Hadoop Tutorial 4: Start an EC2 Instance
--D. Thiebaut 16:01, 18 April 2010 (UTC)
|
Creating an EC2 Instance refers to the action of starting a server on Amazon using one's credential, and then connecting to it using ssh. |
Method #1: Using the AWS Console
Steps
The steps are fairly simple:
- Connect to the AWS console (see Tutorial 3 for a reminder), and then select Amazon EC2.
- In the QuickStart tab, pick "Fedora LAMP Server", as a machine to instantiate.
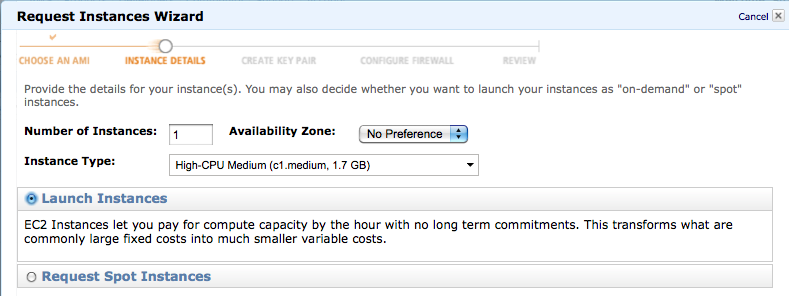
- Select 1 instance, pick the architecture of your choice, and No Preference for the zone.
- Select Launch Instance (Spot Instances are low-rate machines that run only when the demand is low, and the user pays less).
- Click on Continue (make sure your browser window is large enough to see the bottom part of the pop-up!)
- Use defaults for Kernel Id and RamDisk Id.
- No Monitoring
- Click on Continue
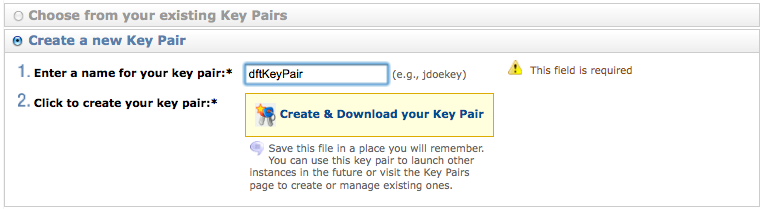
- Pick a name for your key-pair file (e.g. dftKeyPair), then click on Create New Key Pair.
- When prompted, save the key-pair file (dftKeyPair.pem) to a local directory on your computer (Desktop, for example).
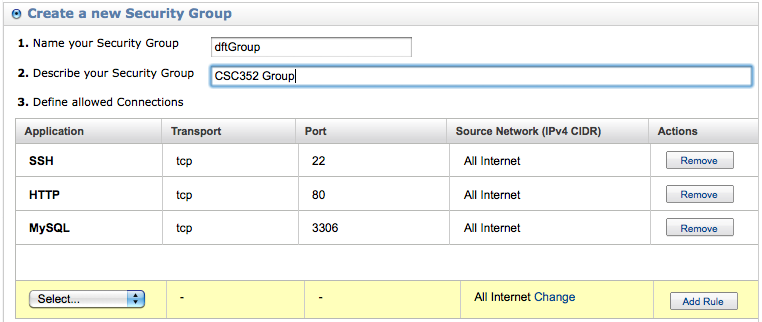
- Follow the directions to create a security group (I called it dftGroup for simplicity).
- Review!
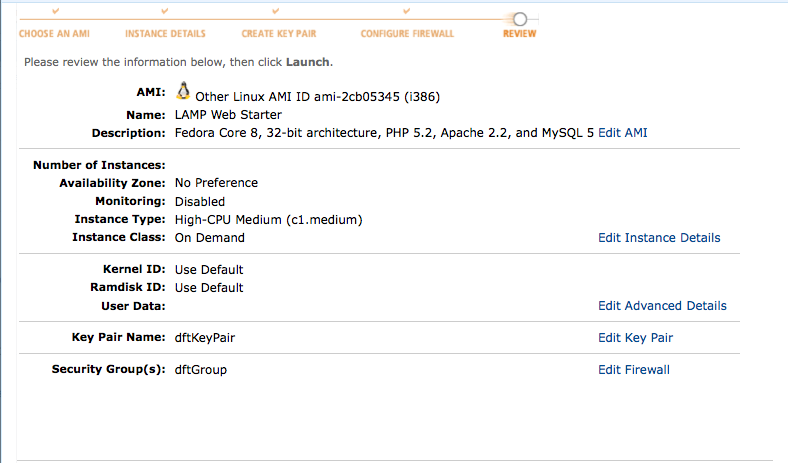
- Launch!
- Watch as the instance is created, and laods up...
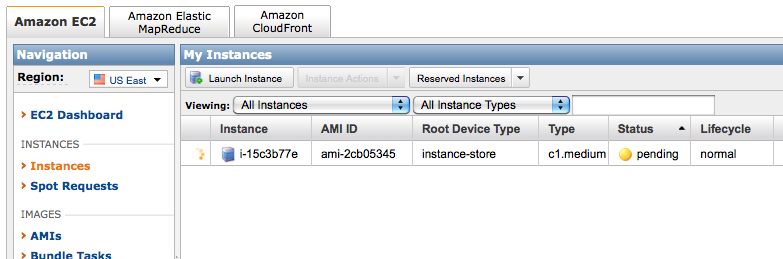
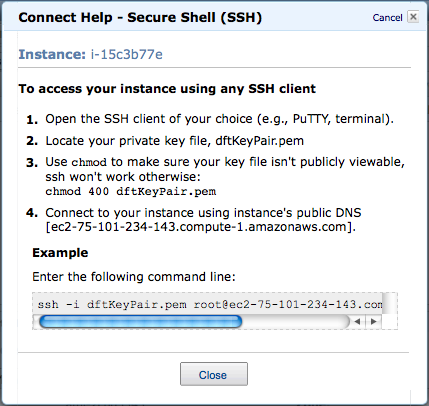
- When the instance is created, right click on it and click on Connect
- Copy/Paste the ssh command into a shell that you will have started
ssh -i dft.pem root@ec2-174-129-165-180.compute-1.amazonaws.com
- Make sure you have downloaded a private key file to your .ssh directory first. This is done by
- Selecting your account
- clicking on Credentials
- selecting the X.509 certificate tab
- and clicking on Create New. A page will open allowing you to download your pem files. One will be the private key, of the form pk-WMxxxxxxxxxx.pem, the other the certicifcate, of the form cert-WMxxxxxxxxxx.pem. Both should be put in your .ssh dirctory.
Method #2: Using the EC2 Tools
Steps
- Download the EC2 Tools from the Amazon EC2 Resource Center.
- install them in ~/bin/ec2-api-tools (see the Getting Started Guide from Amazon for more info).
- Download the pem files containing your private key and certificate from the Amazon EC2 page (see step above)
- Modify your .bash_profile file and set several variables:
PATH=$PATH:/Users/thiebaut/bin/ec2-api-tools/bin # Amazon AWS/EC2 tools export EC2_HOME=/Users/thiebaut/bin/ec2-api-tools export JAVA_HOME=/System/Library/Frameworks/JavaVM.framework/Home export EC2_PRIVATE_KEY=~/.ssh/pk-WMW2M4ZVFMCZJXSXJN4D7ZS4RMTBJ7VV.pem export EC2_CERT=~/.ssh/cert-WMW2M4ZVFMCZJXSXJN4D7ZS4RMTBJ7VV.pem
- Source the .bash_profile file
source .bash_profile
- Test the ec2 tools:
ec2-describe-images -a | grep hadoop-ec2-images
- verify that a list of images is printed out.
IMAGE ami-ee53b687 hadoop-ec2-images/hadoop-0.17.0-i386.manifest.xml 111560892610 available public i386 machine aki-a71cf9ce ari-a51cf9cc instance-store IMAGE ami-f853b691 hadoop-ec2-images/hadoop-0.17.0-x86_64.manifest.xml 111560892610 available public x86_64 machine aki-b51cf9dc ari-b31cf9da instance-store
 |  | |
| ||
 |  |