Difference between revisions of "CSC111 Homework 12 2015"
(→Problem #2) |
|||
| Line 64: | Line 64: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| + | <showafterdate after="20150422 14:00" before="20150601 00:00"> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | =Solution Programs= | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | ==Fractal Tree== | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <source lang="python"> | ||
| + | # fractalTree.py | ||
| + | # D. Thiebaut | ||
| + | # Code taken from http://openbookproject.net/thinkcs/python/english3e/recursion.html | ||
| + | # and adapted to work with graphics111.py. | ||
| + | # | ||
| + | # Draws a fractal tree on the graphic window. | ||
| + | # | ||
| + | from graphics import * | ||
| + | import math | ||
| + | import time | ||
| + | import random | ||
| + | |||
| + | # dimensions of the window | ||
| + | MAXWIDTH = 800 | ||
| + | MAXHEIGHT = 800 | ||
| + | |||
| + | # recursive tree-drawing function | ||
| + | # | ||
| + | def draw_tree(win , # the canvas | ||
| + | order, # the level of recursion. Starts positive. | ||
| + | theta, # angle of new branch leaving this trunk | ||
| + | sz, # size of this branch | ||
| + | x, y, # coordinates of base of this branch | ||
| + | heading, # angle of direction of this branch | ||
| + | color # color | ||
| + | ): | ||
| + | |||
| + | trunk_ratio = 0.29 # How big is the trunk relative to whole tree? | ||
| + | trunk = sz * trunk_ratio # length of trunk | ||
| + | |||
| + | # compute x, y of end of the current branch | ||
| + | delta_x = trunk * math.cos(heading) | ||
| + | delta_y = trunk * math.sin(heading) | ||
| + | x2, y2 = x + delta_x, y + delta_y | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | # draw current branch | ||
| + | branch = Line( Point( x, y), Point( x2, y2 ) ) | ||
| + | branch.setFill( color ) | ||
| + | branch.setWidth( 2 ) | ||
| + | branch.setOutline( color ) | ||
| + | branch.draw( win ) | ||
| + | |||
| + | # if this branch has sub-branches, then recurse | ||
| + | if order > 0: | ||
| + | |||
| + | # make the recursive calls to draw the two subtrees | ||
| + | newsz = sz*(1 - trunk_ratio) | ||
| + | draw_tree(win, | ||
| + | order-1, theta, newsz, x2, y2, heading-theta, | ||
| + | "orange" ) | ||
| + | draw_tree(win, | ||
| + | order-1, theta, newsz, x2, y2, heading+theta, | ||
| + | "blue" ) | ||
| + | |||
| + | # draw orange | ||
| + | if order == 4: | ||
| + | orange = Circle( Point( x, y ), 20 ) | ||
| + | orange.setFill( "orange" ) | ||
| + | orange.draw( win ) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | # draw 1 tree in the middle of the screen, shooting straight up. | ||
| + | def main(): | ||
| + | win = GraphWin("Fractal Tree", MAXWIDTH, MAXHEIGHT ) | ||
| + | theta = 0.8 # use 0.02 for tall skinny trees, 0.7 for fat trees | ||
| + | draw_tree(win, | ||
| + | 9, | ||
| + | theta, | ||
| + | MAXWIDTH*0.9, MAXWIDTH//2, | ||
| + | MAXHEIGHT-50, | ||
| + | -math.pi/2, | ||
| + | "brown" ) | ||
| + | |||
| + | win.getMouse() | ||
| + | win.close() | ||
| + | |||
| + | main() | ||
| + | |||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | </showafterdate> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
[[Category:Homework]][[Category:CSC111]][[Category:Python]] | [[Category:Homework]][[Category:CSC111]][[Category:Python]] | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
Revision as of 17:23, 19 April 2015
--D. Thiebaut (talk) 17:30, 19 April 2015 (EDT)
Contents
Problem #1
Write a program called hw12_1.py that contains a recursive function called minmax() which returns the smallest and largest elements of a list of items. The items may be strings, numbers, or tuples, where the first element of the tuple is either a number or a string.
Example main() program:
def main(): A = [ 1, 10, 20, 3, 2, -1, -10, 5, 5, 5, 5 ] low, high = minmax( A ) print( "smallest item =", low, " largest item = ", high ) # will print # smallest item = -10 largest item = 20 A = [ 1 ] low, high = minmax( A ) print( "smallest item =", low, " largest item = ", high ) # will print # smallest item = 1 largest item = 1 A = [ ] low, high = minmax( A ) print( "smallest item =", low, " largest item = ", high ) # will print # smallest item = None largest item = None A = [ "alpha", "beta", "gamma", "epsilon" ] low, high = minmax( A ) print( "smallest item =", low, " largest item = ", high ) # will print # smallest item = alpha largest item = gamma if __name__=="__main__": main()
Requirements
- The function minmax() must be recursive.
- You cannot use the min() or max() standard Python functions. If you want to find the largest of two items, you need to do the comparison in Python, using <, <=, >, or >=.
Submission
Submit your program to the Moodle section, HW12 PB 1
Problem #2
Write a Python program called hw12_2.py that will generate a tree as close to the tree shown below as possible. You should not reproduce the text in the image; just the tree, its colors, and its fruit.
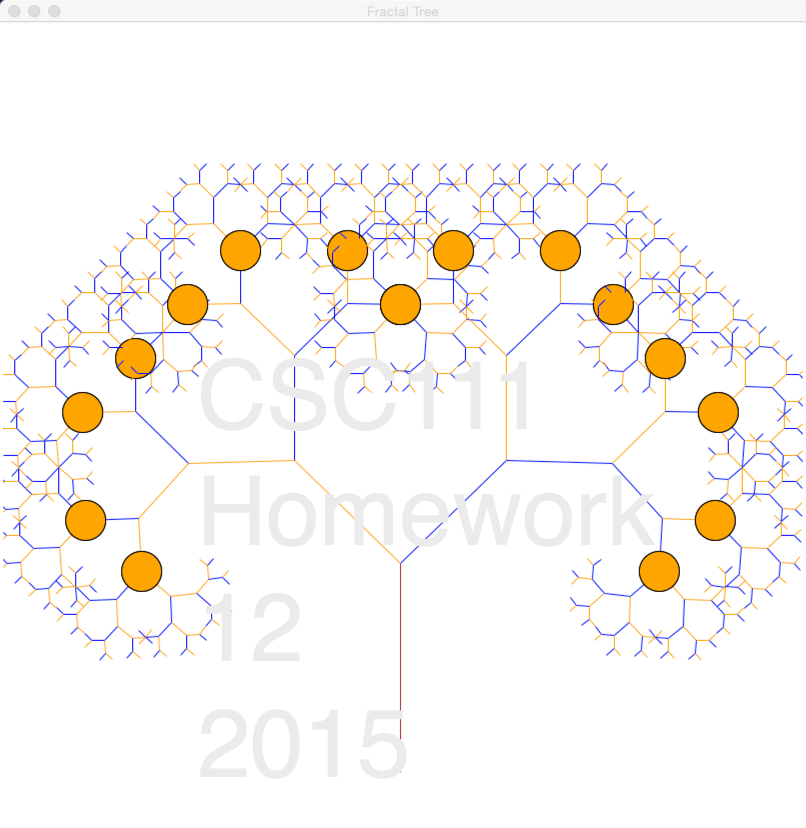
- Submit your program as well as a screen capture of its output to Moodle, in the HW12 PB2 and HW12 Image 2 sections.
- Note: To change the color of a line with the graphics library (use graphics111.py, please), you should use the setOutline() method rather than the setFill() method.
- I used only 3 colors to generate the tree above: "orange", "blue", and "brown".
<showafterdate after="20150422 14:00" before="20150601 00:00">
Solution Programs
Fractal Tree
# fractalTree.py
# D. Thiebaut
# Code taken from http://openbookproject.net/thinkcs/python/english3e/recursion.html
# and adapted to work with graphics111.py.
#
# Draws a fractal tree on the graphic window.
#
from graphics import *
import math
import time
import random
# dimensions of the window
MAXWIDTH = 800
MAXHEIGHT = 800
# recursive tree-drawing function
#
def draw_tree(win , # the canvas
order, # the level of recursion. Starts positive.
theta, # angle of new branch leaving this trunk
sz, # size of this branch
x, y, # coordinates of base of this branch
heading, # angle of direction of this branch
color # color
):
trunk_ratio = 0.29 # How big is the trunk relative to whole tree?
trunk = sz * trunk_ratio # length of trunk
# compute x, y of end of the current branch
delta_x = trunk * math.cos(heading)
delta_y = trunk * math.sin(heading)
x2, y2 = x + delta_x, y + delta_y
# draw current branch
branch = Line( Point( x, y), Point( x2, y2 ) )
branch.setFill( color )
branch.setWidth( 2 )
branch.setOutline( color )
branch.draw( win )
# if this branch has sub-branches, then recurse
if order > 0:
# make the recursive calls to draw the two subtrees
newsz = sz*(1 - trunk_ratio)
draw_tree(win,
order-1, theta, newsz, x2, y2, heading-theta,
"orange" )
draw_tree(win,
order-1, theta, newsz, x2, y2, heading+theta,
"blue" )
# draw orange
if order == 4:
orange = Circle( Point( x, y ), 20 )
orange.setFill( "orange" )
orange.draw( win )
# draw 1 tree in the middle of the screen, shooting straight up.
def main():
win = GraphWin("Fractal Tree", MAXWIDTH, MAXHEIGHT )
theta = 0.8 # use 0.02 for tall skinny trees, 0.7 for fat trees
draw_tree(win,
9,
theta,
MAXWIDTH*0.9, MAXWIDTH//2,
MAXHEIGHT-50,
-math.pi/2,
"brown" )
win.getMouse()
win.close()
main()
</showafterdate>