Difference between revisions of "Hadoop Tutorial 4: Start an EC2 Instance"
(→Steps) |
(→References) |
||
| (18 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | =References= | ||
| + | |||
| + | * A good description for reserving and connecting an AMI from the terminal window using the ec2-tools can be found here: [http://docs.amazonwebservices.com/AWSEC2/2008-08-08/GettingStartedGuide/index.html?running-an-instance.html#authorizing-access-to-an-instance docs.amazonwebservices.com]. | ||
| + | * Alternatively, you can also try this page: [http://paulstamatiou.com/how-to-getting-started-with-amazon-ec2 paulstamatiou.com]. | ||
=Method #1: Using the AWS Console= | =Method #1: Using the AWS Console= | ||
| Line 17: | Line 22: | ||
The steps are fairly simple: | The steps are fairly simple: | ||
| − | * Connect to the AWS console, and then select Amazon EC2 | + | ===Launch instance from AWS console=== |
| − | * Click on '''Launch | + | * Connect to the AWS console (see [[Hadoop Tutorial 3 -- Hadoop on Amazon AWS | Tutorial 3]] for a reminder), and then select Amazon EC2. |
| + | * In the QuickStart tab, pick "Fedora LAMP Server", as a machine to instantiate. | ||
| + | * Select 1 instance, pick the architecture of your choice, and '''No Preference''' for the zone. | ||
| + | * Select '''Launch Instance''' (''Spot Instances'' are low-rate machines that run only when the demand is low, and the user pays less). | ||
| + | * Click on '''Continue''' (make sure your browser window is large enough to see the bottom part of the pop-up!) | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <center>[[Image:AWS_StartNewEC2Instance.png | 500px]]</center> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | * Use defaults for '''Kernel Id''' and '''RamDisk Id'''. | ||
| + | * '''No Monitoring''' | ||
| + | * Click on '''Continue''' | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <center>[[Image:AWS_CreateKeyPairForEC2.png | 500px]]</center> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | * Pick a name for your key-pair file (e.g. ''dftKeyPair''), then click on '''Create New Key Pair'''. | ||
| + | * When prompted, '''save''' the key-pair file (''dftKeyPair.pem'') to a local directory on your computer (Desktop, for example). | ||
| + | * Follow the directions to create a security group (I called it ''dftGroup'' for simplicity). | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <center>[[Image:AWS_SecurityGroupForEC2.png | 500px]]</center> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | * '''Review!''' | ||
| + | <center>[[Image:AWS_ReviewEC2Instance.png | 500px]]</center> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''Launch!''' | ||
| + | * '''Watch''' as the instance is created, and loads up... | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <center>[[Image:AWS_watchingInstanceLaunch.png|500px]]</center> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | |||
* When the instance is created, right click on it and click on '''Connect''' | * When the instance is created, right click on it and click on '''Connect''' | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
[[Image:ConnectToInstanceOnEC2.png | 300px]] | [[Image:ConnectToInstanceOnEC2.png | 300px]] | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Connecting using SSH=== | ||
| + | * First create a working directory '''on your local computer''' (I'll assume you are using a Mac or a Linux box. Similar steps are easy to take for Windows) | ||
| + | * Start a Terminal window | ||
| + | * create a new working directory and copy the Key-Pair file into it: | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''cd /''' | ||
| + | '''mkdir aws''' | ||
| + | '''cd aws''' | ||
| + | '''cp ~/Desktop/dftKeyPair.pem .''' | ||
| + | '''chmod go-r dftKeyPair.pem''' | ||
| + | '''ls -l ''' | ||
| + | total 8 | ||
| + | -rw-------@ 1 thiebaut wheel 1693 Apr 22 08:25 dftKeyPair.pem | ||
* Copy/Paste the ssh command into a shell that you will have started | * Copy/Paste the ssh command into a shell that you will have started | ||
| − | ssh -i | + | ssh -i dftKeyPair.pem root@ec2-75-101-234-143.compute-1.amazonaws.com |
| + | |||
| + | * You should be connected! | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''ssh -i dftKeyPair.pem root@ec2-75-101-234-143.compute-1.amazonaws.com''' | ||
| + | The authenticity of host 'ec2-75-101-234-143.compute-1.amazonaws.com... | ||
| + | RSA key fingerprint is cd:79:eb:e5:e9:2e:d6:a2:9c:... | ||
| + | Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? '''yes''' | ||
| + | Warning: Permanently added 'ec2-75-101-234-143.compute-1.amazonaws.com,7... | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | __| __|_ ) Fedora 8 | ||
| + | _| ( / 32-bit | ||
| + | ___|\___|___| | ||
| + | |||
| + | Welcome to an EC2 Public Image | ||
| + | :-) | ||
| + | |||
| + | Base | ||
| + | |||
| + | --[ see /etc/ec2/release-notes ]-- | ||
| + | |||
| + | [root@ip-10-244-181-219 ~]# | ||
| − | * | + | * You are now '''root''' of a machine on Amazon's cloud. Play with it! |
| − | * | + | * Check that the mysql server is working: |
| − | + | ||
| − | * | + | [root@ip-10-244-181-219 ~]# '''mysql''' |
| − | * | + | Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. |
| + | Your MySQL connection id is 2 | ||
| + | Server version: 5.0.45 Source distribution | ||
| + | |||
| + | Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the buffer. | ||
| + | |||
| + | mysql> '''show databases;''' | ||
| + | +--------------------+ | ||
| + | | Database | | ||
| + | +--------------------+ | ||
| + | | information_schema | | ||
| + | | mysql | | ||
| + | | test | | ||
| + | +--------------------+ | ||
| + | 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) | ||
| + | |||
| + | mysql> '''quit''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Add a new user | ||
| + | |||
| + | [root@ip-10-244-181-219 ~]# '''adduser thiebaut''' | ||
| + | [root@ip-10-244-181-219 ~]# '''ls /home''' | ||
| + | thiebaut webuser | ||
| + | [root@ip-10-244-181-219 ~]# | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Installing Software=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Try editing a file with emacs... | ||
| + | * Oops, emacs is not installed on the EC2 Instance. No big deal, we can install it. The installation package under Fedora is called '''yum''': | ||
| + | |||
| + | yum -y install emacs | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Now try editing with emacs... :-) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <greenbox> | ||
| + | [[Image:ComputerLogo.png|right |100px]] | ||
| + | ;Lab Experiment #1: | ||
| + | : Run the multiprocessing version of the NQueens program on your new Instance and compare its execution time to the best time obtained so far. | ||
| + | |||
| + | : The multiprocessing version of the N-Queens program is available [[CSC352_multiprocessingNQueens.py | here]]. An easy way to time the execution of multiple runs would be: | ||
| + | |||
| + | ::<tt>for i in {15..21} ; do echo -n $i<br /> /usr/bin/time python2.6 multiprocessingNQueens.py $i 2>&1 | grep real<br /> done</tt> | ||
| + | |||
| + | : You will discover that the multiprocessing python module runs only with Python 2.6! So you'll have to install it before running the program. The steps are simple: | ||
| + | :* install gcc first | ||
| + | :* download the source code for Python2.6 | ||
| + | :* untar it into a directory | ||
| + | :* compile it | ||
| + | :* install it | ||
| + | |||
| + | : These steps are shown below | ||
| + | |||
| + | ::<tt> yum -y install gcc </tt> | ||
| + | ::<tt> wget http://www.python.org/ftp/python/2.6.5/Python-2.6.5.tgz</tt> | ||
| + | ::<tt> tar -xzvf Python-2.6.5.tgz</tt> | ||
| + | ::<tt> cd Python-2.6.5</tt> | ||
| + | ::<tt> ./configure</tt> | ||
| + | ::<tt> make</tt> | ||
| + | ::<tt> make install</tt> | ||
| + | |||
| + | : You should have python 2.6 available to you. To invoke it, simply use '''python2.6''' at the command line. | ||
| + | </greenbox> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
=Method #2: Using the EC2 Tools= | =Method #2: Using the EC2 Tools= | ||
| Line 69: | Line 204: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
Latest revision as of 15:24, 22 July 2011
--D. Thiebaut 16:01, 18 April 2010 (UTC)
|
Creating an EC2 Instance refers to the action of starting a server on Amazon using one's credential, and then connecting to it using ssh. |
References
- A good description for reserving and connecting an AMI from the terminal window using the ec2-tools can be found here: docs.amazonwebservices.com.
- Alternatively, you can also try this page: paulstamatiou.com.
Method #1: Using the AWS Console
Steps
The steps are fairly simple:
Launch instance from AWS console
- Connect to the AWS console (see Tutorial 3 for a reminder), and then select Amazon EC2.
- In the QuickStart tab, pick "Fedora LAMP Server", as a machine to instantiate.
- Select 1 instance, pick the architecture of your choice, and No Preference for the zone.
- Select Launch Instance (Spot Instances are low-rate machines that run only when the demand is low, and the user pays less).
- Click on Continue (make sure your browser window is large enough to see the bottom part of the pop-up!)
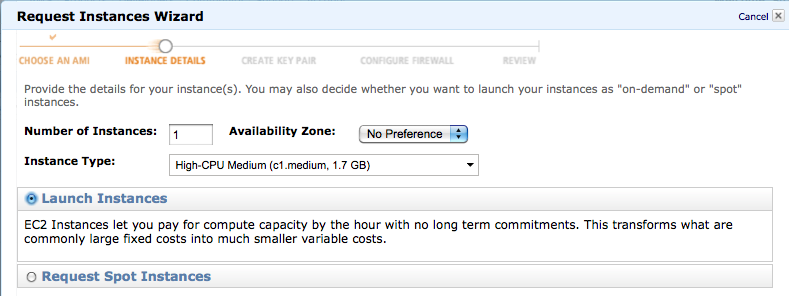
- Use defaults for Kernel Id and RamDisk Id.
- No Monitoring
- Click on Continue
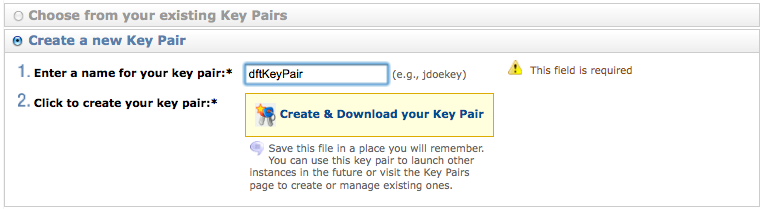
- Pick a name for your key-pair file (e.g. dftKeyPair), then click on Create New Key Pair.
- When prompted, save the key-pair file (dftKeyPair.pem) to a local directory on your computer (Desktop, for example).
- Follow the directions to create a security group (I called it dftGroup for simplicity).
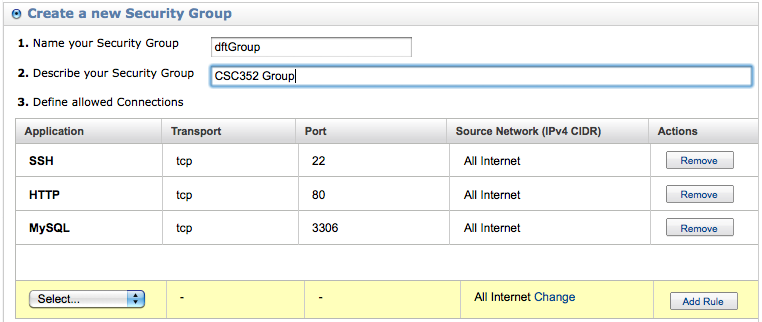
- Review!
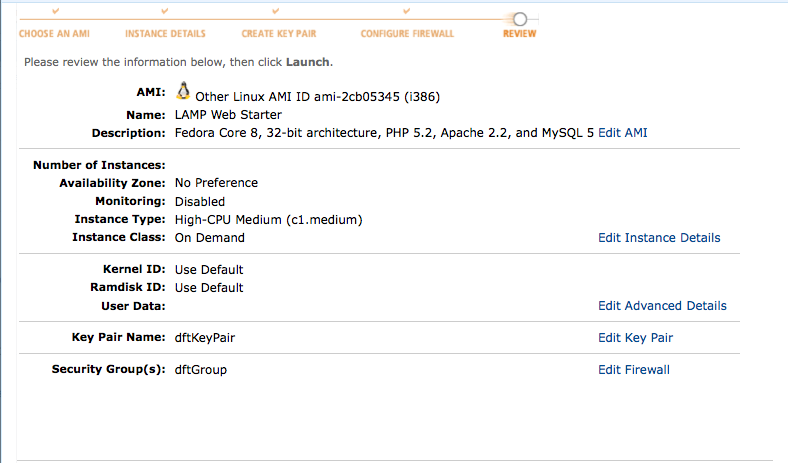
- Launch!
- Watch as the instance is created, and loads up...
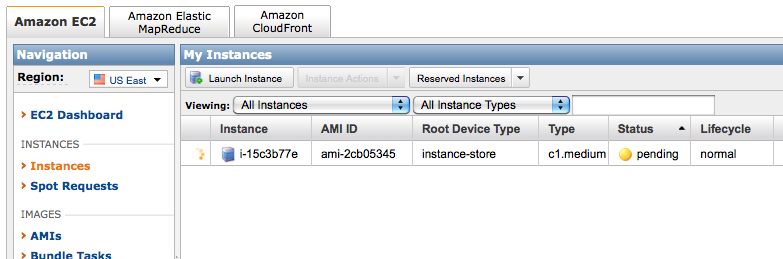
- When the instance is created, right click on it and click on Connect
Connecting using SSH
- First create a working directory on your local computer (I'll assume you are using a Mac or a Linux box. Similar steps are easy to take for Windows)
- Start a Terminal window
- create a new working directory and copy the Key-Pair file into it:
cd / mkdir aws cd aws cp ~/Desktop/dftKeyPair.pem . chmod go-r dftKeyPair.pem ls -l total 8 -rw-------@ 1 thiebaut wheel 1693 Apr 22 08:25 dftKeyPair.pem
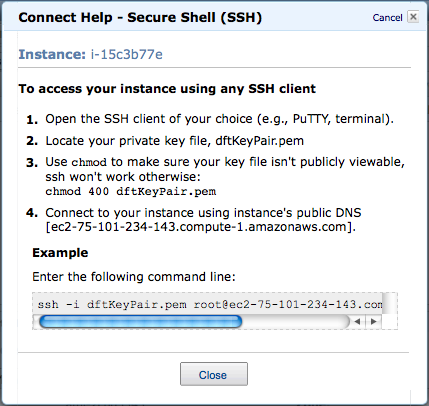
- Copy/Paste the ssh command into a shell that you will have started
ssh -i dftKeyPair.pem root@ec2-75-101-234-143.compute-1.amazonaws.com
- You should be connected!
ssh -i dftKeyPair.pem root@ec2-75-101-234-143.compute-1.amazonaws.com
The authenticity of host 'ec2-75-101-234-143.compute-1.amazonaws.com...
RSA key fingerprint is cd:79:eb:e5:e9:2e:d6:a2:9c:...
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
Warning: Permanently added 'ec2-75-101-234-143.compute-1.amazonaws.com,7...
__| __|_ ) Fedora 8
_| ( / 32-bit
___|\___|___|
Welcome to an EC2 Public Image
:-)
Base
--[ see /etc/ec2/release-notes ]--
[root@ip-10-244-181-219 ~]#
- You are now root of a machine on Amazon's cloud. Play with it!
- Check that the mysql server is working:
[root@ip-10-244-181-219 ~]# mysql Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MySQL connection id is 2 Server version: 5.0.45 Source distribution Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the buffer. mysql> show databases; +--------------------+ | Database | +--------------------+ | information_schema | | mysql | | test | +--------------------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> quit
- Add a new user
[root@ip-10-244-181-219 ~]# adduser thiebaut [root@ip-10-244-181-219 ~]# ls /home thiebaut webuser [root@ip-10-244-181-219 ~]#
Installing Software
- Try editing a file with emacs...
- Oops, emacs is not installed on the EC2 Instance. No big deal, we can install it. The installation package under Fedora is called yum:
yum -y install emacs
- Now try editing with emacs... :-)
 |  | |
| ||
 |  |
Method #2: Using the EC2 Tools
Steps
- Download the EC2 Tools from the Amazon EC2 Resource Center.
- install them in ~/bin/ec2-api-tools (see the Getting Started Guide from Amazon for more info).
- Download the pem files containing your private key and certificate from the Amazon EC2 page (see step above)
- Modify your .bash_profile file and set several variables:
PATH=$PATH:/Users/thiebaut/bin/ec2-api-tools/bin # Amazon AWS/EC2 tools export EC2_HOME=/Users/thiebaut/bin/ec2-api-tools export JAVA_HOME=/System/Library/Frameworks/JavaVM.framework/Home export EC2_PRIVATE_KEY=~/.ssh/pk-WMW2M4ZVFMCZJXSXJN4D7ZS4RMTBJ7VV.pem export EC2_CERT=~/.ssh/cert-WMW2M4ZVFMCZJXSXJN4D7ZS4RMTBJ7VV.pem
- Source the .bash_profile file
source .bash_profile
- Test the ec2 tools:
ec2-describe-images -a | grep hadoop-ec2-images
- verify that a list of images is printed out.
IMAGE ami-ee53b687 hadoop-ec2-images/hadoop-0.17.0-i386.manifest.xml 111560892610 available public i386 machine aki-a71cf9ce ari-a51cf9cc instance-store IMAGE ami-f853b691 hadoop-ec2-images/hadoop-0.17.0-x86_64.manifest.xml 111560892610 available public x86_64 machine aki-b51cf9dc ari-b31cf9da instance-store