Difference between revisions of "CSC111 Homework 12 2015"
| Line 222: | Line 222: | ||
</showafterdate> | </showafterdate> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| + | <!-- ====================================================================== --> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <onlydft> | ||
| + | =VPL= | ||
| + | ==vpl_run.sh== | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <source lang="bash"> | ||
| + | #! /bin/bash | ||
| + | |||
| + | cat > vpl_execution <<EOF | ||
| + | #! /bin/bash | ||
| + | |||
| + | # --- Python ---- | ||
| + | if [[ `hostname -s` = "beowulf2" ]]; then | ||
| + | python=/usr/bin/python3.3 | ||
| + | else | ||
| + | python=/usr/local/bin/python3.4 | ||
| + | fi | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | \$python evaluate.py | ||
| + | |||
| + | EOF | ||
| + | |||
| + | chmod +x vpl_execution | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | ==vpl_debug.sh== | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <source lang="bash"> | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | ==vpl_evaluate.sh== | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <source lang="bash"> | ||
| + | #! /bin/bash | ||
| + | |||
| + | cat > vpl_execution <<EOF | ||
| + | #! /bin/bash | ||
| + | |||
| + | # --- Python ---- | ||
| + | if [[ `hostname -s` = "beowulf2" ]]; then | ||
| + | python=/usr/bin/python3.3 | ||
| + | else | ||
| + | python=/usr/local/bin/python3.4 | ||
| + | fi | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | \$python evaluate.py | ||
| + | |||
| + | EOF | ||
| + | |||
| + | chmod +x vpl_execution | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | ==vpl_evaluate.cases== | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <source lang="text"> | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | ==pyminifier.py== | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <source lang="python"> | ||
| + | #!/usr/bin/env python | ||
| + | # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- | ||
| + | # | ||
| + | # pyminifier.py | ||
| + | # | ||
| + | # Copyright 2009 Dan McDougall <YouKnowWho@YouKnowWhat.com> | ||
| + | # | ||
| + | # This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify | ||
| + | # it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | ||
| + | # the Free Software Foundation; Version 3 of the License | ||
| + | # | ||
| + | # This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | ||
| + | # but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | ||
| + | # MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | ||
| + | # GNU General Public License for more details. | ||
| + | # | ||
| + | # You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | ||
| + | # along with this program; if not, the license can be downloaded here: | ||
| + | # | ||
| + | # http://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Meta | ||
| + | __version__ = '1.4.1' | ||
| + | __license__ = "GNU General Public License (GPL) Version 3" | ||
| + | __version_info__ = (1, 4, 1) | ||
| + | __author__ = 'Dan McDougall <YouKnowWho@YouKnowWhat.com>' | ||
| + | |||
| + | """ | ||
| + | **Python Minifier:** Reduces the size of (minifies) Python code for use on | ||
| + | embedded platforms. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Performs the following: | ||
| + | - Removes docstrings. | ||
| + | - Removes comments. | ||
| + | - Minimizes code indentation. | ||
| + | - Joins multiline pairs of parentheses, braces, and brackets (and removes extraneous whitespace within). | ||
| + | - Preserves shebangs and encoding info (e.g. "# -- coding: utf-8 --"). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Various examples and edge cases are sprinkled throughout the pyminifier code so | ||
| + | that it can be tested by minifying itself. The way to test is thus: | ||
| + | |||
| + | .. code-block:: bash | ||
| + | |||
| + | $ python pyminifier.py pyminifier.py > minified_pyminifier.py | ||
| + | $ python minified_pyminifier.py pyminifier.py > this_should_be_identical.py | ||
| + | $ diff minified_pyminifier.py this_should_be_identical.py | ||
| + | $ | ||
| + | |||
| + | If you get an error executing minified_pyminifier.py or | ||
| + | 'this_should_be_identical.py' isn't identical to minified_pyminifier.py then | ||
| + | something is broken. | ||
| + | """ | ||
| + | |||
| + | import sys, re, tokenize | ||
| + | import io | ||
| + | |||
| + | from optparse import OptionParser | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Compile our regular expressions for speed | ||
| + | multiline_quoted_string = re.compile(r'(\'\'\'|\"\"\")') | ||
| + | not_quoted_string = re.compile(r'(\".*\'\'\'.*\"|\'.*\"\"\".*\')') | ||
| + | trailing_newlines = re.compile(r'\n\n') | ||
| + | shebang = re.compile('^#\!.*$') | ||
| + | encoding = re.compile(".*coding[:=]\s*([-\w.]+)") | ||
| + | multiline_indicator = re.compile('\\\\(\s*#.*)?\n') | ||
| + | # The above also removes trailing comments: "test = 'blah \ # comment here" | ||
| + | |||
| + | # These aren't used but they're a pretty good reference: | ||
| + | double_quoted_string = re.compile(r'((?<!\\)".*?(?<!\\)")') | ||
| + | single_quoted_string = re.compile(r"((?<!\\)'.*?(?<!\\)')") | ||
| + | single_line_single_quoted_string = re.compile(r"((?<!\\)'''.*?(?<!\\)''')") | ||
| + | single_line_double_quoted_string = re.compile(r"((?<!\\)'''.*?(?<!\\)''')") | ||
| + | |||
| + | def remove_comments_and_docstrings(source): | ||
| + | """ | ||
| + | Returns 'source' minus comments and docstrings. | ||
| + | |||
| + | **Note**: Uses Python's built-in tokenize module to great effect. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Example: | ||
| + | |||
| + | .. code-block:: python | ||
| + | |||
| + | def noop(): # This is a comment | ||
| + | ''' | ||
| + | Does nothing. | ||
| + | ''' | ||
| + | pass # Don't do anything | ||
| + | |||
| + | Will become: | ||
| + | |||
| + | .. code-block:: python | ||
| + | |||
| + | def noop(): | ||
| + | pass | ||
| + | """ | ||
| + | io_obj = io.StringIO(source) | ||
| + | out = "" | ||
| + | prev_toktype = tokenize.INDENT | ||
| + | last_lineno = -1 | ||
| + | last_col = 0 | ||
| + | for tok in tokenize.generate_tokens(io_obj.readline): | ||
| + | token_type = tok[0] | ||
| + | token_string = tok[1] | ||
| + | start_line, start_col = tok[2] | ||
| + | end_line, end_col = tok[3] | ||
| + | ltext = tok[4] | ||
| + | # The following two conditionals preserve indentation. | ||
| + | # This is necessary because we're not using tokenize.untokenize() | ||
| + | # (because it spits out code with copious amounts of oddly-placed | ||
| + | # whitespace). | ||
| + | if start_line > last_lineno: | ||
| + | last_col = 0 | ||
| + | if start_col > last_col: | ||
| + | out += (" " * (start_col - last_col)) | ||
| + | # Remove comments: | ||
| + | if token_type == tokenize.COMMENT: | ||
| + | pass | ||
| + | # This series of conditionals removes docstrings: | ||
| + | elif token_type == tokenize.STRING: | ||
| + | if prev_toktype != tokenize.INDENT: | ||
| + | # This is likely a docstring; double-check we're not inside an operator: | ||
| + | if prev_toktype != tokenize.NEWLINE: | ||
| + | # Note regarding NEWLINE vs NL: The tokenize module | ||
| + | # differentiates between newlines that start a new statement | ||
| + | # and newlines inside of operators such as parens, brackes, | ||
| + | # and curly braces. Newlines inside of operators are | ||
| + | # NEWLINE and newlines that start new code are NL. | ||
| + | # Catch whole-module docstrings: | ||
| + | if start_col > 0: | ||
| + | # Unlabelled indentation means we're inside an operator | ||
| + | out += token_string | ||
| + | # Note regarding the INDENT token: The tokenize module does | ||
| + | # not label indentation inside of an operator (parens, | ||
| + | # brackets, and curly braces) as actual indentation. | ||
| + | # For example: | ||
| + | # def foo(): | ||
| + | # "The spaces before this docstring are tokenize.INDENT" | ||
| + | # test = [ | ||
| + | # "The spaces before this string do not get a token" | ||
| + | # ] | ||
| + | else: | ||
| + | out += token_string | ||
| + | prev_toktype = token_type | ||
| + | last_col = end_col | ||
| + | last_lineno = end_line | ||
| + | return out | ||
| + | |||
| + | def reduce_operators(source): | ||
| + | """ | ||
| + | Remove spaces between operators in 'source' and returns the result. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Example: | ||
| + | |||
| + | .. code-block:: python | ||
| + | |||
| + | def foo(foo, bar, blah): | ||
| + | test = "This is a %s" % foo | ||
| + | |||
| + | Will become: | ||
| + | |||
| + | .. code-block:: python | ||
| + | |||
| + | def foo(foo,bar,blah): | ||
| + | test="This is a %s"%foo | ||
| + | """ | ||
| + | io_obj = io.StringIO(source) | ||
| + | remove_columns = [] | ||
| + | out = "" | ||
| + | out_line = "" | ||
| + | prev_toktype = tokenize.INDENT | ||
| + | prev_tok = None | ||
| + | last_lineno = -1 | ||
| + | last_col = 0 | ||
| + | lshift = 1 | ||
| + | for tok in tokenize.generate_tokens(io_obj.readline): | ||
| + | token_type = tok[0] | ||
| + | token_string = tok[1] | ||
| + | start_line, start_col = tok[2] | ||
| + | end_line, end_col = tok[3] | ||
| + | ltext = tok[4] | ||
| + | if start_line > last_lineno: | ||
| + | last_col = 0 | ||
| + | if start_col > last_col: | ||
| + | out_line += (" " * (start_col - last_col)) | ||
| + | if token_type == tokenize.OP: | ||
| + | # Operators that begin a line such as @ or open parens should be | ||
| + | # left alone | ||
| + | start_of_line_types = [ # These indicate we're starting a new line | ||
| + | tokenize.NEWLINE, tokenize.DEDENT, tokenize.INDENT] | ||
| + | if prev_toktype not in start_of_line_types: | ||
| + | # This is just a regular operator; remove spaces | ||
| + | remove_columns.append(start_col) # Before OP | ||
| + | remove_columns.append(end_col+1) # After OP | ||
| + | if token_string.endswith('\n'): | ||
| + | out_line += token_string | ||
| + | if remove_columns: | ||
| + | for col in remove_columns: | ||
| + | col = col - lshift | ||
| + | try: | ||
| + | # This was really handy for debugging (looks nice, worth saving): | ||
| + | #print out_line + (" " * col) + "^" | ||
| + | # The above points to the character we're looking at | ||
| + | if out_line[col] == " ": # Only if it is a space | ||
| + | out_line = out_line[:col] + out_line[col+1:] | ||
| + | lshift += 1 # To re-align future changes on this line | ||
| + | except IndexError: # Reached and end of line, no biggie | ||
| + | pass | ||
| + | out += out_line | ||
| + | remove_columns = [] | ||
| + | out_line = "" | ||
| + | lshift = 1 | ||
| + | else: | ||
| + | out_line += token_string | ||
| + | prev_toktype = token_type | ||
| + | prev_token = tok | ||
| + | last_col = end_col | ||
| + | last_lineno = end_line | ||
| + | # This makes sure to capture the last line if it doesn't end in a newline: | ||
| + | out += out_line | ||
| + | # The tokenize module doesn't recognize @ sign before a decorator | ||
| + | return out | ||
| + | |||
| + | # NOTE: This isn't used anymore... Just here for reference in case someone | ||
| + | # searches the internet looking for a way to remove similarly-styled end-of-line | ||
| + | # comments from non-python code. It also acts as an edge case of sorts with | ||
| + | # that raw triple quoted string inside the "quoted_string" assignment. | ||
| + | def remove_comment(single_line): | ||
| + | """ | ||
| + | Removes the comment at the end of the line (if any) and returns the result. | ||
| + | """ | ||
| + | quoted_string = re.compile( | ||
| + | r'''((?<!\\)".*?(?<!\\)")|((?<!\\)'.*?(?<!\\)')''' | ||
| + | ) | ||
| + | # This divides the line up into sections: | ||
| + | # Those inside single quotes and those that are not | ||
| + | split_line = quoted_string.split(single_line) | ||
| + | # Remove empty items: | ||
| + | split_line = [a for a in split_line if a] | ||
| + | out_line = "" | ||
| + | for section in split_line: | ||
| + | if section.startswith("'") or section.startswith('"'): | ||
| + | # This is a quoted string; leave it alone | ||
| + | out_line += section | ||
| + | elif '#' in section: # A '#' not in quotes? There's a comment here! | ||
| + | # Get rid of everything after the # including the # itself: | ||
| + | out_line += section.split('#')[0] | ||
| + | break # No reason to bother the rest--it's all comments | ||
| + | else: | ||
| + | # This isn't a quoted string OR a comment; leave it as-is | ||
| + | out_line += section | ||
| + | return out_line.rstrip() # Strip trailing whitespace before returning | ||
| + | |||
| + | def join_multiline_pairs(text, pair="()"): | ||
| + | """ | ||
| + | Finds and removes newlines in multiline matching pairs of characters in | ||
| + | 'text'. For example, "(.*\n.*), {.*\n.*}, or [.*\n.*]". | ||
| + | |||
| + | By default it joins parens () but it will join any two characters given via | ||
| + | the 'pair' variable. | ||
| + | |||
| + | **Note:** Doesn't remove extraneous whitespace that ends up between the pair. | ||
| + | Use reduce_operators() for that. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Example: | ||
| + | |||
| + | .. code-block:: python | ||
| + | |||
| + | test = ( | ||
| + | "This is inside a multi-line pair of parentheses" | ||
| + | ) | ||
| + | |||
| + | Will become: | ||
| + | |||
| + | .. code-block:: python | ||
| + | |||
| + | test = ( "This is inside a multi-line pair of parentheses" ) | ||
| + | """ | ||
| + | # Readability variables | ||
| + | opener = pair[0] | ||
| + | closer = pair[1] | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Tracking variables | ||
| + | inside_pair = False | ||
| + | inside_quotes = False | ||
| + | inside_double_quotes = False | ||
| + | inside_single_quotes = False | ||
| + | quoted_string = False | ||
| + | openers = 0 | ||
| + | closers = 0 | ||
| + | linecount = 0 | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Regular expressions | ||
| + | opener_regex = re.compile('\%s' % opener) | ||
| + | closer_regex = re.compile('\%s' % closer) | ||
| + | |||
| + | output = "" | ||
| + | |||
| + | for line in text.split('\n'): | ||
| + | escaped = False | ||
| + | # First we rule out multi-line strings | ||
| + | multline_match = multiline_quoted_string.search(line) | ||
| + | not_quoted_string_match = not_quoted_string.search(line) | ||
| + | if multline_match and not not_quoted_string_match and not quoted_string: | ||
| + | if len(line.split('"""')) > 1 or len(line.split("'''")): | ||
| + | # This is a single line that uses the triple quotes twice | ||
| + | # Treat it as if it were just a regular line: | ||
| + | output += line + '\n' | ||
| + | quoted_string = False | ||
| + | else: | ||
| + | output += line + '\n' | ||
| + | quoted_string = True | ||
| + | elif quoted_string and multiline_quoted_string.search(line): | ||
| + | output += line + '\n' | ||
| + | quoted_string = False | ||
| + | # Now let's focus on the lines containing our opener and/or closer: | ||
| + | elif not quoted_string: | ||
| + | if opener_regex.search(line) or closer_regex.search(line) or inside_pair: | ||
| + | for character in line: | ||
| + | if character == opener: | ||
| + | if not escaped and not inside_quotes: | ||
| + | openers += 1 | ||
| + | inside_pair = True | ||
| + | output += character | ||
| + | else: | ||
| + | escaped = False | ||
| + | output += character | ||
| + | elif character == closer: | ||
| + | if not escaped and not inside_quotes: | ||
| + | if openers and openers == (closers + 1): | ||
| + | closers = 0 | ||
| + | openers = 0 | ||
| + | inside_pair = False | ||
| + | output += character | ||
| + | else: | ||
| + | closers += 1 | ||
| + | output += character | ||
| + | else: | ||
| + | escaped = False | ||
| + | output += character | ||
| + | elif character == '\\': | ||
| + | if escaped: | ||
| + | escaped = False | ||
| + | output += character | ||
| + | else: | ||
| + | escaped = True | ||
| + | output += character | ||
| + | elif character == '"' and escaped: | ||
| + | output += character | ||
| + | escaped = False | ||
| + | elif character == "'" and escaped: | ||
| + | output += character | ||
| + | escaped = False | ||
| + | elif character == '"' and inside_quotes: | ||
| + | if inside_single_quotes: | ||
| + | output += character | ||
| + | else: | ||
| + | inside_quotes = False | ||
| + | inside_double_quotes = False | ||
| + | output += character | ||
| + | elif character == "'" and inside_quotes: | ||
| + | if inside_double_quotes: | ||
| + | output += character | ||
| + | else: | ||
| + | inside_quotes = False | ||
| + | inside_single_quotes = False | ||
| + | output += character | ||
| + | elif character == '"' and not inside_quotes: | ||
| + | inside_quotes = True | ||
| + | inside_double_quotes = True | ||
| + | output += character | ||
| + | elif character == "'" and not inside_quotes: | ||
| + | inside_quotes = True | ||
| + | inside_single_quotes = True | ||
| + | output += character | ||
| + | elif character == ' ' and inside_pair and not inside_quotes: | ||
| + | if not output[-1] in [' ', opener]: | ||
| + | output += ' ' | ||
| + | else: | ||
| + | if escaped: | ||
| + | escaped = False | ||
| + | output += character | ||
| + | if inside_pair == False: | ||
| + | output += '\n' | ||
| + | else: | ||
| + | output += line + '\n' | ||
| + | else: | ||
| + | output += line + '\n' | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Clean up | ||
| + | output = trailing_newlines.sub('\n', output) | ||
| + | |||
| + | return output | ||
| + | |||
| + | def dedent(source): | ||
| + | """ | ||
| + | Minimizes indentation to save precious bytes | ||
| + | |||
| + | Example: | ||
| + | |||
| + | .. code-block:: python | ||
| + | |||
| + | def foo(bar): | ||
| + | test = "This is a test" | ||
| + | |||
| + | Will become: | ||
| + | |||
| + | .. code-block:: python | ||
| + | |||
| + | def foo(bar): | ||
| + | test = "This is a test" | ||
| + | """ | ||
| + | io_obj = io.StringIO(source) | ||
| + | out = "" | ||
| + | last_lineno = -1 | ||
| + | last_col = 0 | ||
| + | prev_start_line = 0 | ||
| + | indentation = "" | ||
| + | indentation_level = 0 | ||
| + | for i,tok in enumerate(tokenize.generate_tokens(io_obj.readline)): | ||
| + | token_type = tok[0] | ||
| + | token_string = tok[1] | ||
| + | start_line, start_col = tok[2] | ||
| + | end_line, end_col = tok[3] | ||
| + | if start_line > last_lineno: | ||
| + | last_col = 0 | ||
| + | if token_type == tokenize.INDENT: | ||
| + | indentation_level += 1 | ||
| + | continue | ||
| + | if token_type == tokenize.DEDENT: | ||
| + | indentation_level -= 1 | ||
| + | continue | ||
| + | indentation = " " * indentation_level | ||
| + | if start_line > prev_start_line: | ||
| + | out += indentation + token_string | ||
| + | elif start_col > last_col: | ||
| + | out += " " + token_string | ||
| + | else: | ||
| + | out += token_string | ||
| + | prev_start_line = start_line | ||
| + | last_col = end_col | ||
| + | last_lineno = end_line | ||
| + | return out | ||
| + | |||
| + | def fix_empty_methods(source): | ||
| + | """ | ||
| + | Appends 'pass' to empty methods/functions (i.e. where there was nothing but | ||
| + | a docstring before we removed it =). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Example: | ||
| + | |||
| + | .. code-block:: python | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Note: This triple-single-quote inside a triple-double-quote is also a | ||
| + | # pyminifier self-test | ||
| + | def myfunc(): | ||
| + | '''This is just a placeholder function.''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Will become: | ||
| + | |||
| + | .. code-block:: python | ||
| + | |||
| + | def myfunc(): pass | ||
| + | """ | ||
| + | def_indentation_level = 0 | ||
| + | output = "" | ||
| + | just_matched = False | ||
| + | previous_line = None | ||
| + | method = re.compile(r'^\s*def\s*.*\(.*\):.*$') | ||
| + | for line in source.split('\n'): | ||
| + | if len(line.strip()) > 0: # Don't look at blank lines | ||
| + | if just_matched == True: | ||
| + | this_indentation_level = len(line.rstrip()) - len(line.strip()) | ||
| + | if def_indentation_level == this_indentation_level: | ||
| + | # This method is empty, insert a 'pass' statement | ||
| + | output += "%s pass\n%s\n" % (previous_line, line) | ||
| + | else: | ||
| + | output += "%s\n%s\n" % (previous_line, line) | ||
| + | just_matched = False | ||
| + | elif method.match(line): | ||
| + | def_indentation_level = len(line) - len(line.strip()) # A commment | ||
| + | just_matched = True | ||
| + | previous_line = line | ||
| + | else: | ||
| + | output += "%s\n" % line # Another self-test | ||
| + | else: | ||
| + | output += "\n" | ||
| + | return output | ||
| + | |||
| + | def remove_blank_lines(source): | ||
| + | """ | ||
| + | Removes blank lines from 'source' and returns the result. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Example: | ||
| + | |||
| + | .. code-block:: python | ||
| + | |||
| + | test = "foo" | ||
| + | |||
| + | test2 = "bar" | ||
| + | |||
| + | Will become: | ||
| + | |||
| + | .. code-block:: python | ||
| + | |||
| + | test = "foo" | ||
| + | test2 = "bar" | ||
| + | """ | ||
| + | io_obj = io.StringIO(source) | ||
| + | source = [a for a in io_obj.readlines() if a.strip()] | ||
| + | return "".join(source) | ||
| + | |||
| + | def minify(source): | ||
| + | """ | ||
| + | Remove all docstrings, comments, blank lines, and minimize code | ||
| + | indentation from 'source' then prints the result. | ||
| + | """ | ||
| + | preserved_shebang = None | ||
| + | preserved_encoding = None | ||
| + | |||
| + | # This is for things like shebangs that must be precisely preserved | ||
| + | for line in source.split('\n')[0:2]: | ||
| + | # Save the first comment line if it starts with a shebang | ||
| + | # (e.g. '#!/usr/bin/env python') <--also a self test! | ||
| + | if shebang.match(line): # Must be first line | ||
| + | preserved_shebang = line | ||
| + | continue | ||
| + | # Save the encoding string (must be first or second line in file) | ||
| + | if encoding.match(line): | ||
| + | preserved_encoding = line | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Remove multilines (e.g. lines that end with '\' followed by a newline) | ||
| + | source = multiline_indicator.sub('', source) | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Remove docstrings (Note: Must run before fix_empty_methods()) | ||
| + | source = remove_comments_and_docstrings(source) | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Remove empty (i.e. single line) methods/functions | ||
| + | source = fix_empty_methods(source) | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Join multiline pairs of parens, brackets, and braces | ||
| + | source = join_multiline_pairs(source) | ||
| + | source = join_multiline_pairs(source, '[]') | ||
| + | source = join_multiline_pairs(source, '{}') | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Remove whitespace between operators: | ||
| + | source = reduce_operators(source) | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Minimize indentation | ||
| + | source = dedent(source) | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Re-add preseved items | ||
| + | if preserved_encoding: | ||
| + | source = preserved_encoding + "\n" + source | ||
| + | if preserved_shebang: | ||
| + | source = preserved_shebang + "\n" + source | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Remove blank lines | ||
| + | source = remove_blank_lines(source).rstrip('\n') # Stubborn last newline | ||
| + | |||
| + | return source | ||
| + | |||
| + | def bz2_pack(source): | ||
| + | "Returns 'source' as a bzip2-compressed, self-extracting python script." | ||
| + | import bz2, base64 | ||
| + | out = "" | ||
| + | compressed_source = bz2.compress(source) | ||
| + | out += 'import bz2, base64\n' | ||
| + | out += "exec bz2.decompress(base64.b64decode('" | ||
| + | out += base64.b64encode((compressed_source)) | ||
| + | out += "'))\n" | ||
| + | return out | ||
| + | |||
| + | def gz_pack(source): | ||
| + | "Returns 'source' as a gzip-compressed, self-extracting python script." | ||
| + | import zlib, base64 | ||
| + | out = "" | ||
| + | compressed_source = zlib.compress(source) | ||
| + | out += 'import zlib, base64\n' | ||
| + | out += "exec zlib.decompress(base64.b64decode('" | ||
| + | out += base64.b64encode((compressed_source)) | ||
| + | out += "'))\n" | ||
| + | return out | ||
| + | |||
| + | # The test.+() functions below are for testing pyminifer... | ||
| + | def test_decorator(f): | ||
| + | """Decorator that does nothing""" | ||
| + | return f | ||
| + | |||
| + | def test_reduce_operators(): | ||
| + | """Test the case where an operator such as an open paren starts a line""" | ||
| + | (a, b) = 1, 2 # The indentation level should be preserved | ||
| + | pass | ||
| + | |||
| + | def test_empty_functions(): | ||
| + | """ | ||
| + | This is a test method. | ||
| + | This should be replaced with 'def empty_method: pass' | ||
| + | """ | ||
| + | |||
| + | class test_class(object): | ||
| + | "Testing indented decorators" | ||
| + | |||
| + | @test_decorator | ||
| + | def foo(self): | ||
| + | pass | ||
| + | |||
| + | def test_function(): | ||
| + | """ | ||
| + | This function encapsulates the edge cases to prevent them from invading the | ||
| + | global namespace. | ||
| + | """ | ||
| + | foo = ("The # character in this string should " # This comment | ||
| + | "not result in a syntax error") # ...and this one should go away | ||
| + | test_multi_line_list = [ | ||
| + | 'item1', | ||
| + | 'item2', | ||
| + | 'item3' | ||
| + | ] | ||
| + | test_multi_line_dict = { | ||
| + | 'item1': 1, | ||
| + | 'item2': 2, | ||
| + | 'item3': 3 | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | # It may seem strange but the code below tests our docstring removal code. | ||
| + | test_string_inside_operators = imaginary_function( | ||
| + | "This string was indented but the tokenizer won't see it that way." | ||
| + | ) # To understand how this could mess up docstring removal code see the | ||
| + | # remove_comments_and_docstrings() function starting at this line: | ||
| + | # "elif token_type == tokenize.STRING:" | ||
| + | # This tests remove_extraneous_spaces(): | ||
| + | this_line_has_leading_indentation = '''<--That extraneous space should be | ||
| + | removed''' # But not these spaces | ||
| + | |||
| + | def removeComments( source ): | ||
| + | return minify(source) | ||
| + | |||
| + | def main(): | ||
| + | usage = '%prog [options] "<input file>"' | ||
| + | parser = OptionParser(usage=usage, version=__version__) | ||
| + | parser.disable_interspersed_args() | ||
| + | parser.add_option( | ||
| + | "-o", "--outfile", | ||
| + | dest="outfile", | ||
| + | default=None, | ||
| + | help="Save output to the given file.", | ||
| + | metavar="<file path>" | ||
| + | ) | ||
| + | parser.add_option( | ||
| + | "--bzip2", | ||
| + | action="store_true", | ||
| + | dest="bzip2", | ||
| + | default=False, | ||
| + | help="bzip2-compress the result into a self-executing python script." | ||
| + | ) | ||
| + | parser.add_option( | ||
| + | "--gzip", | ||
| + | action="store_true", | ||
| + | dest="gzip", | ||
| + | default=False, | ||
| + | help="gzip-compress the result into a self-executing python script." | ||
| + | ) | ||
| + | options, args = parser.parse_args() | ||
| + | try: | ||
| + | source = open(args[0]).read() | ||
| + | except: | ||
| + | parser.print_help() | ||
| + | sys.exit(2) | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Minify our input script | ||
| + | result = minify(source) | ||
| + | # Compress it if we were asked to do so | ||
| + | if options.bzip2: | ||
| + | result = bz2_pack(result) | ||
| + | elif options.gzip: | ||
| + | result = gz_pack(result) | ||
| + | # Either save the result to the output file or print it to stdout | ||
| + | if options.outfile: | ||
| + | f = open(options.outfile, 'w') | ||
| + | f.write(result) | ||
| + | f.close() | ||
| + | else: | ||
| + | print( result ) | ||
| + | |||
| + | if __name__ == "__main__": | ||
| + | #main() | ||
| + | source = open( "hw10Test.py", "r" ).read() | ||
| + | print( "="*80 ) | ||
| + | print( removeComments( source ) ) | ||
| + | print( "="*80 ) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | ==evaluate.py== | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <source lang="python"> | ||
| + | # evaluate.py | ||
| + | # D. Thiebaut | ||
| + | # This program is used to test a student's python program on Moodle. | ||
| + | |||
| + | import sys | ||
| + | import random | ||
| + | import subprocess | ||
| + | import pyminifier | ||
| + | |||
| + | #--- GLOBALS --- | ||
| + | #--- define what the student program is called, and what the solution | ||
| + | #--- program name is. | ||
| + | |||
| + | debug = False #True | ||
| + | studentModule = "hw12_1" | ||
| + | module = "testHw12_1" | ||
| + | solutionModule = "hw12_1sol" | ||
| + | userOutSplitPattern = "" # pattern used to start recording the user | ||
| + | # output. Useful when program does several | ||
| + | # input() statements, and user output starts | ||
| + | # after that. | ||
| + | stripOutputsBeforeCompare = True | ||
| + | # set to True if extra spaces at beginning or | ||
| + | # end of user output is ok | ||
| + | |||
| + | interpreter = sys.executable | ||
| + | |||
| + | def commentLong( line ): | ||
| + | print( "<|--\n" + line + "\n --|>" ) | ||
| + | |||
| + | def commentShort( text ): | ||
| + | print( "Comment :=>> " + text ) | ||
| + | |||
| + | def comment( text ): | ||
| + | commentShort( text ) | ||
| + | |||
| + | def printGrade( grade ): | ||
| + | print( "Grade :=>> ", grade ) | ||
| + | |||
| + | # remove if __name__==... | ||
| + | def removeIfNameEqMain( fileName ): | ||
| + | file = open( fileName, "r" ) | ||
| + | lines = file.read() | ||
| + | file.close() | ||
| + | |||
| + | newLines = "" | ||
| + | for line in lines.split( "\n" ): | ||
| + | if line.find( "__name__" )!=-1 and line.find( "__main__" )!=-1 and line.find( "if True" )==-1: | ||
| + | line = "if True: #" + line | ||
| + | newLines += line + "\n" | ||
| + | |||
| + | # write it back | ||
| + | file = open( fileName, "w" ) | ||
| + | file.write( newLines ) | ||
| + | file.close() | ||
| + | |||
| + | # add if __name__=="__main__": to the program | ||
| + | def addIfNameEqMain( fileName ): | ||
| + | file = open( fileName, "r" ) | ||
| + | lines = file.read() | ||
| + | file.close() | ||
| + | |||
| + | newLines = "" | ||
| + | for line in lines.split( "\n" ): | ||
| + | if line.find( "main()" )==0: | ||
| + | line = 'if __name__=="__main__": main()' | ||
| + | newLines += line + "\n" | ||
| + | |||
| + | # write it back | ||
| + | file = open( fileName, "w" ) | ||
| + | file.write( newLines ) | ||
| + | file.close() | ||
| + | |||
| + | def createEmptyFile( fileName ): | ||
| + | file = open( fileName, "w" ) | ||
| + | file.write( "\n" ) | ||
| + | file.close() | ||
| + | |||
| + | # generateInputFileWithRandomInputs | ||
| + | # generate a file with name "inputFileName" with some random input | ||
| + | # for the program. | ||
| + | # MAKE SURE TO EDIT THIS TO MATCH THE PROGRAM BEING TESTED | ||
| + | def generateTestModule( moduleName, i ): | ||
| + | #--- we don't need an input file for stdin, but we'll generate a | ||
| + | #--- dummy one nonetheless | ||
| + | code = """ | ||
| + | from hw12_1 import * | ||
| + | |||
| + | def main(): | ||
| + | A = %s | ||
| + | low, high = smallestLargest( A ) | ||
| + | print( low, high ) | ||
| + | |||
| + | if __name__=="__main__": | ||
| + | main() | ||
| + | """ | ||
| + | if debug: print( "generateTestModule(", moduleName, ", ", i ,")" ) | ||
| + | if i==0: | ||
| + | s = "[1, -100, 200, 5, 0]" | ||
| + | if i==1: | ||
| + | s = "[100]" | ||
| + | if i==2: | ||
| + | s = "[]" | ||
| + | if i==3: | ||
| + | s = '[ "lucy", "marie", "joe", "larry"]' | ||
| + | |||
| + | file = open( moduleName+".py", "w" ) | ||
| + | file.write( code % s ) | ||
| + | file.write( "\n" ) | ||
| + | file.close() | ||
| + | return s | ||
| + | |||
| + | def generateSolutionModule( moduleName, i ): | ||
| + | #--- we don't need an input file for stdin, but we'll generate a | ||
| + | #--- dummy one nonetheless | ||
| + | code = """ | ||
| + | def smallestLargest( A ): | ||
| + | if len( A )==0: | ||
| + | return None, None | ||
| + | |||
| + | if len( A )==1: | ||
| + | return A[0], A[0] | ||
| + | |||
| + | theMin, theMax = smallestLargest( A[1: ] ) | ||
| + | |||
| + | if A[0] < theMin: | ||
| + | theMin = A[0] | ||
| + | if A[0] > theMax: | ||
| + | theMax = A[0] | ||
| + | |||
| + | return theMin, theMax | ||
| + | |||
| + | def main(): | ||
| + | A = %s | ||
| + | low, high = smallestLargest( A ) | ||
| + | print( low, high ) | ||
| + | |||
| + | if __name__=="__main__": | ||
| + | main() | ||
| + | """ | ||
| + | if i==0: | ||
| + | s = "[1, -100, 200, 5, 0]" | ||
| + | if i==1: | ||
| + | s = "[100]" | ||
| + | if i==2: | ||
| + | s = "[]" | ||
| + | if i==3: | ||
| + | s = '[ "lucy", "marie", "joe", "larry"]' | ||
| + | |||
| + | file = open( moduleName+".py", "w" ) | ||
| + | file.write( code % s ) | ||
| + | file.write( "\n" ) | ||
| + | file.close() | ||
| + | return s | ||
| + | |||
| + | # checkForFunctionPresence | ||
| + | # checks that "functionName" is defined and called in the program. | ||
| + | # MAKE SURE TO EDIT TO MATCH PROGRAM BEING TESTED | ||
| + | def checkForFunctionPresence( module, functionName ): | ||
| + | foundDef = False | ||
| + | foundCall = False | ||
| + | |||
| + | for line in open( module+".py", "r" ).readlines(): | ||
| + | # remove comments | ||
| + | idx = line.find( "#" ) | ||
| + | if ( idx >=0 ): line = line[0:idx] | ||
| + | |||
| + | if line.startswith( "def " + functionName + "(" ): | ||
| + | foundDef = True | ||
| + | continue | ||
| + | if line.startswith( "def " + functionName + " (" ): | ||
| + | foundDef = True | ||
| + | continue | ||
| + | if line.find( functionName+"(" ) != -1: | ||
| + | foundCall = True | ||
| + | continue | ||
| + | |||
| + | return (foundDef, foundCall) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | # ================================================================== | ||
| + | # NO EDITS NEEDED BELOW! | ||
| + | # ================================================================== | ||
| + | |||
| + | def clearLog(): | ||
| + | open( "log.txt", "w" ).write( "" ) | ||
| + | |||
| + | def log( message ): | ||
| + | file = open( "log.txt", "a" ) | ||
| + | file.write( message + "\n" ) | ||
| + | file.flush() | ||
| + | file.close() | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | # checkModuleRunsOK: runs the module as a shell subprocess and | ||
| + | # look for errors in the output. This is required, because otherwise | ||
| + | # importing the module in this program will make this program crash. | ||
| + | # It's not possible (as far as I can tell0 to catch exceptions from | ||
| + | # the import or __module__ statements. | ||
| + | # returns True, none if no errors, otherwise False, string if there's | ||
| + | # an exception, and the error message (string) is in the returned 2nd | ||
| + | # arg. | ||
| + | # The module name is assumed to not include ".py" | ||
| + | def checkModuleRunsOk( module, inputFileName ): | ||
| + | global interpreter | ||
| + | p = subprocess.Popen( [ interpreter, module+".py" ], | ||
| + | stdout=subprocess.PIPE, | ||
| + | stderr=subprocess.PIPE, | ||
| + | stdin=subprocess.PIPE) | ||
| + | |||
| + | #print( "inputFileName = ", inputFileName ) | ||
| + | #print( "open( inputFileName, r).read() = ", open( inputFileName, "r" ).read() ) | ||
| + | |||
| + | p.stdin.write( bytes( open( inputFileName, "r" ).read(), 'UTF-8' ) ) | ||
| + | try: | ||
| + | data = p.communicate( timeout=2 ) # timeout after 10sec | ||
| + | except subprocess.TimeoutExpired: | ||
| + | error = "Your program timed out. Very likely an infinite loop!" | ||
| + | return False, error | ||
| + | p.stdin.close() | ||
| + | |||
| + | error = data[1].decode( 'UTF-8' ) | ||
| + | if len( error ) > 1: | ||
| + | return False, error | ||
| + | return True, None | ||
| + | |||
| + | def firstLastLines( text ): | ||
| + | lines = text.split( "\n" ) | ||
| + | if len( lines ) > 20: | ||
| + | text = "\n".join( lines[0:5] )+"\n...\n" + "\n".join( lines[-5:] ) | ||
| + | return text | ||
| + | |||
| + | # extractTextFromErrorMessage( sys_exc_info ): | ||
| + | def extractTextFromErrorMessage( sys_exc_info ): | ||
| + | if debug: print( "sys_exec_info = ", sys_exc_info ) | ||
| + | text = "" | ||
| + | for field in sys_exc_info: | ||
| + | if type( field )==type( " " ): | ||
| + | text += field + "\n" | ||
| + | |||
| + | return text | ||
| + | |||
| + | # runModule: | ||
| + | # runs the module, passes it data from the input file on its stdin | ||
| + | # and get its output on stdout captured in outputFileName. | ||
| + | # We assume the module will not crash, because we already tested | ||
| + | # it with checkModuleRunsOk(). | ||
| + | def runModule( module, inputFileName, outputFileName ): | ||
| + | global userOutSplitPattern | ||
| + | |||
| + | error = False | ||
| + | |||
| + | #--- make stdin read information from the text file | ||
| + | sys.stdin = open( inputFileName, "r" ) | ||
| + | |||
| + | #--- capture the stdout of the program to test into a file | ||
| + | saveStdOut = sys.stdout | ||
| + | saveStdErr = sys.stderr | ||
| + | |||
| + | sys.stdout = open( outputFileName, "w" ) | ||
| + | sys.stderr = open( "errorOut", "w" ) | ||
| + | |||
| + | #--- run the student program --- | ||
| + | try: | ||
| + | _module = __import__( module ) | ||
| + | _module.main() | ||
| + | except: | ||
| + | error = True | ||
| + | sys.stderr.close() | ||
| + | sys.stderr = saveStdErr | ||
| + | sys.stdout.close() | ||
| + | sys.stdout = saveStdOut | ||
| + | text = sys.exc_info()[0] | ||
| + | text = extractTextFromErrorMessage( text ) | ||
| + | #print( "*** sys.exc_info() = ", text ) | ||
| + | text = open( outputFileName, "r" ).read() + "\n" + text | ||
| + | return error, text, 0 | ||
| + | |||
| + | #--- filter out junk from output of program --- | ||
| + | sys.stdout.close() | ||
| + | sys.stdout = saveStdOut | ||
| + | sys.stderr.close() | ||
| + | sys.stderr = saveStdErr | ||
| + | |||
| + | file = open( outputFileName, "r" ) | ||
| + | text = file.read() | ||
| + | file.close() | ||
| + | if debug: | ||
| + | print( "runModule( ", module, " ) returns text = <", text , ">" ) | ||
| + | |||
| + | return False, text, 0 | ||
| + | |||
| + | def removeBlankLines( lines ): | ||
| + | newLines = [] | ||
| + | log( "removeBlankLines: lines = " + str( lines ) ) | ||
| + | for line in lines.split( "\n" ): | ||
| + | if len( line )==0: | ||
| + | continue | ||
| + | newLines.append( line ) | ||
| + | |||
| + | return ( "\n".join( newLines ) ) + "\n" | ||
| + | |||
| + | def compareUserExpected( inputLines, userOutText, expectedOutText ): | ||
| + | global stripOutputsBeforeCompare | ||
| + | |||
| + | log( "compareUserExpected:\nuserOutText = " + userOutText ) | ||
| + | log( "expectedOutText = " + expectedOutText ) | ||
| + | |||
| + | userOutText = removeBlankLines( userOutText ) | ||
| + | expectedOutText = removeBlankLines( expectedOutText ) | ||
| + | misMatchLineNumbers = [] | ||
| + | userTextOutLines = userOutText.split( "\n" ) | ||
| + | expectedOutTextLines = expectedOutText.split( "\n" ) | ||
| + | |||
| + | log( "-" * 60 ) | ||
| + | log( "userTextOutLines = " + str( userTextOutLines ) ) | ||
| + | log( "expectedOutTextLines = " + str( expectedOutTextLines ) ) | ||
| + | log( "-" * 60 ) | ||
| + | |||
| + | for i in range( len( userTextOutLines ) ): | ||
| + | lineNo = i+1 | ||
| + | userLine = userTextOutLines[i] | ||
| + | if i >= len( expectedOutTextLines ): | ||
| + | misMatchLineNumbers.append( lineNo ) | ||
| + | break | ||
| + | expectedLine = expectedOutTextLines[i] | ||
| + | log( "compareUserExpected: comparing:\n "+userLine+"\n "+expectedLine ) | ||
| + | if stripOutputsBeforeCompare: | ||
| + | userLine = userLine.strip() | ||
| + | expectedLine = expectedLine.strip() | ||
| + | if userLine != expectedLine: | ||
| + | log( "\ndifference:\n user >" + userTextOutLines[i] + "<" ) | ||
| + | log( "\n expected >" + expectedOutTextLines[i] + "<" ) | ||
| + | misMatchLineNumbers.append( lineNo ) | ||
| + | |||
| + | return misMatchLineNumbers | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | def main(): | ||
| + | global module | ||
| + | global solutionModule | ||
| + | |||
| + | #--- remove if __name__=="__main__" statement, if it's here... | ||
| + | addIfNameEqMain( studentModule+ ".py" ) | ||
| + | |||
| + | #--- clear debug log --- | ||
| + | clearLog() | ||
| + | |||
| + | #--- remove comments --- | ||
| + | file = open( studentModule+".py", "r" ) | ||
| + | text = file.read( ) | ||
| + | file.close() | ||
| + | |||
| + | text = pyminifier.removeComments( text ) | ||
| + | file = open( studentModule+".py", "w" ) | ||
| + | file.write( text + "\n" ) | ||
| + | file.close() | ||
| + | |||
| + | #--- check that the main module uses a main() function | ||
| + | foundDef, foundCall = checkForFunctionPresence( studentModule, "min" ) | ||
| + | if foundCall: | ||
| + | commentShort( "You are using the function min(), which was not allowed." ) | ||
| + | printGrade( 5 ) | ||
| + | return | ||
| + | |||
| + | foundDef, foundCall = checkForFunctionPresence( studentModule, "max" ) | ||
| + | if foundCall: | ||
| + | commentShort( "You are using the function max(), which was not allowed." ) | ||
| + | printGrade( 5 ) | ||
| + | return | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | # test that module runs on its own without problem | ||
| + | file = open( "input.txt", "w" ) | ||
| + | file.write( "\n" ) | ||
| + | file.close() | ||
| + | Ok, errorMessage = checkModuleRunsOk( module, "input.txt" ) | ||
| + | if not Ok: | ||
| + | errorMessage = firstLastLines( errorMessage ) | ||
| + | commentLong( "- Your program crashed...\n" | ||
| + | + "Error message:\n" | ||
| + | + errorMessage + "\n" ) | ||
| + | printGrade( 5 ) | ||
| + | return | ||
| + | |||
| + | gradeIncrement = 25 | ||
| + | grade = 0 | ||
| + | for testNo in [0, 1, 2, 3]: | ||
| + | inputList = generateTestModule( module, testNo ) | ||
| + | generateSolutionModule( solutionModule, testNo ) | ||
| + | |||
| + | dummy, expectedOutText, score2 = runModule( solutionModule, | ||
| + | "input.txt", "expectedOut" ) | ||
| + | if debug: print( "runModule solution:", dummy, expectedOutText, score2 ) | ||
| + | |||
| + | # generate user output | ||
| + | error, userOutText, score2 = runModule( module, "input.txt", "userOut" ) | ||
| + | if debug: print( "runModule user:", error, userOutText, score2 ) | ||
| + | if error: | ||
| + | commentLong( "- Your program crashed...\n" | ||
| + | + "Error message:\n" | ||
| + | + userOutText + "\n" ) | ||
| + | |||
| + | missMatches = compareUserExpected( ["\n"], userOutText, expectedOutText ) | ||
| + | if debug: print( " missMatches = ", missMatches ) | ||
| + | if len( missMatches ) != 0: | ||
| + | commentLong( "- Incorrect output...\n" | ||
| + | +"input list = \n" | ||
| + | +"Expected output:\n" | ||
| + | +expectedOutText + "\n" | ||
| + | +"Your output:\n" | ||
| + | +userOutText + "\n" ) | ||
| + | #printGrade( len( missMatches ) * 20 ) | ||
| + | else: | ||
| + | commentLong( "- Your program passes the test\n" | ||
| + | + "Test list = " + str( inputList ) +"\n" ) | ||
| + | grade += gradeIncrement | ||
| + | |||
| + | printGrade( grade ) | ||
| + | |||
| + | main() | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | ==testHw12_1.py== | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <source lang="python"> | ||
| + | from hw12_1 import * | ||
| + | |||
| + | def main(): | ||
| + | A = [ "lucy", "marie", "joe", "larry"] | ||
| + | low, high = smallestLargest( A ) | ||
| + | print( low, high ) | ||
| + | |||
| + | if __name__=="__main__": | ||
| + | main() | ||
| + | |||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | </onlydft> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | |||
[[Category:Homework]][[Category:CSC111]][[Category:Python]] | [[Category:Homework]][[Category:CSC111]][[Category:Python]] | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
Revision as of 19:41, 19 April 2015
--D. Thiebaut (talk) 17:30, 19 April 2015 (EDT)
Contents
Problem #1
Write a program called hw12_1.py that contains a recursive function called smallestLargest() which returns the smallest and largest elements of a list of items. The items may be strings, numbers, or tuples, where the first element of the tuple is either a number or a string.
Example main() program:
def main(): A = [ 1, 10, 20, 3, 2, -1, -10, 5, 5, 5, 5 ] low, high = smallestLargest( A ) print( "smallest item =", low, " largest item = ", high ) # will print # smallest item = -10 largest item = 20 A = [ 1 ] low, high = smallestLargest( A ) print( "smallest item =", low, " largest item = ", high ) # will print # smallest item = 1 largest item = 1 A = [ ] low, high = smallestLargest( A ) print( "smallest item =", low, " largest item = ", high ) # will print # smallest item = None largest item = None A = [ "alpha", "beta", "gamma", "epsilon" ] low, high = smallestLargest( A ) print( "smallest item =", low, " largest item = ", high ) # will print # smallest item = alpha largest item = gamma if __name__=="__main__": main()
Requirements
- The function smallestLargest() must be recursive.
- You cannot use the min() or max() standard Python functions. If you want to find the largest of two items, you need to do the comparison in Python, using <, <=, >, or >=.
Submission
Submit your program to the Moodle section, HW12 PB 1
Problem #2
Write a Python program called hw12_2.py that generates, recursively a tree with fruit, as close to the tree shown below as possible. You should not reproduce the text in the image; just the tree, its colors, and its fruit.
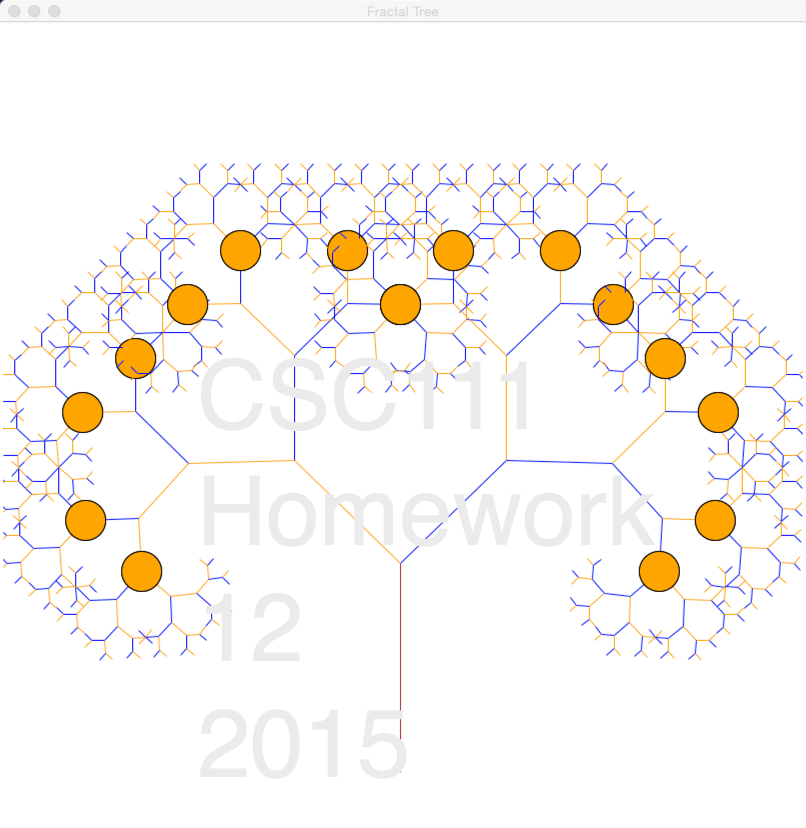
Requirements
- The oranges have a radius of 20. They must be generated inside the recursive function. As a result some of the branches will appear in front, some below the oranges.
- The branches must have different colors, and not be all drawn with the same color.
Submission
- Submit your program as well as a screen capture of its output to Moodle, in the HW12 PB2 and HW12 Image 2 sections.
- Note: To change the color of a line with the graphics library (use graphics111.py, please), you should use the setOutline() method rather than the setFill() method.
- I used only 3 colors to generate the tree above: "orange", "blue", and "brown".
<showafterdate after="20150422 14:00" before="20150601 00:00">
Solution Programs
Recursive MinMax
# hw12_1.py # D. Thiebaut # Solution program for Homework 12 def minmax( A ): """recursive function that returns the min and max of a list of comparable items""" # stopping condition #1 if len( A )==0: return None, None # stopping condition #2 if len( A )==1: return A[0], A[0] # recursive step theMin, theMax = minmax( A[1: ] ) # do a bit of work... if A[0] < theMin: theMin = A[0] if A[0] > theMax: theMax = A[0] # return the smallest or largest of what we kept # and what the recursive call brought back return theMin, theMax def main(): A = [ 1, 10, 20, 3, 2, -1, -10, 5, 5, 5, 5 ] low, high = minmax( A ) print( "smallest item =", low, " largest item = ", high ) # will print # smallest item = -10 largest item = 20 A = [ 1 ] low, high = minmax( A ) print( "smallest item =", low, " largest item = ", high ) # will print # smallest item = 1 largest item = 1 A = [ ] low, high = minmax( A ) print( "smallest item =", low, " largest item = ", high ) # will print # smallest item = None largest item = None A = [ "alpha", "beta", "gamma", "epsilon" ] low, high = minmax( A ) print( "smallest item =", low, " largest item = ", high ) # will print # smallest item = alpha largest item = gamma if __name__=="__main__": main()
Fractal Tree
# fractalTree.py
# D. Thiebaut
# Code taken from http://openbookproject.net/thinkcs/python/english3e/recursion.html
# and adapted to work with graphics111.py.
#
# Draws a fractal tree on the graphic window.
#
from graphics import *
import math
import time
import random
# dimensions of the window
MAXWIDTH = 800
MAXHEIGHT = 800
# recursive tree-drawing function
#
def draw_tree(win , # the canvas
order, # the level of recursion. Starts positive.
theta, # angle of new branch leaving this trunk
sz, # size of this branch
x, y, # coordinates of base of this branch
heading, # angle of direction of this branch
color # color
):
trunk_ratio = 0.29 # How big is the trunk relative to whole tree?
trunk = sz * trunk_ratio # length of trunk
# compute x, y of end of the current branch
delta_x = trunk * math.cos(heading)
delta_y = trunk * math.sin(heading)
x2, y2 = x + delta_x, y + delta_y
# draw current branch
branch = Line( Point( x, y), Point( x2, y2 ) )
branch.setFill( color )
branch.setWidth( 2 )
branch.setOutline( color )
branch.draw( win )
# if this branch has sub-branches, then recurse
if order > 0:
# make the recursive calls to draw the two subtrees
newsz = sz*(1 - trunk_ratio)
draw_tree(win,
order-1, theta, newsz, x2, y2, heading-theta,
"orange" )
draw_tree(win,
order-1, theta, newsz, x2, y2, heading+theta,
"blue" )
# draw orange
if order == 4:
orange = Circle( Point( x, y ), 20 )
orange.setFill( "orange" )
orange.draw( win )
# draw 1 tree in the middle of the screen, shooting straight up.
def main():
win = GraphWin("Fractal Tree", MAXWIDTH, MAXHEIGHT )
theta = 0.8 # use 0.02 for tall skinny trees, 0.7 for fat trees
draw_tree(win,
9,
theta,
MAXWIDTH*0.9, MAXWIDTH//2,
MAXHEIGHT-50,
-math.pi/2,
"brown" )
win.getMouse()
win.close()
main()
</showafterdate>