Week Topics
Reading
Week 1
Week 2
Monday
Review of Hello World
Q&A
Mini Lab #1 to get everybody up to speed.
Wednesday
Friday
Week 3
Get the list of all the assembly programs seen in class: ls -ltr ~231a/handout Get one of the files into your 231a-xx account: getcopy movStrings1.asm sftp 231a-xx@beowulf.csc.smith.edu (and then use put filename or get filename to transfer files) Architecture of a simplified Pentium:
Registers
ALU
CU
Address and Data buses
The mother of all instructions: MOV (covered here )
byte, word, double-word variables. Friday
Week 4
Monday
Q&A
Solutions to HW #2 posted (see above).
The ADD instruction int a = 3, b = 5, result = 0;
result = a + b;
Wednesday
Friday
AND, OR, XOR, NOT (review Boolean Algebra )
range of unsigned byte, words, dwords, and quadwords.
Reading
Sections 2.2, 2.2.1, 2.2.2, 2.2.3, and 2.2.4 in the Nasm Manual
Sections 3.1 to 3.2.1 in the Nasm Manual
The INC instruction.
Week 5
Wednesday
Friday
Review of 2's Complement: Exercise in need of a solution...
Extending the sign from byte to word, or word to double-word.
CBW : The CBW (convert byte to word) instruction copies the sign (bit 7) in the source operand (AL) into every bit in the AH register. [1]
CWDE : The CWDE instruction copies the sign (bit 15) of the word in the AX register into every bit position of the high word of the EAX register [1]
Masking with AND, OR, and NOT, an example
Week 6
Wednesday
Bitwise operators vs logical operators in Java. Example
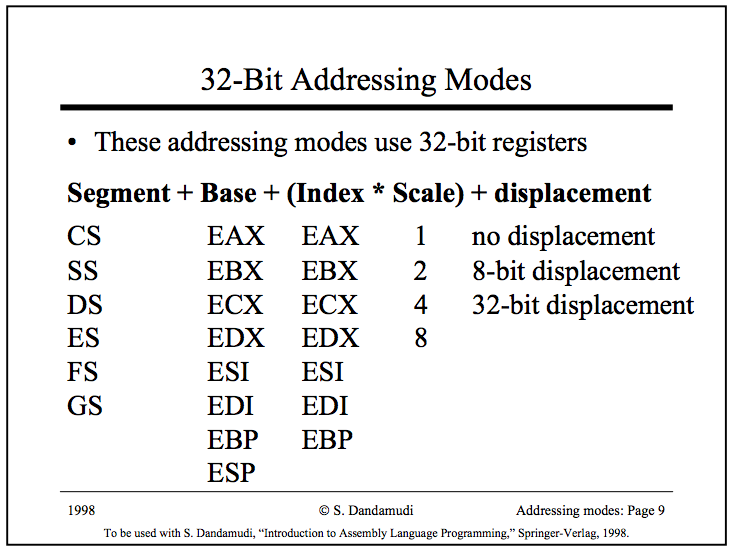
More Addressing modes:
base/indirect
base/indirect with diplacement
base/inderect indexed
base/indirect indexed with displacement
The Loop instruction. Exercises with Loops
Fibonacci with loops and new addressing modes: Examples
Friday
Week 7
Monday
A word on the LOOP instruction offset
condition codes & status register (flags)
Conditional Jumps: JA, JAE, JB, JBE, JC, JCXZ, JE, JG, JGE, JL, JLE, JNA, JNAE, JNB, JNBE, JNC, JNE, JNG, JNGE, JNL, JNLE, JNO, JNP, JNS, JNZ, JO, JP, JPE, JPO, JS, JZ (more info here ).
Flag bits set by the CMP instruction
Wednesday
Friday
No homework assignment this week.
Week 8
Monday
Using a Makefile
Another trick. Keep the nasm, ld, and run commands in one line in your history: nasm -f elf -F stabs myProg.asm ; ld -melf_i386 -o myProg myProg.o ; ./myProg shl reg, 1
shl mem, 1
shl reg, imm
shl mem, imm
shl reg, cl
shl mem, cl
Week 9
Monday
No class, thanks to Hurricane Sandy!
Wednesday
Friday
Reading
Functions and the topics associated with passing parameters are covered in Carter's Manual on Assembly Language, in Chapter 4 , titled Subprograms .
Week 10
Monday
Finish the top-down example
Review the actions of passing parameters through registers. The concept of functions returning values is directly implementable using registers (in most cases).
Using EBP to pass more than 4/6 dword parameters: int main() {
int a=3, b=5, res;
res = sum( a, b );
...
}
int sum( int x, int y ) {
return x+y;
}
Wednesday
review passing of value parameters through the stack
functions returning values... Friday
Why is this code buggy?
local variables...
Some ideas for exercises
write a function that receives 3 dwords and returns the largest (in eax or in the stack)
write a function that receives a number and a char and prints a line with that many copies of it.
write a function that copies one array into another one.
write a function that receives two arrays: scans first one for patterns and updates second one as it does so.
Reading
Functions and the topics associated with passing parameters are covered in Carter's Manual on Assembly Language, in Chapter 4 , titled Subprograms .
Week 11
Monday
Wednesday
Some ideas for exercises
write a function that receives 3 dwords and returns the largest (in eax or in the stack)
write a function that receives a number and a char and prints a line with that many copies of it.
write a function that copies one array into another one. (we discovered a new instruction in the process: movsb )
write a function that receives two arrays: scans first one for patterns and updates second one as it does so.
write a function (in C, we would write it: swap( int *x, int *y) ) that swaps the values in x and y.
A look at the solution programs for Homework 8.
Friday
Week 12
Monday
Continuation of recursion. "Walking" the factorial example (see listing )
List of Factorials
Questions:
Any limiting factors?
Could we have computed the factorial any other way?
Unrolling recursion
Sketching the Towers of Hanoi problem in assembly...
Wednesday Thanksgiving Break
Friday Thanksgiving Break
Week 13
Monday
Wednesday
Q&A
Continuation with the Towers of Hanoi
Observe hanoi2.py and its indented output
Question 1: how much stack space is used when moving N disks?
Question 2: How large a number of disks can we move with a stack of 1000 bytes?
Question 3: Removing the tail recursion. How does it affect the stack?
Binary Search
What does the recursion tree look like for the Binary Search algorithm?
Would removing the tail recursion help Binary Search?
Printing an integer in decimal.
The DIV instruction
Sketching a solution
A program
Limitations of the program?
Friday : No Class
Reading
The DIV instruction is covered in Page 34 of Carter's book ].
Recursion is still covered in Section 4.8 of Carter's text.
Week 14
Monday
Wednesday
Friday : No Class
Week 15