ) = &Sigma( 0, 1, 2, 3, 7 )
Exercise 4
Draw the logic diagram of the same functions with 8-to-1 multiplexers.
Exercise 5
Same question as for Exercise 3, but this time we know that minterms m5, m7, m12, and m13 correspond to don't care conditions for the function h(), and that minterm m6 is a don't care condition for function k().
Exercise 6
Implement a 16-to-1 multiplexer with only 4-to-1 multiplexers.