CSC352 Homework 4 Solution
--D. Thiebaut 20:24, 25 April 2010 (UTC)
Contents
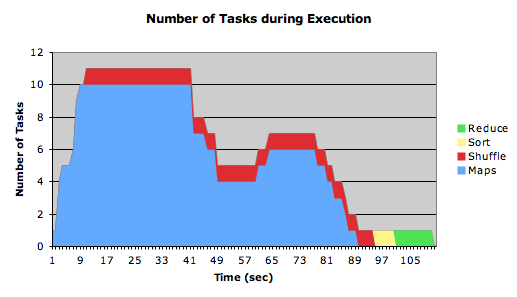
Problem #1: Timeline
Several observations were in order:
- The cluster only has 5 task-tracker nodes
- The default for Hadoop is two map tasks per task-tracker per job.
- This explains the maximum of 10 map tasks running first, then stopping, and then closing down, then 6 map tasks taking over, with an overlap of 4 map tasks.
- 4 files of approximately 180 MB comprise the input. Hadoop splits input files into splits of 64 MB.
- 180 MB will correspond to 3 or 4 splits, depending on the exact size of the file. This means between 12 to 16 splits for the 4 files.
Because we see that 16 (12+4) map tasks run altogether, we deduce that we had 16 splits total, requiring 16 tasks. 12 ran first, then were taken down while 4 more were started.
Problem #2: Unique Categories
Below is a Map/Reduce pair of Python streaming programs for a job similar to what was required. Instead of reporting the unique categories, the program return the categories and a list of Ids of wiki pages in which they appear.
Examples of output
category:(10th century in ireland) [10130001]category:(1976 films) [10000001] category:(argentine films) [10000001] category:(economy of côte d'ivoire) [10160001] category:(estuaries in england) [100001,200002] category:(hospitals in north carolina) [1010001] category:(lists of hospitals in the united states) [1010001]
Note that attempts to use regular expressions to grab strings in html tags were not successful. Even though the program ran fine in a serial form, from the command line, it wouldn't run to completion under Hadoop. Instead a simpler method of locating the position of the tags and splicing the string between the indexes was used. (Debugging parallel program has always been and still is a challenging task).
Mapper
hadoop@hadoop1:~/352/dft/hw4$ cat mapper_cat.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# mapper_cat.py
# D. Thiebaut
#
# parses a wiki page that is in xml format
# and included in <xml> ... </xml> tags.
# Example:
#
#<xml>
#<title>Breydon Water</title>
#<id>100001</id>
#<contributors>
#<contrib>
#<ip>89.240.43.102</ip>
#
#<length>3119</length></contrib>
#</contributors>
#<categories>
#<cat>Estuaries in England</cat>
#<cat>Ramsar sites in England</cat>
#<cat>Royal Society for the Protection of Birds reserves in England</cat>
#<cat>Norfolk Broads</cat>
#<cat>Sites of Special Scientific Interest in Norfolk</cat>
#</categories>
#<pagelinks>
#<page>Arthur Henry Patterson</page>
#<page>Arthur Ransome</page>
#<page>Avocets</page>
#<page>Bewick's Swan</page>
#</pagelinks>
#<text>
#Image. Breydon-north.jpg thumb 250px ... Broads . Category. Sites of Special Scientific Interest in Norfolk . . . .
#</text>
#</xml>
#
# the program outputs the categories
#
# cat 10000001.xml | ./mapper.py
#
#
# 1976 films 10000001
# Argentine films 10000001
# films 4 10000001
# category 3 10000001
# argentine 3 10000001
# 1976 3 10000001
# spanish 2 10000001
# language 2 10000001
# spanishlanguage 1 10000001
# que 1 10000001
# list 1 10000001
#
import sys
def grab( tag, xml ):
"""grabs the text between <tag> and </tag> in the xml text"""
try:
index1 = xml.find( '<%s>' % tag )
index2 = xml.find( '</%s>' % tag, index1 )
return xml[ index1+len( '<%s>' % tag ): index2 ]
except:
return ""
def grabAll( tag, xml ):
"""grabs all the strings between <tag> and </tag> in xml, and
returns them in a list"""
index2 = 0
list = []
while True:
index1 = xml.find( '<%s>' % tag, index2 )
if index1==-1: break
index2 = xml.find( '</%s>' % tag, index1 )
if index2==-1: break
list.append( xml[ index1+len( '<%s>' % tag): index2 ] )
return list
def processInput( debug=False ):
#--- accumulate input lines from stdin ---
xmlText = ""
for line in sys.stdin:
xmlText += line.lower()
#--- grag the Id, and the categories ---
id = grab( "id", xmlText )
categoryList = grabAll( "cat", xmlText )
return ( id, categoryList )
def main( debug=False ):
#--- get page Id, categories (if user wants them), and text ---
id, categoryList = processInput( debug )
for cat in categoryList:
print "%s\t%s" % ( cat, id )
#--- debugging information ---
if debug:
print "-"*60
print "DEBUG"
print "-"*60
print "id = ", id
for cat in categoryList:
print "cat:", cat
print "-"*60
main( False )
Reducer
#!/usr/bin/env python
import sys
#--- get ready to read category, Id pairs ---
lastCategory = None
listOfIds = []
#--- input comes from STDIN ---
for line in sys.stdin:
#--- remove leading and trailing whitespace ---
line = line.strip()
category, Id = line.split('\t', 1)
#--- accumulate Ids for the same category ---
if category==lastCategory:
listOfIds.append( Id )
else:
if lastCategory is not None:
print "category:(%s)\t[%s]" % ( lastCategory, ','.join( listOfIds ) )
lastCategory = category
listOfIds = [ Id ]
#--- write last category processed to stdout ---
if len( listOfIds )!= 0:
print 'category:(%s)\t[%s]' % ( lastCategory, ','.join( listOfIds ) )
Java Solution
Here's a java solution provided by Yang and Xiaoting.
/**
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
* or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
* distributed with this work for additional information
* regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
* to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
* "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
* with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.hadoop.hadoop;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
import java.util.regex.*;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configured;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.JobClient;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.JobConf;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.MapReduceBase;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.OutputCollector;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.Reporter;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.Tool;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.ToolRunner;
/**
* This is an example Hadoop Map/Reduce application.
* It reads the text input files, breaks each line into words
* and reports the number of unique categories and the number of times.
*
* To run: bin/hadoop jar build/hadoop-examples.jar catcount
* [-m <i>maps</i>] [-r <i>reduces</i>] <i>in-dir</i> <i>out-dir</i>
*/
public class CatCount extends Configured implements Tool {
/**
* define my own counters
*/
enum MyCounters {
MAPFUNCTIONCALLS,
REDUCEFUNCTIONCALLS,
BUCK
}
/**
* Counts the words in each line.
* For each line of input, break the line into words and emit them as
* (<b>word</b>, <b>1</b>).
*
*
*/
public static class MapClass extends MapReduceBase
implements Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable> {
private final static IntWritable one = new IntWritable(1);
private Text word = new Text();
public void map(LongWritable key, Text value,
OutputCollector<Text, IntWritable> output,
Reporter reporter) throws IOException {
// increment task counter
reporter.incrCounter( MyCounters.MAPFUNCTIONCALLS, 1 );
// use regex to match category name
Pattern p = Pattern.compile("<cat>([\\w\\s]*)</cat>");
Matcher m = p.matcher(value.toString());
while (m.find()){
word.set(m.group(1));
output.collect(word,one);
}
}
}
/**
* A reducer class that just emits the sum of the input values.
*/
public static class Reduce extends MapReduceBase
implements Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> {
public void reduce(Text key, Iterator<IntWritable> values,
OutputCollector<Text, IntWritable> output,
Reporter reporter) throws IOException {
// increment reduce counter
reporter.incrCounter( MyCounters.REDUCEFUNCTIONCALLS, 1 );
int sum = 0;
while (values.hasNext()) {
sum += values.next().get();
}
output.collect(key, new IntWritable(sum));
}
}
static int printUsage() {
System.out.println("catcount [-m <maps>] [-r <reduces>] <input> <output>");
ToolRunner.printGenericCommandUsage(System.out);
return -1;
}
/**
* The main driver for word count map/reduce program.
* Invoke this method to submit the map/reduce job.
* @throws IOException When there is communication problems with the
* job tracker.
*/
public int run(String[] args) throws Exception {
JobConf conf = new JobConf(getConf(), CatCount.class);
conf.setJobName("catcount");
// the keys are words (strings)
conf.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
// the values are counts (ints)
conf.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
conf.setMapperClass(MapClass.class);
conf.setCombinerClass(Reduce.class);
conf.setReducerClass(Reduce.class);
List<String> other_args = new ArrayList<String>();
for(int i=0; i < args.length; ++i) {
try {
if ("-m".equals(args[i])) {
conf.setNumMapTasks(Integer.parseInt(args[++i]));
} else if ("-r".equals(args[i])) {
conf.setNumReduceTasks(Integer.parseInt(args[++i]));
} else {
other_args.add(args[i]);
}
} catch (NumberFormatException except) {
System.out.println("ERROR: Integer expected instead of " + args[i]);
return printUsage();
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException except) {
System.out.println("ERROR: Required parameter missing from " +
args[i-1]);
return printUsage();
}
}
// Make sure there are exactly 2 parameters left.
if (other_args.size() != 2) {
System.out.println("ERROR: Wrong number of parameters: " +
other_args.size() + " instead of 2.");
return printUsage();
}
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(conf, other_args.get(0));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(conf, new Path(other_args.get(1)));
JobClient.runJob(conf);
return 0;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int res = ToolRunner.run(new Configuration(), new CatCount(), args);
System.exit(res);
}
}
Problem #3: Unique Words
Below is a pair of Map/Reduce programs for counting unique words in xml blocks.
Note that attempts to use regular expressions to grab strings in html tags were not successful. Instead a simpler method of locating the position of the tags and splicing the string between the indexes was used.
Mapper
#!/usr/bin/env python
# mapper_word.py
# D. Thiebaut
#
# parses a wiki page that is in xml format
# and included in <xml> ... </xml> tags.
# Example:
#
#<xml>
#<title>Breydon Water</title>
#<id>100001</id>
#<contributors>
#<contrib>
#<ip>89.240.43.102</ip>
#
#<length>3119</length></contrib>
#</contributors>
#<categories>
#<cat>Estuaries in England</cat>
#<cat>Ramsar sites in England</cat>
#<cat>Royal Society for the Protection of Birds reserves in England</cat>
#<cat>Norfolk Broads</cat>
#<cat>Sites of Special Scientific Interest in Norfolk</cat>
#</categories>
#<pagelinks>
#<page>Arthur Henry Patterson</page>
#<page>Arthur Ransome</page>
#<page>Avocets</page>
#<page>Bewick's Swan</page>
#</pagelinks>
#<text>
#Image. Breydon-north.jpg thumb 250px ... Broads . Category. Sites of Special Scientific Interest in Norfolk . . . .
#</text>
#</xml>
#
# the program outputs the five most frequent words.
#
# ivoire 2
#aquatic 5
# estuary 10
# photo 1
# rob 4
# years 1
import sys
import string
stopwords = {'all': 1, "she'll": 1, "don't": 1, 'being': 1, 'over': 1, 'through': 1, 'yourselves': 1, 'its': 1,
'before': 1, "he's": 1, "when's": 1, "we've": 1, 'had': 1, 'should': 1, "he'd": 1, 'to': 1,
'only': 1, "there's": 1, 'those': 1, 'under': 1, 'has': 1, "haven't": 1, 'do': 1, 'them': 1,
'his': 1, "they'll": 1, 'very': 1, "who's": 1, "they'd": 1, 'cannot': 1, "you've": 1, 'they': 1,
'not': 1, 'during': 1, 'yourself': 1, 'him': 1, 'nor': 1, "we'll": 1, 'did': 1, "they've": 1,
'this': 1, 'she': 1, 'each': 1, "won't": 1, 'where': 1, "mustn't": 1, "isn't": 1, "i'll": 1,
"why's": 1, 'because': 1, "you'd": 1, 'doing': 1, 'some': 1, 'up': 1, 'are': 1, 'further': 1,
'out': 1, 'what': 1, 'for': 1, 'while': 1, "wasn't": 1, 'does': 1, "shouldn't": 1, 'above': 1,
'between': 1, 'be': 1, 'we': 1, 'who': 1, "you're": 1, 'were': 1, 'here': 1, 'hers': 1, "aren't": 1,
'by': 1, 'both': 1, 'about': 1, 'would': 1, 'of': 1, 'could': 1, 'against': 1, "i'd": 1,
"weren't": 1, "i'm": 1, 'or': 1, "can't": 1, 'own': 1, 'into': 1, 'whom': 1, 'down': 1, "hadn't": 1,
"couldn't": 1, 'your': 1, "doesn't": 1, 'from': 1, "how's": 1, 'her': 1, 'their': 1, "it's": 1,
'there': 1, 'been': 1, 'why': 1, 'few': 1, 'too': 1, 'themselves': 1, 'was': 1, 'until': 1,
'more': 1, 'himself': 1, "where's": 1, "i've": 1, 'with': 1, "didn't": 1, "what's": 1, 'but': 1,
'herself': 1, 'than': 1, "here's": 1, 'he': 1, 'me': 1, "they're": 1, 'myself': 1, 'these': 1,
"hasn't": 1, 'below': 1, 'ought': 1, 'theirs': 1, 'my': 1, "wouldn't": 1, "we'd": 1, 'and': 1,
'then': 1, 'is': 1, 'am': 1, 'it': 1, 'an': 1, 'as': 1, 'itself': 1, 'at': 1, 'have': 1, 'in': 1,
'any': 1, 'if': 1, 'again': 1, 'no': 1, 'that': 1, 'when': 1, 'same': 1, 'how': 1, 'other': 1,
'which': 1, 'you': 1, "shan't": 1, ' ourselves': 1, 'our': 1, 'after': 1, "let's": 1, 'most': 1,
'ours ': 1, 'such': 1, 'on': 1, "he'll": 1, 'a': 1, 'off': 1, 'i': 1, "she'd": 1, 'yours': 1,
"you'll": 1, 'so': 1, "we're": 1, "she's": 1, 'the': 1, "that's": 1, 'having': 1, 'once': 1, 's':1}
def grab( tag, xml ):
"""grabs string between <tag> and </tag> in xml string"""
try:
index1 = xml.find( '<%s>' % tag )
index2 = xml.find( '</%s>' % tag )
return xml[ index1+len( '<%s>' % tag ): index2 ]
except:
return ""
def processInput( debug=False ):
#--- accumulate input lines from stdin ---
xmlText = ""
for line in sys.stdin:
xmlText += line.lower()
#--- grab text and Id from xml input ---
text = grab( "text", xmlText )
id = grab( "id", xmlText )
return ( id, text )
def getMostFreq( text, debug=False ):
"""computes 5 most frequent words"""
global stopwords
#--- remove punctuation (except quote) ---
table = string.maketrans( "", "" )
punctuation = '!"#$%&()*+,-./:;<=>?@[\\]^_`{|}~'
text = text.translate( table, punctuation )
words = text.lower().split()
wordDico = {}
for word in words:
#--- skip stop-words ---
if stopwords.has_key( word ):
continue
#--- accumulate count ---
if wordDico.has_key( word ):
wordDico[ word ] += 1
else:
wordDico[ word ] = 1
L = [ (freq,word) for (word,freq) in wordDico.items() ]
L.sort()
L = L[-10:]
L.reverse()
return L
def main( debug=False ):
#--- get Id and text from stdin ---
id, text = processInput( debug )
#--- output most frquent words, if requested for ---
mostFreqWords = getMostFreq( text, debug )
for freq, word in mostFreqWords:
print "%s\t%s" % ( word, freq )
#--- debugging information ---
if debug:
print "-"*60
print "DEBUG"
print "-"*60
print "id = ", id
print "text = ", text[0:20],"...", text[-20:]
print "mostFreqWords = ", mostFreqWords
print "-"*60
main( False )
Reducer
#!/usr/bin/env python
# reducer_word.py
#
import sys
# maps words to their counts
word2count = {}
# input comes from STDIN
for line in sys.stdin:
# remove leading and trailing whitespace
line = line.strip()
# parse the input we got from mapper.py
word, count = line.split('\t', 1)
# convert count (currently a string) to int
try:
count = int(count)
except ValueError:
continue
try:
word2count[word] = word2count[word]+count
except:
word2count[word] = count
# write the results to STDOUT (standard output)
for word in word2count.keys():
print '%s\t%s'% ( word, word2count[word] )
Slightly Different solution
This solution outputs tuples of the form:
... refer 1:1020001 breydon 11:200002,11:100001 water 8:200002,8:100001 que 1:10000001 article 2:10080001 ...
where the first part is a word, and the second part is a coma-separated list of count:Id, where count is the number of times the word appears in the <text></text> part of the Wiki-page with the given Id.
Mapper.py
hadoop@hadoop1:~/352/dft/hw4$ cat mapper_word2.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# mapper_word2.py
# D. Thiebaut
#
import sys
import string
stopwords = {'all': 1, "she'll": 1, "don't": 1, 'being': 1, 'over': 1, 'through': 1, 'yourselves': 1, 'its': 1,
'before': 1, "he's": 1, "when's": 1, "we've": 1, 'had': 1, 'should': 1, "he'd": 1, 'to': 1,
'only': 1, "there's": 1, 'those': 1, 'under': 1, 'has': 1, "haven't": 1, 'do': 1, 'them': 1,
'his': 1, "they'll": 1, 'very': 1, "who's": 1, "they'd": 1, 'cannot': 1, "you've": 1, 'they': 1,
'not': 1, 'during': 1, 'yourself': 1, 'him': 1, 'nor': 1, "we'll": 1, 'did': 1, "they've": 1,
'this': 1, 'she': 1, 'each': 1, "won't": 1, 'where': 1, "mustn't": 1, "isn't": 1, "i'll": 1,
"why's": 1, 'because': 1, "you'd": 1, 'doing': 1, 'some': 1, 'up': 1, 'are': 1, 'further': 1,
'out': 1, 'what': 1, 'for': 1, 'while': 1, "wasn't": 1, 'does': 1, "shouldn't": 1, 'above': 1,
'between': 1, 'be': 1, 'we': 1, 'who': 1, "you're": 1, 'were': 1, 'here': 1, 'hers': 1, "aren't": 1,
'by': 1, 'both': 1, 'about': 1, 'would': 1, 'of': 1, 'could': 1, 'against': 1, "i'd": 1,
"weren't": 1, "i'm": 1, 'or': 1, "can't": 1, 'own': 1, 'into': 1, 'whom': 1, 'down': 1, "hadn't": 1,
"couldn't": 1, 'your': 1, "doesn't": 1, 'from': 1, "how's": 1, 'her': 1, 'their': 1, "it's": 1,
'there': 1, 'been': 1, 'why': 1, 'few': 1, 'too': 1, 'themselves': 1, 'was': 1, 'until': 1,
'more': 1, 'himself': 1, "where's": 1, "i've": 1, 'with': 1, "didn't": 1, "what's": 1, 'but': 1,
'herself': 1, 'than': 1, "here's": 1, 'he': 1, 'me': 1, "they're": 1, 'myself': 1, 'these': 1,
"hasn't": 1, 'below': 1, 'ought': 1, 'theirs': 1, 'my': 1, "wouldn't": 1, "we'd": 1, 'and': 1,
'then': 1, 'is': 1, 'am': 1, 'it': 1, 'an': 1, 'as': 1, 'itself': 1, 'at': 1, 'have': 1, 'in': 1,
'any': 1, 'if': 1, 'again': 1, 'no': 1, 'that': 1, 'when': 1, 'same': 1, 'how': 1, 'other': 1,
'which': 1, 'you': 1, "shan't": 1, ' ourselves': 1, 'our': 1, 'after': 1, "let's": 1, 'most': 1,
'ours ': 1, 'such': 1, 'on': 1, "he'll": 1, 'a': 1, 'off': 1, 'i': 1, "she'd": 1, 'yours': 1,
"you'll": 1, 'so': 1, "we're": 1, "she's": 1, 'the': 1, "that's": 1, 'having': 1, 'once': 1, 's':1}
def grab( tag, xml ):
try:
index1 = xml.find( '<%s>' % tag )
index2 = xml.find( '</%s>' % tag )
return xml[ index1+len( '<%s>' % tag ): index2 ]
except:
return ""
def processInput( debug=False ):
#--- accumulate input lines from stdin ---
xmlText = ""
for line in sys.stdin:
xmlText += line.lower()
text = grab( "text", xmlText )
id = grab( "id", xmlText )
return ( id, text )
def getMostFreq( text, debug=False ):
global stopwords
table = string.maketrans( "", "" )
punctuation = '!"#$%&()*+,-./:;<=>?@[\\]^_`{|}~'
text = text.translate( table, punctuation )
words = text.lower().split()
wordDico = {}
for word in words:
if stopwords.has_key( word ):
continue
if wordDico.has_key( word ):
wordDico[ word ] += 1
else:
wordDico[ word ] = 1
L = [ (freq,word) for (word,freq) in wordDico.items() ]
L.sort()
L = L[-10:]
L.reverse()
return L
def main( debug=False ):
#--- get arguments from command line ---
Id, text = processInput( debug )
#--- output most frquent words, if requested for ---
mostFreqWords = getMostFreq( text, debug )
for freq, word in mostFreqWords:
print "%s\t%s %s" % ( word, freq, Id )
#--- debugging information ---
if debug:
print "-"*60
print "DEBUG"
print "-"*60
print "id = ", id
print "text = ", text[0:20],"...", text[-20:]
print "mostFreqWords = ", mostFreqWords
print "-"*60
main( False )
Reducer.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# reduce_word2.py
#
import sys
# maps words to their counts
word2count = {}
# input comes from STDIN
for line in sys.stdin:
# remove leading and trailing whitespace
line = line.strip()
# parse the input we got from mapper.py
word, pair = line.split('\t', 1)
count, id = pair.split()
try:
word2count[word].append( "%s:%s" % (count,id) )
except:
word2count[word] = [ "%s:%s" % (count,id) ]
# write the results to STDOUT (standard output)
for word in word2count.keys():
print '%s\t%s'% ( word, ",".join( word2count[word] ) )