Hadoop Tutorial 2.1 -- Streaming XML Files
|
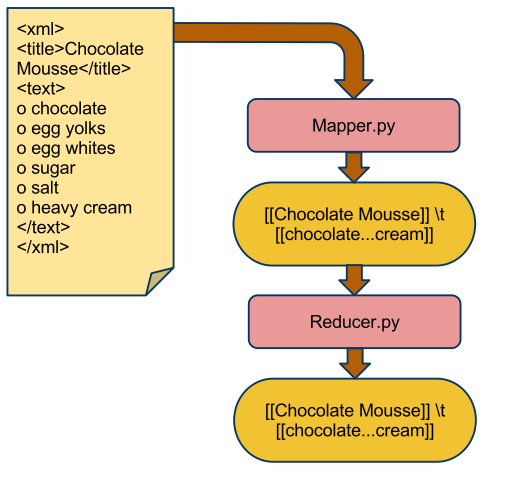
This tutorial is the continuation of Tutorial 2, and uses streaming to process XML files as a block. In this setup each Map task gets a whole xml file and breaks it down into tuples.
|
The Setup
The setup is simple:
- we have a lot of xml files, similar to the one shown above. They are delimited by <xml> and </xml> at the beginning and end of the contents.
- One field of interest is sandwiched between <title> tags
- The other field of interest is sandwiched between <text> tags.
- The mapper function (mapper.py) gets the whole file as input (as opposed as the default of feeding only one line of the file to the map function, as in the wordcount program of Tutorial 2).
- The mapper outputs a tuple with the title string as key and a shortened version of the text string as value.
- The reducer is the Identity function and outputs what it receives.
Input Files
- Set yourself up in a new directory
- Create a few files with the XML format shown above. Call them file1.xml, file2.xml and file3.xml.
- Create a subdirectory in your HDFS directory (we use dft here as the user directory. Adjust and replace with your own name/initials).
hadoop dfs -mkdir dft/xml
- Copy the xml files from local storage to HDFS
hadoop dfs -copyFromLocal file*.xml dft/xml
The Mapper program
Create a mapper.py program in your working directory.
#!/usr/bin/env python
# mapper.py
# D. Thiebaut
# takes a complete xml file, extract the title and
# text part of the file, and outputs a tuple
# <title \t text> where text is shortened to just a few
# characters.
import sys
list = []
title = "Unknown"
inText = False
for line in sys.stdin:
line = line.strip()
if line.find( "<title>" )!= -1:
title = line[ len( "<title>" ) : -len( "</title>" ) ]
if line.find( "<text>" ) != -1:
inText = True
continue
if line.find( "</text>" ) != -1:
inText = False
continue
if inText:
list.append( line )
text = ' '.join( list )
text = text[0:10] + "..." + text[-10:]
print '((%s))\t((%s))' % (title, text)
- Make it executable
chmod a+x mapper.py
Testing
- Test the mapper on one of the xml files:
cat file1.xml | mapper.py
- Verify that you get the correct title and shortened text.
The Reducer program
#!/usr/bin/env python
import sys
for line in sys.stdin:
line = line.strip()
title, page = line.split('\t', 1)
print '[[%s]]\t[[%s]]'% ( title, page[0:10]+"..."+page[-10:] )
- Create a file called reducer.py in your working directory with the code above.
- Make it executable
chmod a+x reducer.py
Testing
- Test it by feeding it the output of the mapper:
cat file1.xml | mapper.py | reducer.py
- Verify that you get the same output as the output of the mapper in the mapper test section above.
Running the Hadoop Streaming Program
- Run your hadoop streaming mapper/reducer pair, and specify that the RecordReader part of MapReduce stack should not feed one line at a time to the mapper, as done by default, but it should read the xml file and feed every character between xml and /xml.
hadoop jar /home/hadoop/hadoop/contrib/streaming/hadoop-0.19.2-streaming.jar \
-inputreader "StreamXmlRecordReader,begin=xml,end=/xml" \
-file ./mapper.py -mapper ./mapper.py \
-file ./reducer.py -reducer ./reducer.py \
-input dft/xml -output dft-out
- Remember to replace dft in the command above by your own initials/name!