Tutorial: Using Tensorflow with Docker
--D. Thiebaut (talk) 22:42, 12 February 2017 (EST)
|
|
These are very quick instructions for installing Docker under Mac OSX and for running Tensorflow on it. This is a summarized version of the longer explanations given on the official TensorFlow Install page:
and the Docker Install page:
Install Docker
- Go there: https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-mac/
- Download
- Click on the package (do not worry about the warning)
Run Docker
- Find Docker in the Applications and run it
- It will open a Terminal window
- Note the IP that is specified at the end (should be http://192.168.99.100/)
## . ## ## ## == ## ## ## ## ## === /"""""""""""""""""\___/ === ~~~ {~~ ~~~~ ~~~ ~~~~ ~~~ ~ / ===- ~~~ \______ o __/ \ \ __/ \____\_______/ docker is configured to use the default machine with IP 192.168.99.100 For help getting started, check out the docs at https://docs.docker.com
docker is configured to use the default machine with IP 192.168.99.100 For help getting started, check out the docs at https://docs.docker.com
- Quick Docker by pressing Ctrl-C twice and return to the command line
Install TensorFlow "in" Docker
- Run the following command at the prompt, in the same Terminal session:
docker run -it -p 8888:8888 gcr.io/tensorflow/tensorflow
- This will download tensorflow and will take a few minutes (~ 8 minutes)
- Make a note of the URL that is given. It will be of the form:
http://localhost:8888/tree?token=someLongSeriesOfHexadecimalDigits
Create a Script to Start Docker Automatically
If you are using a Mac or Linux machine, create a script called startDocker.sh in your bin directory:
#! /bin/bash docker run -it -p 8888:8888 gcr.io/tensorflow/tensorflow
Make your script executable:
chmod +x startDocker.sh
Start Jupiter
Jupiter is an application that runs in a browser and presents the user a virtual disk where the user can create folders and write programs.
- To start the Jupiter connected to Docker, open your browser and enter the URL that was given to you in the previous step.
http://localhost:8888/tree?token=someLongSeriesOfHexadecimalDigits
- If you get an error message, replace localhost by the IP given next to the whale logo, above (I got 192.168.99.100 when I started Docker).
http://192.168.99.100:8888/tree?token=someLongSeriesOfHexadecimalDigits
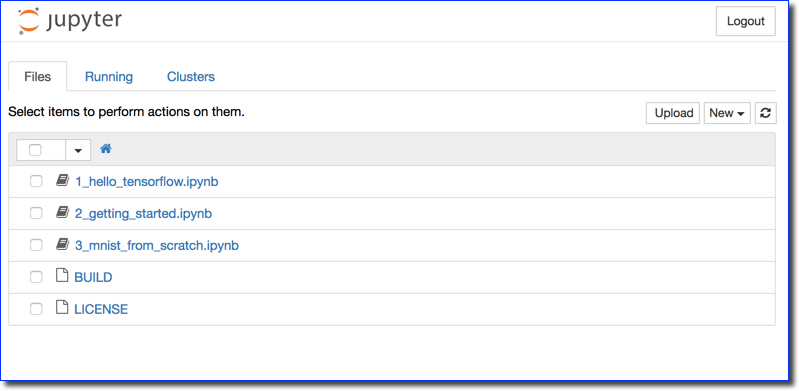
- You should end up with a window similar to this one:
- Double-click on the 1_hello_tensorflow.ipynb Jupiter notebook to open it.
- You may get an error when the notebook opens. Just click on Cell then Run All to get rid of the error.
- If the page appears without errors, then all the Tensorflow mini-programs will have run without errors, and you're all set!
Using Jupiter
Hello TensorFlow!
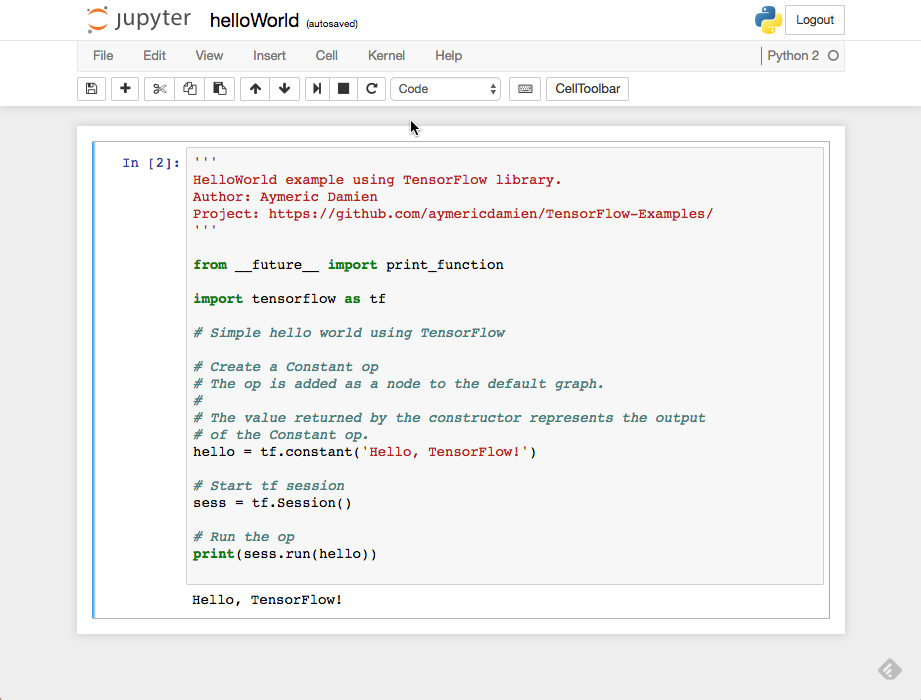
In Jupyter, create a new notebook, and paste the following code into it:
''' HelloWorld example using TensorFlow library. Author: Aymeric Damien Project: https://github.com/aymericdamien/TensorFlow-Examples/ ''' from __future__ import print_function import tensorflow as tf # Simple hello world using TensorFlow # Create a Constant op # The op is added as a node to the default graph. # # The value returned by the constructor represents the output # of the Constant op. hello = tf.constant('Hello, TensorFlow!') # Start tf session sess = tf.Session() # Run the op print(sess.run(hello))
- Click on Cell, Run Cells. You should see the "Hello TensorFlow! message appear on the page.
- Your installation of TensorFlow works!
Quick Tutorial on how to use Jupyter
- Here's a quick tutorial on using the Jupyter dashboard.