Tutorial: Moodle VPL -- Testing a class with an derived class
--D. Thiebaut (talk) 18:13, 10 September 2014 (EDT)
This tutorial generates a VPL activity that allows automatic evaluation of a Java program with 1 class submitted by the student, which is derived from another class (given to the students, but not submitted by the students). The program is tested by a class provided by the instructor. This class outputs a series of lines. The vpl_run.sh script tests how many keywords appear in the output and decides on the correctness of the program from the number of keywords output, and not on the exact output by the student program.
Setup
- Moodle Version 2.7 + (Build: 20140529)
- VPL Version 3.0.1
- For details on how Moodle and VPL were installed, go to this page.
Requested File
- Only one: Snake.java, that's the file the student must submit.
Execution Files
vpl_run.sh
cat > vpl_execution << 'EOF'
#! /bin/bash
javac -J-Xmx128m *.java
java SnakeTest | grep "not adult" | wc -l
java SnakeTest | grep -v "not adult" | grep "adult" | wc -l
EOF
chmod +x vpl_execution
vpl_evaluate.cases
- The evaluation is really to check that the output will contain 6 keywords "not adult", and 4 keywords "adult".
case Test 1 output = "6 4 "
Animal.java
- The main class that the student class will inherit from should be included in the Execution Files section.
public class Animal { boolean isVaccinated; boolean isTattooed; String name; int age; Animal( String n, int a, boolean v, boolean t ) { name = n; age = a; isVaccinated = v; isTattooed = t; } public void displayBasicInfo( ) { String v = "vaccinated"; if ( !isVaccinated ) v = "not " + v; String t = "tattooed"; if ( !isTattooed ) t = "not " + t; System.out.print( String.format( "%s (%d), %s, %s", name, age, t, v ) ); } public static void main(String[] args) { Animal a = new Animal( "Max", 3, false, true ); a.displayBasicInfo(); System.out.println(); } }
SnakeTest.java
- This file must also be included in the Execution Files section. It contains a class that will inherit the class submitted by the student. It energizes all the features of the student's submitted class.
public class SnakeTest extends Snake { SnakeTest(String n, int a, boolean v, boolean t, int l, int temp) { super(n, a, v, t, l, temp); } public void displayBasicInfo() { String v = "vaccinated"; if (!isVaccinated) v = "not " + v; String t = "tattooed"; if (!isTattooed) t = "not " + t; System.out.print(String.format("%s (%d), %s, %s", name, age, t, v)); String adult; if (isAdult()) adult = "adult"; else adult = "not adult"; System.out.println(String.format( ", %d-inches long, best at %d degrees F, %s.", length, temperature, adult)); } public static void main(String[] args) { // create Snake object, named "python", not vaccinated or tattooed, // 50 inch long, and liking a temperature of 80 degrees F. SnakeTest s1 = new SnakeTest("python", 1, false, false, 50, 80); for (int year = 0; year < 10; year++) { s1.addLength(3); s1.displayBasicInfo(); } } }
Files to Keep When Running
- vpl_run.sh
- vpl_evaluate.cases
- Animal.java
- SnakeTest.java
Test Activity
- Click Edit and enter a solution program, extending the class Animal.
- Click on Run, and check the output:
6 4
- This is the correct output: 6 keywords of one type, 4 of another.
- Click on Evaluate:
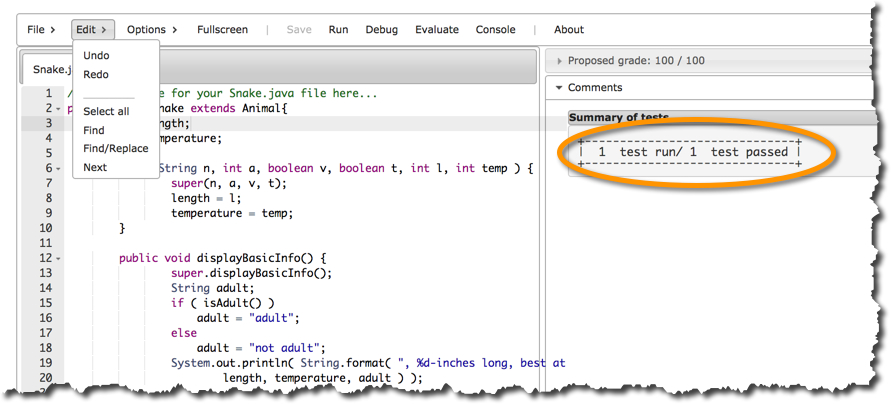
This concludes this tutorial.
